User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


Improving Colorectal Cancer Screening via Mailed Fecal Immunochemical Testing in a Veterans Affairs Health System
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
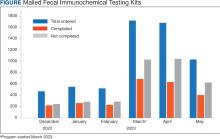
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
new article test headline
new display headline
this is a test body
this is a test body
this is a test body
new display headline
new display headline
test article drupal 10 fix
test article drupal 10 fix
test article drupal 10 fix
test article drupal 10 fix
LLIMOmNdYY_article_4281293752
mBlFDBYXbT_article_0904368422
GmAhNLtnQX_article_4182336649
XLXhexxNlX_article_0103680007
test video 1
test body
test body
test body

Veterans and Nonveterans Show Similar Mammogram Rates
TOPLINE: A national survey of 8996 females reveals comparable mammography screening rates between those who identify as veterans (57.9%) and nonveterans (55.2%).
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers analyzed data from the 2019 National Health Interview Survey, a cross-sectional national survey tracking health information.
Female respondents aged 40 to 74 years without history of breast cancer were included in the analysis.
Analysis evaluated the association between screening and veteran status through logistic regression, adjusting for potential confounders.
Survey procedures accounted for complex sampling design to obtain valid estimates for the civilian, noninstitutionalized US population.
TAKEAWAY:
Analysis included 8996 female survey respondents, including 169 veterans (1.9%) and 320 (3.2%) reported having military health coverage.
Mammography screening rates within the last year were comparable between veterans (57.9%) and nonveterans (55.2%).
Veteran status showed no significant association with differences in mammography screening percentages (P = .96).
Among insured participants, military health insurance demonstrated no significant association with mammography screening percentages (P = .13).
The authors suggest that radiology practices should design proactive outreach strategies to address the needs of the growing number of female veterans who may face increased breast cancer risk due to military environmental exposures.
IN PRACTICE: “Although the results from our study demonstrate comparable mammography screening percentages, veterans may face additional risk factors for breast cancer due to occupational,” the authors argue.
SOURCE: This summary is based on a preprint published online in the Journal of the American College of Radiology: Milton A, Miles R, Gettle LM, Van Geertruyden P, Narayan AK. Utilization of Mammography Screening in Female Veterans: Cross-Sectional Survey Results from the National Health Interview Survey. J Am Coll Radiol. Published online April 24, 2025. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2025.04.017
LIMITATIONS: The study relied on self-reported adherence data, which could overestimate screening percentages. Data collection occurred prior to updated United States Preventive Services Task Force guidelines recommending routine mammography screening for women starting at age 40 years every 2 years. The relatively small number of female veteran respondents limited the precision of population estimates. Additionally, the data were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic, which has been associated with reduced mammographic screening, particularly in medically underserved populations.
DISCLOSURES: Anand Narayan disclosed receiving financial support from Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation and National Academy of Medicine. The study did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The remaining authors reported no potential conflicts of interest. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: A national survey of 8996 females reveals comparable mammography screening rates between those who identify as veterans (57.9%) and nonveterans (55.2%).
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers analyzed data from the 2019 National Health Interview Survey, a cross-sectional national survey tracking health information.
Female respondents aged 40 to 74 years without history of breast cancer were included in the analysis.
Analysis evaluated the association between screening and veteran status through logistic regression, adjusting for potential confounders.
Survey procedures accounted for complex sampling design to obtain valid estimates for the civilian, noninstitutionalized US population.
TAKEAWAY:
Analysis included 8996 female survey respondents, including 169 veterans (1.9%) and 320 (3.2%) reported having military health coverage.
Mammography screening rates within the last year were comparable between veterans (57.9%) and nonveterans (55.2%).
Veteran status showed no significant association with differences in mammography screening percentages (P = .96).
Among insured participants, military health insurance demonstrated no significant association with mammography screening percentages (P = .13).
The authors suggest that radiology practices should design proactive outreach strategies to address the needs of the growing number of female veterans who may face increased breast cancer risk due to military environmental exposures.
IN PRACTICE: “Although the results from our study demonstrate comparable mammography screening percentages, veterans may face additional risk factors for breast cancer due to occupational,” the authors argue.
SOURCE: This summary is based on a preprint published online in the Journal of the American College of Radiology: Milton A, Miles R, Gettle LM, Van Geertruyden P, Narayan AK. Utilization of Mammography Screening in Female Veterans: Cross-Sectional Survey Results from the National Health Interview Survey. J Am Coll Radiol. Published online April 24, 2025. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2025.04.017
LIMITATIONS: The study relied on self-reported adherence data, which could overestimate screening percentages. Data collection occurred prior to updated United States Preventive Services Task Force guidelines recommending routine mammography screening for women starting at age 40 years every 2 years. The relatively small number of female veteran respondents limited the precision of population estimates. Additionally, the data were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic, which has been associated with reduced mammographic screening, particularly in medically underserved populations.
DISCLOSURES: Anand Narayan disclosed receiving financial support from Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation and National Academy of Medicine. The study did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The remaining authors reported no potential conflicts of interest. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: A national survey of 8996 females reveals comparable mammography screening rates between those who identify as veterans (57.9%) and nonveterans (55.2%).
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers analyzed data from the 2019 National Health Interview Survey, a cross-sectional national survey tracking health information.
Female respondents aged 40 to 74 years without history of breast cancer were included in the analysis.
Analysis evaluated the association between screening and veteran status through logistic regression, adjusting for potential confounders.
Survey procedures accounted for complex sampling design to obtain valid estimates for the civilian, noninstitutionalized US population.
TAKEAWAY:
Analysis included 8996 female survey respondents, including 169 veterans (1.9%) and 320 (3.2%) reported having military health coverage.
Mammography screening rates within the last year were comparable between veterans (57.9%) and nonveterans (55.2%).
Veteran status showed no significant association with differences in mammography screening percentages (P = .96).
Among insured participants, military health insurance demonstrated no significant association with mammography screening percentages (P = .13).
The authors suggest that radiology practices should design proactive outreach strategies to address the needs of the growing number of female veterans who may face increased breast cancer risk due to military environmental exposures.
IN PRACTICE: “Although the results from our study demonstrate comparable mammography screening percentages, veterans may face additional risk factors for breast cancer due to occupational,” the authors argue.
SOURCE: This summary is based on a preprint published online in the Journal of the American College of Radiology: Milton A, Miles R, Gettle LM, Van Geertruyden P, Narayan AK. Utilization of Mammography Screening in Female Veterans: Cross-Sectional Survey Results from the National Health Interview Survey. J Am Coll Radiol. Published online April 24, 2025. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2025.04.017
LIMITATIONS: The study relied on self-reported adherence data, which could overestimate screening percentages. Data collection occurred prior to updated United States Preventive Services Task Force guidelines recommending routine mammography screening for women starting at age 40 years every 2 years. The relatively small number of female veteran respondents limited the precision of population estimates. Additionally, the data were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic, which has been associated with reduced mammographic screening, particularly in medically underserved populations.
DISCLOSURES: Anand Narayan disclosed receiving financial support from Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation and National Academy of Medicine. The study did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The remaining authors reported no potential conflicts of interest. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
UK Funds AI Blood Test for Early Cancer Detection
A clinical trial of a promising blood test that could offer faster and more accurate diagnoses for common cancers has received funding from the Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC).
The miONCO-Dx test detects cancer at an early stage by analysing microRNA expression in blood.
It uses artificial intelligence to identify the presence and origin of the disease.
The test was developed by Xgenera, a University of Southampton spinout, in collaboration with the National Institute for Health and Care Research.
Initial analysis of data from more than 20,000 patients showed that the test detected 12 of the most common and lethal cancers at an early stage and with over 99% accuracy.
Bowel Cancer Among Key Targets
Bowel cancer, the fourth most common cancer in the United Kingdom, is a principal target for the test.
Around 44,000 people in the UK are diagnosed with bowel cancer each year. At stage 1, approximately 90% of people survive for 5 years or more, but this drops to around 10% at stage 4.
Wes Streeting, Secretary of State for Health and Social Care, said in a press release, “The key to surviving cancer is catching it as early as possible, so this government is taking the urgent action needed to make sure that happens.”
£2.4 Million Awarded for Clinical Trial
The DHSC has awarded Xgenera £2.4 million to advance development of the test, which has now been refined into a cheaper, faster, and more scalable version.
The funding will support a clinical trial involving 8000 patients. The DHSC described this as “a formal and significant step towards bringing the test closer to patients by ensuring it is fit for purpose in the NHS.”
The trial will be run by Cancer Research UK Southampton Clinical Trials Unit.
Potential for NHS Use
Dr Victoria Goss, head of early diagnosis and translational research at the trials unit, said in a press release, “A reliable test such as this could have the potential to see a major shift in cancer screening, making it easier and cheaper to provide on the NHS, cutting health inequalities, and ultimately reducing the number of people who die from the disease.”
Xgenera co-founder Dr Andy Shapanis, a research fellow at the University of Southampton, said that the new study would evaluate the useability, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of the test for use within the NHS in future.
“The hope is that if the test is shown to be successful in the early diagnosis of the 12 cancers we have currently identified biomarkers for, then it could be expanded to look at over 50 other cancers in the future,” he said.
Comparison With Other Tests
The miONCO-Dx test follows other attempts at multicancer early detection, such as the Galleri test from Grail, which is already being trialled in the NHS.
Galleri screens for altered DNA methylation patterns in blood and claims to detect more than 50 types of cancer. It raised hopes for earlier diagnosis, less invasive treatment, and potential cost savings.
However, critics have raised concerns about low detection rates in early-stage cancers, high false-positive rates, imprecise cancer origin analysis, cost, and unproven mortality gains. Questions have also been expressed about possible political influence in its selection for NHS trials.
A Broader Screening Platform
Xgenera co-founder Professor Paul Skipp, director of the Centre for Proteomic Research at the University of Southampton, said earlier this year that the miONCO-Dx test was “a real game-changer.”
The test can detect lung, breast, prostate, pancreatic, colorectal, ovarian, liver, brain, oesophageal, bladder, and gastric cancer and bone and soft-tissue sarcoma. It works by identifying imbalances in microRNAs, a class of small noncoding RNAs with functions in posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression, influencing cellular activities including cell growth, differentiation, development, and apoptosis.
The presence of microRNA imbalances can be identified from just 10-15 drops of blood, across all stages of tumour growth.
In comparison, according to Skipp, screening is only available currently for three types of cancer in the UK, and each test targets a single type.
Xgenera has also received external investment from the innovation investment companies Qantx, Empirical Ventures, and Ascension Ventures to further develop the test.
Dr Sheena Meredith is an established medical writer, editor, and consultant in healthcare communications, with extensive experience writing for medical professionals and the general public. She is qualified in medicine and in law and medical ethics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A clinical trial of a promising blood test that could offer faster and more accurate diagnoses for common cancers has received funding from the Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC).
The miONCO-Dx test detects cancer at an early stage by analysing microRNA expression in blood.
It uses artificial intelligence to identify the presence and origin of the disease.
The test was developed by Xgenera, a University of Southampton spinout, in collaboration with the National Institute for Health and Care Research.
Initial analysis of data from more than 20,000 patients showed that the test detected 12 of the most common and lethal cancers at an early stage and with over 99% accuracy.
Bowel Cancer Among Key Targets
Bowel cancer, the fourth most common cancer in the United Kingdom, is a principal target for the test.
Around 44,000 people in the UK are diagnosed with bowel cancer each year. At stage 1, approximately 90% of people survive for 5 years or more, but this drops to around 10% at stage 4.
Wes Streeting, Secretary of State for Health and Social Care, said in a press release, “The key to surviving cancer is catching it as early as possible, so this government is taking the urgent action needed to make sure that happens.”
£2.4 Million Awarded for Clinical Trial
The DHSC has awarded Xgenera £2.4 million to advance development of the test, which has now been refined into a cheaper, faster, and more scalable version.
The funding will support a clinical trial involving 8000 patients. The DHSC described this as “a formal and significant step towards bringing the test closer to patients by ensuring it is fit for purpose in the NHS.”
The trial will be run by Cancer Research UK Southampton Clinical Trials Unit.
Potential for NHS Use
Dr Victoria Goss, head of early diagnosis and translational research at the trials unit, said in a press release, “A reliable test such as this could have the potential to see a major shift in cancer screening, making it easier and cheaper to provide on the NHS, cutting health inequalities, and ultimately reducing the number of people who die from the disease.”
Xgenera co-founder Dr Andy Shapanis, a research fellow at the University of Southampton, said that the new study would evaluate the useability, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of the test for use within the NHS in future.
“The hope is that if the test is shown to be successful in the early diagnosis of the 12 cancers we have currently identified biomarkers for, then it could be expanded to look at over 50 other cancers in the future,” he said.
Comparison With Other Tests
The miONCO-Dx test follows other attempts at multicancer early detection, such as the Galleri test from Grail, which is already being trialled in the NHS.
Galleri screens for altered DNA methylation patterns in blood and claims to detect more than 50 types of cancer. It raised hopes for earlier diagnosis, less invasive treatment, and potential cost savings.
However, critics have raised concerns about low detection rates in early-stage cancers, high false-positive rates, imprecise cancer origin analysis, cost, and unproven mortality gains. Questions have also been expressed about possible political influence in its selection for NHS trials.
A Broader Screening Platform
Xgenera co-founder Professor Paul Skipp, director of the Centre for Proteomic Research at the University of Southampton, said earlier this year that the miONCO-Dx test was “a real game-changer.”
The test can detect lung, breast, prostate, pancreatic, colorectal, ovarian, liver, brain, oesophageal, bladder, and gastric cancer and bone and soft-tissue sarcoma. It works by identifying imbalances in microRNAs, a class of small noncoding RNAs with functions in posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression, influencing cellular activities including cell growth, differentiation, development, and apoptosis.
The presence of microRNA imbalances can be identified from just 10-15 drops of blood, across all stages of tumour growth.
In comparison, according to Skipp, screening is only available currently for three types of cancer in the UK, and each test targets a single type.
Xgenera has also received external investment from the innovation investment companies Qantx, Empirical Ventures, and Ascension Ventures to further develop the test.
Dr Sheena Meredith is an established medical writer, editor, and consultant in healthcare communications, with extensive experience writing for medical professionals and the general public. She is qualified in medicine and in law and medical ethics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A clinical trial of a promising blood test that could offer faster and more accurate diagnoses for common cancers has received funding from the Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC).
The miONCO-Dx test detects cancer at an early stage by analysing microRNA expression in blood.
It uses artificial intelligence to identify the presence and origin of the disease.
The test was developed by Xgenera, a University of Southampton spinout, in collaboration with the National Institute for Health and Care Research.
Initial analysis of data from more than 20,000 patients showed that the test detected 12 of the most common and lethal cancers at an early stage and with over 99% accuracy.
Bowel Cancer Among Key Targets
Bowel cancer, the fourth most common cancer in the United Kingdom, is a principal target for the test.
Around 44,000 people in the UK are diagnosed with bowel cancer each year. At stage 1, approximately 90% of people survive for 5 years or more, but this drops to around 10% at stage 4.
Wes Streeting, Secretary of State for Health and Social Care, said in a press release, “The key to surviving cancer is catching it as early as possible, so this government is taking the urgent action needed to make sure that happens.”
£2.4 Million Awarded for Clinical Trial
The DHSC has awarded Xgenera £2.4 million to advance development of the test, which has now been refined into a cheaper, faster, and more scalable version.
The funding will support a clinical trial involving 8000 patients. The DHSC described this as “a formal and significant step towards bringing the test closer to patients by ensuring it is fit for purpose in the NHS.”
The trial will be run by Cancer Research UK Southampton Clinical Trials Unit.
Potential for NHS Use
Dr Victoria Goss, head of early diagnosis and translational research at the trials unit, said in a press release, “A reliable test such as this could have the potential to see a major shift in cancer screening, making it easier and cheaper to provide on the NHS, cutting health inequalities, and ultimately reducing the number of people who die from the disease.”
Xgenera co-founder Dr Andy Shapanis, a research fellow at the University of Southampton, said that the new study would evaluate the useability, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of the test for use within the NHS in future.
“The hope is that if the test is shown to be successful in the early diagnosis of the 12 cancers we have currently identified biomarkers for, then it could be expanded to look at over 50 other cancers in the future,” he said.
Comparison With Other Tests
The miONCO-Dx test follows other attempts at multicancer early detection, such as the Galleri test from Grail, which is already being trialled in the NHS.
Galleri screens for altered DNA methylation patterns in blood and claims to detect more than 50 types of cancer. It raised hopes for earlier diagnosis, less invasive treatment, and potential cost savings.
However, critics have raised concerns about low detection rates in early-stage cancers, high false-positive rates, imprecise cancer origin analysis, cost, and unproven mortality gains. Questions have also been expressed about possible political influence in its selection for NHS trials.
A Broader Screening Platform
Xgenera co-founder Professor Paul Skipp, director of the Centre for Proteomic Research at the University of Southampton, said earlier this year that the miONCO-Dx test was “a real game-changer.”
The test can detect lung, breast, prostate, pancreatic, colorectal, ovarian, liver, brain, oesophageal, bladder, and gastric cancer and bone and soft-tissue sarcoma. It works by identifying imbalances in microRNAs, a class of small noncoding RNAs with functions in posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression, influencing cellular activities including cell growth, differentiation, development, and apoptosis.
The presence of microRNA imbalances can be identified from just 10-15 drops of blood, across all stages of tumour growth.
In comparison, according to Skipp, screening is only available currently for three types of cancer in the UK, and each test targets a single type.
Xgenera has also received external investment from the innovation investment companies Qantx, Empirical Ventures, and Ascension Ventures to further develop the test.
Dr Sheena Meredith is an established medical writer, editor, and consultant in healthcare communications, with extensive experience writing for medical professionals and the general public. She is qualified in medicine and in law and medical ethics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.