User login
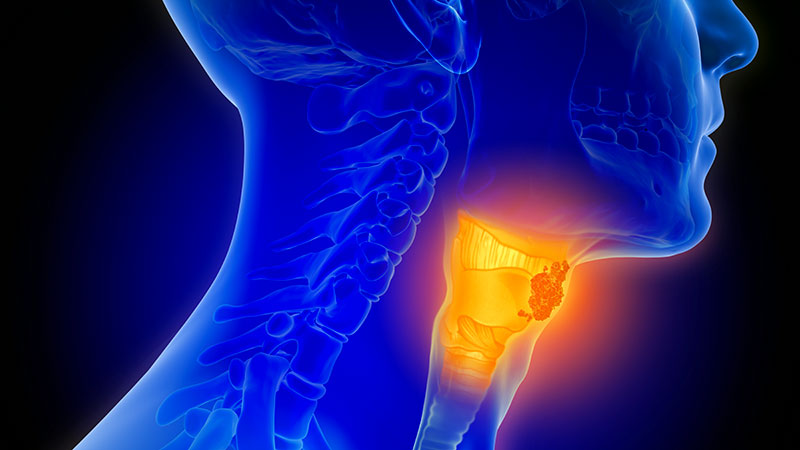
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
PHOENIX – A 70-year-old Vietnam veteran with oropharyngeal cancer presented challenges beyond his disease.
He couldn’t afford transportation for daily radiation treatments and had lost > 10% of his body weight due to pain and eating difficulties, recalled radiation oncologist Vinita Takiar, MD, PhD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
To make matters more difficult, his wife held medical power of attorney despite his apparent competence to make decisions, said Takiar, who formerly worked with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Cincinnati Healthcare System and is now chair of radiation oncology at Penn State University.
All these factors would likely have derailed his treatment if not for a coordinated team intervention, Takiar said. Fortunately, the clinic launched a multifaceted effort involving representatives from the social work, dentistry, ethics, nutrition, and chaplaincy departments.
When surgery became impossible because the patient couldn’t lie on the operating table for adequate tumor exposure, she said, the existing team framework enabled a seamless and rapid transition to radiation with concurrent chemotherapy.
The patient completed treatment with an excellent response, offering a lesson in the importance of multidisciplinary care in head-and-neck cancers, she said.
In fact, when it comes to these forms of cancer, coordinated care “is probably more impactful than any treatment that we’re going to come up with,” she said. “The data show that when we do multidisciplinary care and we do it well, it actually improves the patient experience and outcomes.”
As Takiar noted, teamwork matters in many ways. It leads to better logistics and can address disparities, reduce financial burden and stigma, and even increase clinical trial involvement.
She pointed to studies linking teamwork to better outcomes, support for patients, and overall survival.
Takiar highlighted different parts of teams headed by radiation oncologists who act as “a node to improve multimodal care delivery.”
Speech and swallowing specialists, for example, are helpful in head-and-neck cancer because “there’s an impact on speech, swallowing, and appearance. Our patients don’t want to go out to dinner with friends because they can’t do it.”
Dentists and prosthodontists are key team members too: “I have dentists who have my cell phone number. They just call me: ‘Can I do this extraction? Was this in your radiation field? What was the dose?’”
Other team members include ear, nose, and throat specialists, palliative and supportive care specialists, medical oncologists, nurses, pathologists, transportation workers, and service connection specialists. She noted that previous military experience can affect radiation therapy. For example, the physical restraints required during treatment present particular challenges for veterans who’ve had wartime trauma. These patients may require therapy adjustments.
What’s next on the horizon? Takiar highlighted precision oncology and molecular profiling, artificial intelligence in care decisions and in radiation planning, telemedicine and virtual tumor boards, and expanded survivorship programs.
As for now, she urged colleagues to not be afraid to chat with radiation oncologists. “Please talk to us. We prioritize open communication and shared decision-making with the entire team,” she said. “If you see something and think your radiation oncologist should know about it, you think it was caused by the radiation, you should reach out to us.”
Takiar reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – A 70-year-old Vietnam veteran with oropharyngeal cancer presented challenges beyond his disease.
He couldn’t afford transportation for daily radiation treatments and had lost > 10% of his body weight due to pain and eating difficulties, recalled radiation oncologist Vinita Takiar, MD, PhD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
To make matters more difficult, his wife held medical power of attorney despite his apparent competence to make decisions, said Takiar, who formerly worked with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Cincinnati Healthcare System and is now chair of radiation oncology at Penn State University.
All these factors would likely have derailed his treatment if not for a coordinated team intervention, Takiar said. Fortunately, the clinic launched a multifaceted effort involving representatives from the social work, dentistry, ethics, nutrition, and chaplaincy departments.
When surgery became impossible because the patient couldn’t lie on the operating table for adequate tumor exposure, she said, the existing team framework enabled a seamless and rapid transition to radiation with concurrent chemotherapy.
The patient completed treatment with an excellent response, offering a lesson in the importance of multidisciplinary care in head-and-neck cancers, she said.
In fact, when it comes to these forms of cancer, coordinated care “is probably more impactful than any treatment that we’re going to come up with,” she said. “The data show that when we do multidisciplinary care and we do it well, it actually improves the patient experience and outcomes.”
As Takiar noted, teamwork matters in many ways. It leads to better logistics and can address disparities, reduce financial burden and stigma, and even increase clinical trial involvement.
She pointed to studies linking teamwork to better outcomes, support for patients, and overall survival.
Takiar highlighted different parts of teams headed by radiation oncologists who act as “a node to improve multimodal care delivery.”
Speech and swallowing specialists, for example, are helpful in head-and-neck cancer because “there’s an impact on speech, swallowing, and appearance. Our patients don’t want to go out to dinner with friends because they can’t do it.”
Dentists and prosthodontists are key team members too: “I have dentists who have my cell phone number. They just call me: ‘Can I do this extraction? Was this in your radiation field? What was the dose?’”
Other team members include ear, nose, and throat specialists, palliative and supportive care specialists, medical oncologists, nurses, pathologists, transportation workers, and service connection specialists. She noted that previous military experience can affect radiation therapy. For example, the physical restraints required during treatment present particular challenges for veterans who’ve had wartime trauma. These patients may require therapy adjustments.
What’s next on the horizon? Takiar highlighted precision oncology and molecular profiling, artificial intelligence in care decisions and in radiation planning, telemedicine and virtual tumor boards, and expanded survivorship programs.
As for now, she urged colleagues to not be afraid to chat with radiation oncologists. “Please talk to us. We prioritize open communication and shared decision-making with the entire team,” she said. “If you see something and think your radiation oncologist should know about it, you think it was caused by the radiation, you should reach out to us.”
Takiar reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – A 70-year-old Vietnam veteran with oropharyngeal cancer presented challenges beyond his disease.
He couldn’t afford transportation for daily radiation treatments and had lost > 10% of his body weight due to pain and eating difficulties, recalled radiation oncologist Vinita Takiar, MD, PhD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
To make matters more difficult, his wife held medical power of attorney despite his apparent competence to make decisions, said Takiar, who formerly worked with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Cincinnati Healthcare System and is now chair of radiation oncology at Penn State University.
All these factors would likely have derailed his treatment if not for a coordinated team intervention, Takiar said. Fortunately, the clinic launched a multifaceted effort involving representatives from the social work, dentistry, ethics, nutrition, and chaplaincy departments.
When surgery became impossible because the patient couldn’t lie on the operating table for adequate tumor exposure, she said, the existing team framework enabled a seamless and rapid transition to radiation with concurrent chemotherapy.
The patient completed treatment with an excellent response, offering a lesson in the importance of multidisciplinary care in head-and-neck cancers, she said.
In fact, when it comes to these forms of cancer, coordinated care “is probably more impactful than any treatment that we’re going to come up with,” she said. “The data show that when we do multidisciplinary care and we do it well, it actually improves the patient experience and outcomes.”
As Takiar noted, teamwork matters in many ways. It leads to better logistics and can address disparities, reduce financial burden and stigma, and even increase clinical trial involvement.
She pointed to studies linking teamwork to better outcomes, support for patients, and overall survival.
Takiar highlighted different parts of teams headed by radiation oncologists who act as “a node to improve multimodal care delivery.”
Speech and swallowing specialists, for example, are helpful in head-and-neck cancer because “there’s an impact on speech, swallowing, and appearance. Our patients don’t want to go out to dinner with friends because they can’t do it.”
Dentists and prosthodontists are key team members too: “I have dentists who have my cell phone number. They just call me: ‘Can I do this extraction? Was this in your radiation field? What was the dose?’”
Other team members include ear, nose, and throat specialists, palliative and supportive care specialists, medical oncologists, nurses, pathologists, transportation workers, and service connection specialists. She noted that previous military experience can affect radiation therapy. For example, the physical restraints required during treatment present particular challenges for veterans who’ve had wartime trauma. These patients may require therapy adjustments.
What’s next on the horizon? Takiar highlighted precision oncology and molecular profiling, artificial intelligence in care decisions and in radiation planning, telemedicine and virtual tumor boards, and expanded survivorship programs.
As for now, she urged colleagues to not be afraid to chat with radiation oncologists. “Please talk to us. We prioritize open communication and shared decision-making with the entire team,” she said. “If you see something and think your radiation oncologist should know about it, you think it was caused by the radiation, you should reach out to us.”
Takiar reported no disclosures.
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
'Distress is the Norm': How Oncologists Can Open the Door to Patient Mental Health
'Distress is the Norm': How Oncologists Can Open the Door to Patient Mental Health
For patients with cancer, the determining factor in whether they pursue mental health services is often whether their oncologist explicitly says it is a good idea, a psychologist said during the July Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, on treating veterans with renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Kysa Christie, PhD, of the West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Medical Center, presented findings from a 2018 study in which researchers asked Swiss patients with cancer whether their oncologist discussed their emotional health with them.
In terms of boosting intake, it did not matter if oncologists acknowledged distress or pointed out that psychosocial services existed. Instead, a direct recommendation made a difference, increasing the likelihood of using the services over a 4-month period after initial assessment (odds ratio, 6.27).
“What it took was, ‘I really recommend this. This is something that I would want you to try,’” Christie said.
Oncologists are crucial links between patients and mental health services, Christie said: “If people don’t ask about [distress], you’re not going to see it, but it’s there. Distress is the norm, right? It is not a weakness. It is something that we expect to see.”
Christie noted that an estimated 20% of cancer patients have major depressive disorder, and 35% to 40% have a diagnosable psychiatric condition. RCC shows disproportionately high rates of mental strain. According to Christie, research suggests that about three-fourths of the population report elevated levels of distress as evidenced by patients who scored ≥ 5 on the NCCN Distress Thermometer. Patients with cancer have an estimated 20% higher risk of suicide, especially during the first 12 months after diagnosis and at end of life, she added.
“Early during a diagnosis phase, where you’re having a lot of tests being done, you know something is happening. But you don’t know what,” Christie said. “It could be very serious. That’s just a lot of stress to hold and not know how to plan for.”
After diagnosis, routine could set in and lower distress, she said. Then terminal illness may spike it back up again. Does mental health treatment work in patients with cancer?
“There’s a really strong body of evidence-based treatments for depression, anxiety, adjustment disorders, and coping with different cancers,” Christie said. But it is a step too far to expect patients to ask for help while they are juggling appointments, tests, infusions, and more. “It’s a big ask, right? It’s setting people up for failure.”
To help, Christie said she is embedded with a medical oncology team and routinely talks with the staff about which patients may need help. “One thing I like to do is try to have brief visits with veterans and introduce myself when they come to clinic. I treat it like an opt-out rather than an opt-in program: I’ll just pop into the exam room. They don’t have to ask to see me.”
Christie focuses on open-ended questions and talks about resources ranging from support groups and brief appointments to extensive individual therapy.
Another approach is a strategy known as the “warm handoff,” when an oncologist directly introduces a patient to a mental health professional. “It’s a transfer of care in front of the veteran: It’s much more time-efficient than putting in a referral.”
Christie explained how this can work. A clinician will ask her to meet with a patient during an appointment, perhaps in a couple minutes.
“Then I pop into the room, and the oncologist says, ‘Thanks for joining us. This is Mr. Jones. He has been experiencing feelings of anxiety and sadness, and we’d appreciate your help in exploring some options that might help.’ I turn to the patient and ask, ‘What more would you add?’ Then I either take Mr. Jones back to my office or stay in clinic, and we’re off to the races.”
Christie reported no disclosures.
For patients with cancer, the determining factor in whether they pursue mental health services is often whether their oncologist explicitly says it is a good idea, a psychologist said during the July Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, on treating veterans with renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Kysa Christie, PhD, of the West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Medical Center, presented findings from a 2018 study in which researchers asked Swiss patients with cancer whether their oncologist discussed their emotional health with them.
In terms of boosting intake, it did not matter if oncologists acknowledged distress or pointed out that psychosocial services existed. Instead, a direct recommendation made a difference, increasing the likelihood of using the services over a 4-month period after initial assessment (odds ratio, 6.27).
“What it took was, ‘I really recommend this. This is something that I would want you to try,’” Christie said.
Oncologists are crucial links between patients and mental health services, Christie said: “If people don’t ask about [distress], you’re not going to see it, but it’s there. Distress is the norm, right? It is not a weakness. It is something that we expect to see.”
Christie noted that an estimated 20% of cancer patients have major depressive disorder, and 35% to 40% have a diagnosable psychiatric condition. RCC shows disproportionately high rates of mental strain. According to Christie, research suggests that about three-fourths of the population report elevated levels of distress as evidenced by patients who scored ≥ 5 on the NCCN Distress Thermometer. Patients with cancer have an estimated 20% higher risk of suicide, especially during the first 12 months after diagnosis and at end of life, she added.
“Early during a diagnosis phase, where you’re having a lot of tests being done, you know something is happening. But you don’t know what,” Christie said. “It could be very serious. That’s just a lot of stress to hold and not know how to plan for.”
After diagnosis, routine could set in and lower distress, she said. Then terminal illness may spike it back up again. Does mental health treatment work in patients with cancer?
“There’s a really strong body of evidence-based treatments for depression, anxiety, adjustment disorders, and coping with different cancers,” Christie said. But it is a step too far to expect patients to ask for help while they are juggling appointments, tests, infusions, and more. “It’s a big ask, right? It’s setting people up for failure.”
To help, Christie said she is embedded with a medical oncology team and routinely talks with the staff about which patients may need help. “One thing I like to do is try to have brief visits with veterans and introduce myself when they come to clinic. I treat it like an opt-out rather than an opt-in program: I’ll just pop into the exam room. They don’t have to ask to see me.”
Christie focuses on open-ended questions and talks about resources ranging from support groups and brief appointments to extensive individual therapy.
Another approach is a strategy known as the “warm handoff,” when an oncologist directly introduces a patient to a mental health professional. “It’s a transfer of care in front of the veteran: It’s much more time-efficient than putting in a referral.”
Christie explained how this can work. A clinician will ask her to meet with a patient during an appointment, perhaps in a couple minutes.
“Then I pop into the room, and the oncologist says, ‘Thanks for joining us. This is Mr. Jones. He has been experiencing feelings of anxiety and sadness, and we’d appreciate your help in exploring some options that might help.’ I turn to the patient and ask, ‘What more would you add?’ Then I either take Mr. Jones back to my office or stay in clinic, and we’re off to the races.”
Christie reported no disclosures.
For patients with cancer, the determining factor in whether they pursue mental health services is often whether their oncologist explicitly says it is a good idea, a psychologist said during the July Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, on treating veterans with renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Kysa Christie, PhD, of the West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Medical Center, presented findings from a 2018 study in which researchers asked Swiss patients with cancer whether their oncologist discussed their emotional health with them.
In terms of boosting intake, it did not matter if oncologists acknowledged distress or pointed out that psychosocial services existed. Instead, a direct recommendation made a difference, increasing the likelihood of using the services over a 4-month period after initial assessment (odds ratio, 6.27).
“What it took was, ‘I really recommend this. This is something that I would want you to try,’” Christie said.
Oncologists are crucial links between patients and mental health services, Christie said: “If people don’t ask about [distress], you’re not going to see it, but it’s there. Distress is the norm, right? It is not a weakness. It is something that we expect to see.”
Christie noted that an estimated 20% of cancer patients have major depressive disorder, and 35% to 40% have a diagnosable psychiatric condition. RCC shows disproportionately high rates of mental strain. According to Christie, research suggests that about three-fourths of the population report elevated levels of distress as evidenced by patients who scored ≥ 5 on the NCCN Distress Thermometer. Patients with cancer have an estimated 20% higher risk of suicide, especially during the first 12 months after diagnosis and at end of life, she added.
“Early during a diagnosis phase, where you’re having a lot of tests being done, you know something is happening. But you don’t know what,” Christie said. “It could be very serious. That’s just a lot of stress to hold and not know how to plan for.”
After diagnosis, routine could set in and lower distress, she said. Then terminal illness may spike it back up again. Does mental health treatment work in patients with cancer?
“There’s a really strong body of evidence-based treatments for depression, anxiety, adjustment disorders, and coping with different cancers,” Christie said. But it is a step too far to expect patients to ask for help while they are juggling appointments, tests, infusions, and more. “It’s a big ask, right? It’s setting people up for failure.”
To help, Christie said she is embedded with a medical oncology team and routinely talks with the staff about which patients may need help. “One thing I like to do is try to have brief visits with veterans and introduce myself when they come to clinic. I treat it like an opt-out rather than an opt-in program: I’ll just pop into the exam room. They don’t have to ask to see me.”
Christie focuses on open-ended questions and talks about resources ranging from support groups and brief appointments to extensive individual therapy.
Another approach is a strategy known as the “warm handoff,” when an oncologist directly introduces a patient to a mental health professional. “It’s a transfer of care in front of the veteran: It’s much more time-efficient than putting in a referral.”
Christie explained how this can work. A clinician will ask her to meet with a patient during an appointment, perhaps in a couple minutes.
“Then I pop into the room, and the oncologist says, ‘Thanks for joining us. This is Mr. Jones. He has been experiencing feelings of anxiety and sadness, and we’d appreciate your help in exploring some options that might help.’ I turn to the patient and ask, ‘What more would you add?’ Then I either take Mr. Jones back to my office or stay in clinic, and we’re off to the races.”
Christie reported no disclosures.
'Distress is the Norm': How Oncologists Can Open the Door to Patient Mental Health
'Distress is the Norm': How Oncologists Can Open the Door to Patient Mental Health
Contraceptive Care Clinic Focuses on Military Readiness
SAN DIEGO — Not surprisingly, the contraception clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center near Tacoma, Wash., is popular among female soldiers seeking to avoid pregnancy. However, about half of the patients drop by for other reasons, the military pharmacist who runs the program told colleagues here at the Joint Federal Pharmacy Seminar.
“They come to suppress menstruation, to get help with pain, to get help with PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] symptoms. They're coming for a wide range of indications that we use contraception to treat,” said Sarah Abel, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist.
Regardless of the reason, Abel emphasized that contraceptives can significantly impact the ability of female soldiers to do their jobs. “If you have heavy periods and can't make it in work, or you have endometriosis and requiring a lot of doctor's appointments, or you're deployed and you get pregnant, these are all situations where contraceptive care matters,” she said. Rates of unintended pregnancy are higher in servicewomen than in the general population.
Abel, who opened the medical center’s contraceptive clinic about 10 years ago, stressed that it’s crucial to military readiness considering that the percentage of women in the American military is approaching 20%.
Thanks to a 2022 edict, military hospitals and clinics are required to offer walk-in contraceptive services with same-day access, no requirements for appointments or referrals. An announcement about the mandate noted that these contraceptive services, such as preventing unplanned pregnancy and decreasing menstrual periods, “support the overall well-being of the force and optimize personal warrior readiness.”
As Abel noted, 29 states and Washington D.C. allow pharmacists to prescribe contraception to outpatients, although the requirements vary. “Can we start practicing at the top of our license and start prescribing in the outpatient setting? Absolutely we should,” she said. “Pharmacists have a very unique opportunity to be a part of this.”
Abel also shared that setting up a contraceptive program requires patience and education. “I cannot tell you how many women have come to me who don't know the different names of their body parts, women who've had two babies that don't understand how their body works. So, I constantly find myself taking extra time to do general sexual education,” she said.
There are many lessons to impart to patients about sexual health. For example, birth control drugs and devices do not prevent transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). “So I have bowls of condoms literally everywhere because condoms are the only thing that protects against STIs,” Abel said.
In terms of devices, “we have diaphragms available and cervical caps,” she said. “The Caya diaphragm is a TRICARE-covered benefit. It’s a small purple diaphragm, one size fits most. We can prescribe it, and it is good for 2 years. Unfortunately, spermicide, which you have to use with these things, is not a TRICARE-covered benefit.”
Hormonal contraceptives are also available, with Abel recommending the continuous monophasic type for most women. “Please don't tell women they have to have their periods. They don't,” she said. “What I'm trying to do is give a woman some stability in her hormones. She can know and expect what she's going to feel like. She's not going to wake up and say, ‘Oh God, today's the day. I'm going to be like this for a week.’”
Patches are another option, and a flurry of patients have been asking about them because of recent TikTok videos promoting their use. “We have the Xulane patch, our bread and butter. They wear it on their shoulder, their hip, their butt, or their back. They leave it in place for a week at a time. And every week, they will change that patch. I usually have to walk patients through a whole month to help them understand how that works.”
Another option, the NuvaRing, is notable because it’s linked to low amounts of breakthrough bleeding Abel noted. An extended form is now available that doesn’t need to be removed during menstrual periods.
Medroxyprogesterone injections, which are linked to bone loss, and subdermal implants, which may be less effective in women over 130% of their ideal weight are also available, she said.
Finally, IUDs are an option, although when they fail, they’re linked to ectopic pregnancies.
Abel has no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — Not surprisingly, the contraception clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center near Tacoma, Wash., is popular among female soldiers seeking to avoid pregnancy. However, about half of the patients drop by for other reasons, the military pharmacist who runs the program told colleagues here at the Joint Federal Pharmacy Seminar.
“They come to suppress menstruation, to get help with pain, to get help with PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] symptoms. They're coming for a wide range of indications that we use contraception to treat,” said Sarah Abel, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist.
Regardless of the reason, Abel emphasized that contraceptives can significantly impact the ability of female soldiers to do their jobs. “If you have heavy periods and can't make it in work, or you have endometriosis and requiring a lot of doctor's appointments, or you're deployed and you get pregnant, these are all situations where contraceptive care matters,” she said. Rates of unintended pregnancy are higher in servicewomen than in the general population.
Abel, who opened the medical center’s contraceptive clinic about 10 years ago, stressed that it’s crucial to military readiness considering that the percentage of women in the American military is approaching 20%.
Thanks to a 2022 edict, military hospitals and clinics are required to offer walk-in contraceptive services with same-day access, no requirements for appointments or referrals. An announcement about the mandate noted that these contraceptive services, such as preventing unplanned pregnancy and decreasing menstrual periods, “support the overall well-being of the force and optimize personal warrior readiness.”
As Abel noted, 29 states and Washington D.C. allow pharmacists to prescribe contraception to outpatients, although the requirements vary. “Can we start practicing at the top of our license and start prescribing in the outpatient setting? Absolutely we should,” she said. “Pharmacists have a very unique opportunity to be a part of this.”
Abel also shared that setting up a contraceptive program requires patience and education. “I cannot tell you how many women have come to me who don't know the different names of their body parts, women who've had two babies that don't understand how their body works. So, I constantly find myself taking extra time to do general sexual education,” she said.
There are many lessons to impart to patients about sexual health. For example, birth control drugs and devices do not prevent transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). “So I have bowls of condoms literally everywhere because condoms are the only thing that protects against STIs,” Abel said.
In terms of devices, “we have diaphragms available and cervical caps,” she said. “The Caya diaphragm is a TRICARE-covered benefit. It’s a small purple diaphragm, one size fits most. We can prescribe it, and it is good for 2 years. Unfortunately, spermicide, which you have to use with these things, is not a TRICARE-covered benefit.”
Hormonal contraceptives are also available, with Abel recommending the continuous monophasic type for most women. “Please don't tell women they have to have their periods. They don't,” she said. “What I'm trying to do is give a woman some stability in her hormones. She can know and expect what she's going to feel like. She's not going to wake up and say, ‘Oh God, today's the day. I'm going to be like this for a week.’”
Patches are another option, and a flurry of patients have been asking about them because of recent TikTok videos promoting their use. “We have the Xulane patch, our bread and butter. They wear it on their shoulder, their hip, their butt, or their back. They leave it in place for a week at a time. And every week, they will change that patch. I usually have to walk patients through a whole month to help them understand how that works.”
Another option, the NuvaRing, is notable because it’s linked to low amounts of breakthrough bleeding Abel noted. An extended form is now available that doesn’t need to be removed during menstrual periods.
Medroxyprogesterone injections, which are linked to bone loss, and subdermal implants, which may be less effective in women over 130% of their ideal weight are also available, she said.
Finally, IUDs are an option, although when they fail, they’re linked to ectopic pregnancies.
Abel has no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — Not surprisingly, the contraception clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center near Tacoma, Wash., is popular among female soldiers seeking to avoid pregnancy. However, about half of the patients drop by for other reasons, the military pharmacist who runs the program told colleagues here at the Joint Federal Pharmacy Seminar.
“They come to suppress menstruation, to get help with pain, to get help with PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] symptoms. They're coming for a wide range of indications that we use contraception to treat,” said Sarah Abel, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist.
Regardless of the reason, Abel emphasized that contraceptives can significantly impact the ability of female soldiers to do their jobs. “If you have heavy periods and can't make it in work, or you have endometriosis and requiring a lot of doctor's appointments, or you're deployed and you get pregnant, these are all situations where contraceptive care matters,” she said. Rates of unintended pregnancy are higher in servicewomen than in the general population.
Abel, who opened the medical center’s contraceptive clinic about 10 years ago, stressed that it’s crucial to military readiness considering that the percentage of women in the American military is approaching 20%.
Thanks to a 2022 edict, military hospitals and clinics are required to offer walk-in contraceptive services with same-day access, no requirements for appointments or referrals. An announcement about the mandate noted that these contraceptive services, such as preventing unplanned pregnancy and decreasing menstrual periods, “support the overall well-being of the force and optimize personal warrior readiness.”
As Abel noted, 29 states and Washington D.C. allow pharmacists to prescribe contraception to outpatients, although the requirements vary. “Can we start practicing at the top of our license and start prescribing in the outpatient setting? Absolutely we should,” she said. “Pharmacists have a very unique opportunity to be a part of this.”
Abel also shared that setting up a contraceptive program requires patience and education. “I cannot tell you how many women have come to me who don't know the different names of their body parts, women who've had two babies that don't understand how their body works. So, I constantly find myself taking extra time to do general sexual education,” she said.
There are many lessons to impart to patients about sexual health. For example, birth control drugs and devices do not prevent transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). “So I have bowls of condoms literally everywhere because condoms are the only thing that protects against STIs,” Abel said.
In terms of devices, “we have diaphragms available and cervical caps,” she said. “The Caya diaphragm is a TRICARE-covered benefit. It’s a small purple diaphragm, one size fits most. We can prescribe it, and it is good for 2 years. Unfortunately, spermicide, which you have to use with these things, is not a TRICARE-covered benefit.”
Hormonal contraceptives are also available, with Abel recommending the continuous monophasic type for most women. “Please don't tell women they have to have their periods. They don't,” she said. “What I'm trying to do is give a woman some stability in her hormones. She can know and expect what she's going to feel like. She's not going to wake up and say, ‘Oh God, today's the day. I'm going to be like this for a week.’”
Patches are another option, and a flurry of patients have been asking about them because of recent TikTok videos promoting their use. “We have the Xulane patch, our bread and butter. They wear it on their shoulder, their hip, their butt, or their back. They leave it in place for a week at a time. And every week, they will change that patch. I usually have to walk patients through a whole month to help them understand how that works.”
Another option, the NuvaRing, is notable because it’s linked to low amounts of breakthrough bleeding Abel noted. An extended form is now available that doesn’t need to be removed during menstrual periods.
Medroxyprogesterone injections, which are linked to bone loss, and subdermal implants, which may be less effective in women over 130% of their ideal weight are also available, she said.
Finally, IUDs are an option, although when they fail, they’re linked to ectopic pregnancies.
Abel has no disclosures.
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Identical Survival for Abiraterone and Enzalutamide in Vets With Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
Abiraterone and enzalutamide showed identical survival outcomes when used as first-line treatment for metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC), according to a new study using US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) data. The report represents the first head-to-head clinical analysis of these commonly used androgen receptor inhibitors.
Among 1258 veterans treated with abiraterone and 311 treated with enzalutamide, median overall survival was 36.2 months for both drugs. Patients were followed for a mean of 28.7 months (abiraterone) and 30.8 months (enzalutamide), reported by Martin W. Schoen, MD, MPH, from Saint Louis University School of Medicine and the St. Louis VA Medical Center, in JAMA Network Open.
Notably, there was no significant difference in outcomes among Black veterans, who often have poorer outcomes in prostate cancer, and in patients with cardiovascular disease.
“This is the first direct comparison of abiraterone and enzalutamide for mHSPC in a clinical practice setting,” Schoen told Federal Practitioner. “At the population level, there are no differences based on initial treatment choice.”
Abiraterone Is Preferred in the VA Due to Cost
According to Schoen, abiraterone and enzalutamide are the most commonly used androgen receptor inhibitors to treat mHSPC within the VA. A 2025 study by Schoen and colleagues found that 53.7% of veterans with mHSPC in 2022 received androgen receptor inhibitor therapy, up from 16.9% in 2017.
“In the VA, the preference for most patients is abiraterone since it is the least expensive agent,” he said. A generic version has been available for several years.
Additionally, abiraterone “has been on the market for the longest, and therefore clinicians are familiar with its use,” Schoen said. However, “clinicians have little idea of the comparative efficacy between these 2 agents,” he added.
The authors suggest that the cost and toxicities of the medications should guide clinician decisions, Schoen said. “There is data that abiraterone may worsen diabetes, since it is given with prednisone and could increase the risk of cardiovascular events,” he said.
He added that 2 newer drugs, apalutamide and darolutamide, are also “viable options.” Chemotherapies and certain targeted drugs are also available, “but they are only used in a select group of patients.”
Outside Specialist: Diverse Study Population Is a Plus
Hematologist-oncologist Natalie Reizine, MD, of the University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, told Federal Practitioner that the real-world data are valuable given the limitations of clinical trial populations.
“It’s difficult to compare clinical trials because they enroll different groups of patients,” she said. And, she said, they often exclude patients with significant comorbidities. “If they have bad cardiovascular disease, for instance, or poorly controlled diabetes, they're excluded from the clinical trial. But in real life, many of our patients have other medical problems that we have to manage.”
Reizine also emphasized the significance of the study’s diverse patient population. “Black men are very underrepresented in clinical trials. Many clinical trials that lead to drug approval will have only few or no Black men at all, yet these drugs go on to be widely prescribed to all men with prostate cancer.”
Results Are ‘Reassuring’
Reizine described the overall study findings as “reassuring,” especially in light of “studies that show that abiraterone and prednisone may be associated with worse cardiovascular outcomes. This study showed that in this VA population, even for patients who had cardiovascular disease, there was not a difference in how they did.”
As for choosing between agents, she recommended considering comorbidities and potential drug-drug interactions. “One of the big reasons that you may not be able to safely prescribe enzalutamide, for instance, is if a patient is on an anticoagulant, which is incredibly common in cancer patients. Enzalutamide has more drug-drug interactions than abiraterone and prednisone.”
Study Demographics and Findings
The study included all patients with mHSPC who initiated abiraterone or enzalutamide between July 2017 and April 2023.
Median ages were 73 (abiraterone) and 74 years (enzalutamide, P = .29). Racial distribution was similar between groups: abiraterone (68.1% White, 25.0% Black, 6.9% other/unknown) and enzalutamide (66.6% White, 27.0% Black, 6.4% other/unknown; P = .74). Ethnicity was 89.2% non-Hispanic, 4.4% Hispanic, and 6.4% unknown in the abiraterone group vs 88.4% non-Hispanic, 3.5% Hispanic, and 8.0% unknown in the enzalutamide group (P = .50).
The groups had similar rates of the most common comorbidities: diabetes (40.5% vs 46.3%, respectively, P = .07), peripheral vascular disease (40.2% vs 37.6%, respectively, P = .44), and chronic pulmonary disease (37.0% vs 40.5%, P = .29).
In an inverse probability weighting analysis with abiraterone as reference, weighted median overall survival was comparable across the entire cohort (36.2 months, P = .32), Black veterans (39.7 months, P = .90), and those with cardiovascular disease (31.5 months, P = .30).
The authors noted limitations such as the observational cohort design and data constraints.
The study was supported by the American Society of Clinical Oncology Conquer Cancer Foundation, the Prostate Cancer Foundation, and the Blavatnik Family Foundation.
Schoen discloses relationships with the Prostate Cancer Foundation, Astellas, and US Department of Defense. Other authors disclose relationships with the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Pfizer, Exelixis, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Merck, Seagen, Bellicum, and BMS.
Outside the submitted work. Reizine discloses relationships with the US Department of Defense, Sanofi, Exelexis, Janssen, AstraZeneca, EMD Serono, Janssen, Merck, and Tempus.
Abiraterone and enzalutamide showed identical survival outcomes when used as first-line treatment for metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC), according to a new study using US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) data. The report represents the first head-to-head clinical analysis of these commonly used androgen receptor inhibitors.
Among 1258 veterans treated with abiraterone and 311 treated with enzalutamide, median overall survival was 36.2 months for both drugs. Patients were followed for a mean of 28.7 months (abiraterone) and 30.8 months (enzalutamide), reported by Martin W. Schoen, MD, MPH, from Saint Louis University School of Medicine and the St. Louis VA Medical Center, in JAMA Network Open.
Notably, there was no significant difference in outcomes among Black veterans, who often have poorer outcomes in prostate cancer, and in patients with cardiovascular disease.
“This is the first direct comparison of abiraterone and enzalutamide for mHSPC in a clinical practice setting,” Schoen told Federal Practitioner. “At the population level, there are no differences based on initial treatment choice.”
Abiraterone Is Preferred in the VA Due to Cost
According to Schoen, abiraterone and enzalutamide are the most commonly used androgen receptor inhibitors to treat mHSPC within the VA. A 2025 study by Schoen and colleagues found that 53.7% of veterans with mHSPC in 2022 received androgen receptor inhibitor therapy, up from 16.9% in 2017.
“In the VA, the preference for most patients is abiraterone since it is the least expensive agent,” he said. A generic version has been available for several years.
Additionally, abiraterone “has been on the market for the longest, and therefore clinicians are familiar with its use,” Schoen said. However, “clinicians have little idea of the comparative efficacy between these 2 agents,” he added.
The authors suggest that the cost and toxicities of the medications should guide clinician decisions, Schoen said. “There is data that abiraterone may worsen diabetes, since it is given with prednisone and could increase the risk of cardiovascular events,” he said.
He added that 2 newer drugs, apalutamide and darolutamide, are also “viable options.” Chemotherapies and certain targeted drugs are also available, “but they are only used in a select group of patients.”
Outside Specialist: Diverse Study Population Is a Plus
Hematologist-oncologist Natalie Reizine, MD, of the University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, told Federal Practitioner that the real-world data are valuable given the limitations of clinical trial populations.
“It’s difficult to compare clinical trials because they enroll different groups of patients,” she said. And, she said, they often exclude patients with significant comorbidities. “If they have bad cardiovascular disease, for instance, or poorly controlled diabetes, they're excluded from the clinical trial. But in real life, many of our patients have other medical problems that we have to manage.”
Reizine also emphasized the significance of the study’s diverse patient population. “Black men are very underrepresented in clinical trials. Many clinical trials that lead to drug approval will have only few or no Black men at all, yet these drugs go on to be widely prescribed to all men with prostate cancer.”
Results Are ‘Reassuring’
Reizine described the overall study findings as “reassuring,” especially in light of “studies that show that abiraterone and prednisone may be associated with worse cardiovascular outcomes. This study showed that in this VA population, even for patients who had cardiovascular disease, there was not a difference in how they did.”
As for choosing between agents, she recommended considering comorbidities and potential drug-drug interactions. “One of the big reasons that you may not be able to safely prescribe enzalutamide, for instance, is if a patient is on an anticoagulant, which is incredibly common in cancer patients. Enzalutamide has more drug-drug interactions than abiraterone and prednisone.”
Study Demographics and Findings
The study included all patients with mHSPC who initiated abiraterone or enzalutamide between July 2017 and April 2023.
Median ages were 73 (abiraterone) and 74 years (enzalutamide, P = .29). Racial distribution was similar between groups: abiraterone (68.1% White, 25.0% Black, 6.9% other/unknown) and enzalutamide (66.6% White, 27.0% Black, 6.4% other/unknown; P = .74). Ethnicity was 89.2% non-Hispanic, 4.4% Hispanic, and 6.4% unknown in the abiraterone group vs 88.4% non-Hispanic, 3.5% Hispanic, and 8.0% unknown in the enzalutamide group (P = .50).
The groups had similar rates of the most common comorbidities: diabetes (40.5% vs 46.3%, respectively, P = .07), peripheral vascular disease (40.2% vs 37.6%, respectively, P = .44), and chronic pulmonary disease (37.0% vs 40.5%, P = .29).
In an inverse probability weighting analysis with abiraterone as reference, weighted median overall survival was comparable across the entire cohort (36.2 months, P = .32), Black veterans (39.7 months, P = .90), and those with cardiovascular disease (31.5 months, P = .30).
The authors noted limitations such as the observational cohort design and data constraints.
The study was supported by the American Society of Clinical Oncology Conquer Cancer Foundation, the Prostate Cancer Foundation, and the Blavatnik Family Foundation.
Schoen discloses relationships with the Prostate Cancer Foundation, Astellas, and US Department of Defense. Other authors disclose relationships with the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Pfizer, Exelixis, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Merck, Seagen, Bellicum, and BMS.
Outside the submitted work. Reizine discloses relationships with the US Department of Defense, Sanofi, Exelexis, Janssen, AstraZeneca, EMD Serono, Janssen, Merck, and Tempus.
Abiraterone and enzalutamide showed identical survival outcomes when used as first-line treatment for metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC), according to a new study using US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) data. The report represents the first head-to-head clinical analysis of these commonly used androgen receptor inhibitors.
Among 1258 veterans treated with abiraterone and 311 treated with enzalutamide, median overall survival was 36.2 months for both drugs. Patients were followed for a mean of 28.7 months (abiraterone) and 30.8 months (enzalutamide), reported by Martin W. Schoen, MD, MPH, from Saint Louis University School of Medicine and the St. Louis VA Medical Center, in JAMA Network Open.
Notably, there was no significant difference in outcomes among Black veterans, who often have poorer outcomes in prostate cancer, and in patients with cardiovascular disease.
“This is the first direct comparison of abiraterone and enzalutamide for mHSPC in a clinical practice setting,” Schoen told Federal Practitioner. “At the population level, there are no differences based on initial treatment choice.”
Abiraterone Is Preferred in the VA Due to Cost
According to Schoen, abiraterone and enzalutamide are the most commonly used androgen receptor inhibitors to treat mHSPC within the VA. A 2025 study by Schoen and colleagues found that 53.7% of veterans with mHSPC in 2022 received androgen receptor inhibitor therapy, up from 16.9% in 2017.
“In the VA, the preference for most patients is abiraterone since it is the least expensive agent,” he said. A generic version has been available for several years.
Additionally, abiraterone “has been on the market for the longest, and therefore clinicians are familiar with its use,” Schoen said. However, “clinicians have little idea of the comparative efficacy between these 2 agents,” he added.
The authors suggest that the cost and toxicities of the medications should guide clinician decisions, Schoen said. “There is data that abiraterone may worsen diabetes, since it is given with prednisone and could increase the risk of cardiovascular events,” he said.
He added that 2 newer drugs, apalutamide and darolutamide, are also “viable options.” Chemotherapies and certain targeted drugs are also available, “but they are only used in a select group of patients.”
Outside Specialist: Diverse Study Population Is a Plus
Hematologist-oncologist Natalie Reizine, MD, of the University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, told Federal Practitioner that the real-world data are valuable given the limitations of clinical trial populations.
“It’s difficult to compare clinical trials because they enroll different groups of patients,” she said. And, she said, they often exclude patients with significant comorbidities. “If they have bad cardiovascular disease, for instance, or poorly controlled diabetes, they're excluded from the clinical trial. But in real life, many of our patients have other medical problems that we have to manage.”
Reizine also emphasized the significance of the study’s diverse patient population. “Black men are very underrepresented in clinical trials. Many clinical trials that lead to drug approval will have only few or no Black men at all, yet these drugs go on to be widely prescribed to all men with prostate cancer.”
Results Are ‘Reassuring’
Reizine described the overall study findings as “reassuring,” especially in light of “studies that show that abiraterone and prednisone may be associated with worse cardiovascular outcomes. This study showed that in this VA population, even for patients who had cardiovascular disease, there was not a difference in how they did.”
As for choosing between agents, she recommended considering comorbidities and potential drug-drug interactions. “One of the big reasons that you may not be able to safely prescribe enzalutamide, for instance, is if a patient is on an anticoagulant, which is incredibly common in cancer patients. Enzalutamide has more drug-drug interactions than abiraterone and prednisone.”
Study Demographics and Findings
The study included all patients with mHSPC who initiated abiraterone or enzalutamide between July 2017 and April 2023.
Median ages were 73 (abiraterone) and 74 years (enzalutamide, P = .29). Racial distribution was similar between groups: abiraterone (68.1% White, 25.0% Black, 6.9% other/unknown) and enzalutamide (66.6% White, 27.0% Black, 6.4% other/unknown; P = .74). Ethnicity was 89.2% non-Hispanic, 4.4% Hispanic, and 6.4% unknown in the abiraterone group vs 88.4% non-Hispanic, 3.5% Hispanic, and 8.0% unknown in the enzalutamide group (P = .50).
The groups had similar rates of the most common comorbidities: diabetes (40.5% vs 46.3%, respectively, P = .07), peripheral vascular disease (40.2% vs 37.6%, respectively, P = .44), and chronic pulmonary disease (37.0% vs 40.5%, P = .29).
In an inverse probability weighting analysis with abiraterone as reference, weighted median overall survival was comparable across the entire cohort (36.2 months, P = .32), Black veterans (39.7 months, P = .90), and those with cardiovascular disease (31.5 months, P = .30).
The authors noted limitations such as the observational cohort design and data constraints.
The study was supported by the American Society of Clinical Oncology Conquer Cancer Foundation, the Prostate Cancer Foundation, and the Blavatnik Family Foundation.
Schoen discloses relationships with the Prostate Cancer Foundation, Astellas, and US Department of Defense. Other authors disclose relationships with the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Pfizer, Exelixis, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Merck, Seagen, Bellicum, and BMS.
Outside the submitted work. Reizine discloses relationships with the US Department of Defense, Sanofi, Exelexis, Janssen, AstraZeneca, EMD Serono, Janssen, Merck, and Tempus.
VA Performs Its First ‘Bloodless’ Stem Cell Transplant
PHOENIX ‑ A US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital in Tennessee has performed the first “bloodless” autologous stem cell transplant within the Veterans Health Administration, treating a 61-year-old Jehovah’s Witness patient with multiple myeloma who traveled from California for the procedure.
The case, presented at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, stated that “we should not withhold any therapies for patients who are Jehovah’s Witnesses out of fear of them bleeding out or having complications from anemia,” said Bhagirathbhai Dholaria, MBBS, an associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center who worked with the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System in Nashville.
While Jehovah’s Witnesses accept medical treatment, their faith forbids blood transfusions, including of preoperative autologous blood, due to its interpretation of the Bible. The faith allows individuals to decide whether to accept stem cells collected from their blood or someone else’s “provided that blood components are not intentionally collected, stored, and reinfused along with the stem cells.”
There are an estimated 1.2 million Jehovah’s Witnesses in the US.
Traditional Stem Cell Transplants Require Blood Support
In conventional autologous stem cell transplants for multiple myeloma, high-dose chemotherapy temporarily wipes out the patient’s bone marrow for about 2 to 3 weeks, Dholaria explained. During this period, patients typically receive 2 units of packed red blood cells and platelet transfusions to prevent severe complications from anemia and low platelet counts.
“Because of this reason, Jehovah’s Witnesses have been traditionally denied these therapies,” Dholaria said.
However, bloodless autologous transplants have been performed for about 2 decades, and Vanderbilt University has been offering the procedures for about 3 years, according to Dholaria.
For the first bloodless procedure in the VA, the patient–who had an aggressive, newly diagnosed IgG kappa multiple myeloma–was evaluated.
“He had been treated by local doctors in California. Otherwise, he was actually in really good shape. Physically, he didn’t have any major issues,” Dholaria said. “So, he met the criteria for our bloodless protocol, and we decided to offer him the procedure.”
The team consulted ethics and legal departments and noted the patient’s blood product preferences in his electronic health record. The patient then underwent a preoptimization protocol that included erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, intravenous iron, and vitamin B12 supplementation to boost blood counts before the transplant, according to the case presentation.
Special Protocol Required in ‘Bloodless’ Procedures
After stem cell collection and chemotherapy, patients undergoing bloodless procedures receive aggressive growth factor support to minimize the duration and severity of cytopenia, Dholaria said. As part of the protocol, the care team uses pediatric tubes for blood draws to minimize blood loss and monitors patients closely on cardiac monitors, he added. In addition, blood draws are only performed every 3 days.
“We watch for any cardiac decompensation because these patients have severe anemia for a brief period of time. We make sure they don’t [have a] heart attack or arrhythmias,” Dholaria said. “Or if the platelets are too low, and they start oozing blood from the nose, gums, or gut, that needs to be dealt with accordingly.”
For bleeding complications, the team uses clotting factors and intravenous and oral medications to support remaining platelet function rather than platelet transfusions.
The patient in this case tolerated the transplant “exceptionally well with minimal complications,” according to the case presentation. He achieved full engraftment on day 14 after transplant and was discharged from inpatient care with continued monitoring through day 30.
“The patient was very compliant,” said Salyka Sengsayadeth, MD, medical director of the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System Stem Cell Transplant and Cellular Therapy Program and associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt.
“He tolerated everything that we needed to do,” she said. “He called us when he needed to call us and did everything that we asked and recommended for him.”
The patient’s roughly 30-day hospital stay matched that of typical transplant patients, Sengsayadeth noted. His myeloma responded to treatment, and he returned to California, Dholaria said.
‘Bloodless’ Procedures Not for All Stem Cell Transplants
The case highlights the availability of stem cell transplants in the VA–they are only performed in Seattle and Nashville–and opportunities for patients who wish to avoid blood transfusions. Sengsayadeth said the bloodless protocol is available for patients without religious objections who simply prefer to avoid blood products.
Dholaria cautioned that bloodless protocol applies specifically to autologous transplants, where patients receive their own stem cells. The team does not plan to offer bloodless allogeneic transplants, which use donor stem cells for conditions like leukemia, due to higher risks. In addition, most Jehovah’s Witnesses decline allogeneic transplants because they do not accept stem cells from another person, Dholaria said.
Beyond multiple myeloma, the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System offers bloodless autologous transplants for various blood cancers, including non-Hodgkin lymphomas such as large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma, as well as lymphomas affecting the brain, Dholaria said.
Clinicians “should start thinking about this early on, as soon as the cancer diagnosis is made, to make the referral and get the patient on our radar,” Dholaria said.
Sengsayadeth said physicians within the VA typically know how to refer appropriate patients to her team. “They just send us an email or give us a call or a message to say ‘I have this patient. Do you think they’re someone I should send to you?’ We usually answer right back, and then we can proceed with the full evaluation if we think that’s a reasonable thing to do.”
‘Treated Like Family’
The patient, a Marine Corps veteran named Keith Cody, spoke about the procedure in a video interview. Cody said he was reluctant at first to undergo the procedure because he didn’t understand what it would accomplish.
“As I was doing the massive chemo every week, and then suffering with the side effects, I decided to ask again about this procedure and how it improves my quality of life,” he said.
At the time of the taping of the video, Cody was getting ready to go home to California. “They’ve told me that I’ll still need more time to get my energy back, but I do feel much better already,” he said.
He also praised the staff. “Everybody that we came across, I enjoyed the interactions. It’s actually sad to leave people behind that you really felt treated you like family.”
Dholaria discloses relationships with Janssen, Angiocrine, Pfizer, Poseida, MEI, Orcabio, Wugen, Allovir, Adicet, BMS, Molecular Templates, Atara, MJH, Arvinas, Janssen, ADC, Gilead, GSK, Caribou, F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Autolus, and Pierre Fabre.
Sengsayadeth has no disclosures.
PHOENIX ‑ A US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital in Tennessee has performed the first “bloodless” autologous stem cell transplant within the Veterans Health Administration, treating a 61-year-old Jehovah’s Witness patient with multiple myeloma who traveled from California for the procedure.
The case, presented at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, stated that “we should not withhold any therapies for patients who are Jehovah’s Witnesses out of fear of them bleeding out or having complications from anemia,” said Bhagirathbhai Dholaria, MBBS, an associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center who worked with the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System in Nashville.
While Jehovah’s Witnesses accept medical treatment, their faith forbids blood transfusions, including of preoperative autologous blood, due to its interpretation of the Bible. The faith allows individuals to decide whether to accept stem cells collected from their blood or someone else’s “provided that blood components are not intentionally collected, stored, and reinfused along with the stem cells.”
There are an estimated 1.2 million Jehovah’s Witnesses in the US.
Traditional Stem Cell Transplants Require Blood Support
In conventional autologous stem cell transplants for multiple myeloma, high-dose chemotherapy temporarily wipes out the patient’s bone marrow for about 2 to 3 weeks, Dholaria explained. During this period, patients typically receive 2 units of packed red blood cells and platelet transfusions to prevent severe complications from anemia and low platelet counts.
“Because of this reason, Jehovah’s Witnesses have been traditionally denied these therapies,” Dholaria said.
However, bloodless autologous transplants have been performed for about 2 decades, and Vanderbilt University has been offering the procedures for about 3 years, according to Dholaria.
For the first bloodless procedure in the VA, the patient–who had an aggressive, newly diagnosed IgG kappa multiple myeloma–was evaluated.
“He had been treated by local doctors in California. Otherwise, he was actually in really good shape. Physically, he didn’t have any major issues,” Dholaria said. “So, he met the criteria for our bloodless protocol, and we decided to offer him the procedure.”
The team consulted ethics and legal departments and noted the patient’s blood product preferences in his electronic health record. The patient then underwent a preoptimization protocol that included erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, intravenous iron, and vitamin B12 supplementation to boost blood counts before the transplant, according to the case presentation.
Special Protocol Required in ‘Bloodless’ Procedures
After stem cell collection and chemotherapy, patients undergoing bloodless procedures receive aggressive growth factor support to minimize the duration and severity of cytopenia, Dholaria said. As part of the protocol, the care team uses pediatric tubes for blood draws to minimize blood loss and monitors patients closely on cardiac monitors, he added. In addition, blood draws are only performed every 3 days.
“We watch for any cardiac decompensation because these patients have severe anemia for a brief period of time. We make sure they don’t [have a] heart attack or arrhythmias,” Dholaria said. “Or if the platelets are too low, and they start oozing blood from the nose, gums, or gut, that needs to be dealt with accordingly.”
For bleeding complications, the team uses clotting factors and intravenous and oral medications to support remaining platelet function rather than platelet transfusions.
The patient in this case tolerated the transplant “exceptionally well with minimal complications,” according to the case presentation. He achieved full engraftment on day 14 after transplant and was discharged from inpatient care with continued monitoring through day 30.
“The patient was very compliant,” said Salyka Sengsayadeth, MD, medical director of the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System Stem Cell Transplant and Cellular Therapy Program and associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt.
“He tolerated everything that we needed to do,” she said. “He called us when he needed to call us and did everything that we asked and recommended for him.”
The patient’s roughly 30-day hospital stay matched that of typical transplant patients, Sengsayadeth noted. His myeloma responded to treatment, and he returned to California, Dholaria said.
‘Bloodless’ Procedures Not for All Stem Cell Transplants
The case highlights the availability of stem cell transplants in the VA–they are only performed in Seattle and Nashville–and opportunities for patients who wish to avoid blood transfusions. Sengsayadeth said the bloodless protocol is available for patients without religious objections who simply prefer to avoid blood products.
Dholaria cautioned that bloodless protocol applies specifically to autologous transplants, where patients receive their own stem cells. The team does not plan to offer bloodless allogeneic transplants, which use donor stem cells for conditions like leukemia, due to higher risks. In addition, most Jehovah’s Witnesses decline allogeneic transplants because they do not accept stem cells from another person, Dholaria said.
Beyond multiple myeloma, the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System offers bloodless autologous transplants for various blood cancers, including non-Hodgkin lymphomas such as large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma, as well as lymphomas affecting the brain, Dholaria said.
Clinicians “should start thinking about this early on, as soon as the cancer diagnosis is made, to make the referral and get the patient on our radar,” Dholaria said.
Sengsayadeth said physicians within the VA typically know how to refer appropriate patients to her team. “They just send us an email or give us a call or a message to say ‘I have this patient. Do you think they’re someone I should send to you?’ We usually answer right back, and then we can proceed with the full evaluation if we think that’s a reasonable thing to do.”
‘Treated Like Family’
The patient, a Marine Corps veteran named Keith Cody, spoke about the procedure in a video interview. Cody said he was reluctant at first to undergo the procedure because he didn’t understand what it would accomplish.
“As I was doing the massive chemo every week, and then suffering with the side effects, I decided to ask again about this procedure and how it improves my quality of life,” he said.
At the time of the taping of the video, Cody was getting ready to go home to California. “They’ve told me that I’ll still need more time to get my energy back, but I do feel much better already,” he said.
He also praised the staff. “Everybody that we came across, I enjoyed the interactions. It’s actually sad to leave people behind that you really felt treated you like family.”
Dholaria discloses relationships with Janssen, Angiocrine, Pfizer, Poseida, MEI, Orcabio, Wugen, Allovir, Adicet, BMS, Molecular Templates, Atara, MJH, Arvinas, Janssen, ADC, Gilead, GSK, Caribou, F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Autolus, and Pierre Fabre.
Sengsayadeth has no disclosures.
PHOENIX ‑ A US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital in Tennessee has performed the first “bloodless” autologous stem cell transplant within the Veterans Health Administration, treating a 61-year-old Jehovah’s Witness patient with multiple myeloma who traveled from California for the procedure.
The case, presented at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, stated that “we should not withhold any therapies for patients who are Jehovah’s Witnesses out of fear of them bleeding out or having complications from anemia,” said Bhagirathbhai Dholaria, MBBS, an associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center who worked with the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System in Nashville.
While Jehovah’s Witnesses accept medical treatment, their faith forbids blood transfusions, including of preoperative autologous blood, due to its interpretation of the Bible. The faith allows individuals to decide whether to accept stem cells collected from their blood or someone else’s “provided that blood components are not intentionally collected, stored, and reinfused along with the stem cells.”
There are an estimated 1.2 million Jehovah’s Witnesses in the US.
Traditional Stem Cell Transplants Require Blood Support
In conventional autologous stem cell transplants for multiple myeloma, high-dose chemotherapy temporarily wipes out the patient’s bone marrow for about 2 to 3 weeks, Dholaria explained. During this period, patients typically receive 2 units of packed red blood cells and platelet transfusions to prevent severe complications from anemia and low platelet counts.
“Because of this reason, Jehovah’s Witnesses have been traditionally denied these therapies,” Dholaria said.
However, bloodless autologous transplants have been performed for about 2 decades, and Vanderbilt University has been offering the procedures for about 3 years, according to Dholaria.
For the first bloodless procedure in the VA, the patient–who had an aggressive, newly diagnosed IgG kappa multiple myeloma–was evaluated.
“He had been treated by local doctors in California. Otherwise, he was actually in really good shape. Physically, he didn’t have any major issues,” Dholaria said. “So, he met the criteria for our bloodless protocol, and we decided to offer him the procedure.”
The team consulted ethics and legal departments and noted the patient’s blood product preferences in his electronic health record. The patient then underwent a preoptimization protocol that included erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, intravenous iron, and vitamin B12 supplementation to boost blood counts before the transplant, according to the case presentation.
Special Protocol Required in ‘Bloodless’ Procedures
After stem cell collection and chemotherapy, patients undergoing bloodless procedures receive aggressive growth factor support to minimize the duration and severity of cytopenia, Dholaria said. As part of the protocol, the care team uses pediatric tubes for blood draws to minimize blood loss and monitors patients closely on cardiac monitors, he added. In addition, blood draws are only performed every 3 days.
“We watch for any cardiac decompensation because these patients have severe anemia for a brief period of time. We make sure they don’t [have a] heart attack or arrhythmias,” Dholaria said. “Or if the platelets are too low, and they start oozing blood from the nose, gums, or gut, that needs to be dealt with accordingly.”
For bleeding complications, the team uses clotting factors and intravenous and oral medications to support remaining platelet function rather than platelet transfusions.
The patient in this case tolerated the transplant “exceptionally well with minimal complications,” according to the case presentation. He achieved full engraftment on day 14 after transplant and was discharged from inpatient care with continued monitoring through day 30.
“The patient was very compliant,” said Salyka Sengsayadeth, MD, medical director of the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System Stem Cell Transplant and Cellular Therapy Program and associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt.
“He tolerated everything that we needed to do,” she said. “He called us when he needed to call us and did everything that we asked and recommended for him.”
The patient’s roughly 30-day hospital stay matched that of typical transplant patients, Sengsayadeth noted. His myeloma responded to treatment, and he returned to California, Dholaria said.
‘Bloodless’ Procedures Not for All Stem Cell Transplants
The case highlights the availability of stem cell transplants in the VA–they are only performed in Seattle and Nashville–and opportunities for patients who wish to avoid blood transfusions. Sengsayadeth said the bloodless protocol is available for patients without religious objections who simply prefer to avoid blood products.
Dholaria cautioned that bloodless protocol applies specifically to autologous transplants, where patients receive their own stem cells. The team does not plan to offer bloodless allogeneic transplants, which use donor stem cells for conditions like leukemia, due to higher risks. In addition, most Jehovah’s Witnesses decline allogeneic transplants because they do not accept stem cells from another person, Dholaria said.
Beyond multiple myeloma, the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System offers bloodless autologous transplants for various blood cancers, including non-Hodgkin lymphomas such as large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma, as well as lymphomas affecting the brain, Dholaria said.
Clinicians “should start thinking about this early on, as soon as the cancer diagnosis is made, to make the referral and get the patient on our radar,” Dholaria said.
Sengsayadeth said physicians within the VA typically know how to refer appropriate patients to her team. “They just send us an email or give us a call or a message to say ‘I have this patient. Do you think they’re someone I should send to you?’ We usually answer right back, and then we can proceed with the full evaluation if we think that’s a reasonable thing to do.”
‘Treated Like Family’
The patient, a Marine Corps veteran named Keith Cody, spoke about the procedure in a video interview. Cody said he was reluctant at first to undergo the procedure because he didn’t understand what it would accomplish.
“As I was doing the massive chemo every week, and then suffering with the side effects, I decided to ask again about this procedure and how it improves my quality of life,” he said.
At the time of the taping of the video, Cody was getting ready to go home to California. “They’ve told me that I’ll still need more time to get my energy back, but I do feel much better already,” he said.
He also praised the staff. “Everybody that we came across, I enjoyed the interactions. It’s actually sad to leave people behind that you really felt treated you like family.”
Dholaria discloses relationships with Janssen, Angiocrine, Pfizer, Poseida, MEI, Orcabio, Wugen, Allovir, Adicet, BMS, Molecular Templates, Atara, MJH, Arvinas, Janssen, ADC, Gilead, GSK, Caribou, F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Autolus, and Pierre Fabre.
Sengsayadeth has no disclosures.
Head and Neck Cancer: VA Dietitian Advocates Whole Foods Over Supplements
PHOENIX — Patients with head and neck cancer face high rates of malnutrition during treatment, and oral supplements are often recommended. But they are not the entire answer, a dietician told colleagues at the Association of Veterans Affairs (VA) Hematology/Oncology annual meeting.
“Patients should consume the most liberal diet possible throughout treatment,” said advanced practice oncology dietician Brittany Leneweaver, RD, CSO, CES, at the VA Washington DC Healthcare System. “This means not solely relying on oral nutrition supplements like Ensure if possible.”
While Leneweaver said many patients will need supplements, she stressed these products “are meant to supplement the diet and not be the sole source of nutrition, ideally.” Encouraging the intake of whole foods “is really key to make the transition back to solid foods after they’re done with treatment. This makes it so much easier when they’re already swallowing those thicker textures, rather than just liquid the entire time.”
Malnutrition: Common and Damaging
As Leneweaver noted, malnutrition is common in patients with head and neck cancer, and can lead to “increased treatment toxicity, increased risk of infection, decreased survival, increased surgical complication, delayed healing, decreased physical function, and decreased quality of life.”
Malnutrition data in patients with head and neck cancer in the US is sparse. However, a 2024 study found malnutrition in 20% of patients undergoing head and neck cancer surgery and linked the condition to increased length of stay (β, 5.20 additional days), higher costs (β, $15,722) higher odds of potentially preventable complications (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.04), and lower odds of discharge to home (aOR, 0.34).
Leneweaver said her role involves addressing “nutrition impact symptoms” that reduce veteran food intake such as difficulty swallowing, taste disorders, dry mouth, and inflammation of the mucus membranes.
“I can’t tell you how much time I spend just talking to the patient about their medication regimens, making sure they have antiemetics on board, letting the radiation oncologist know, ‘Hey, it’s probably time for medicine,’” she said. “We’re constantly looking at side effects and addressing to alert the team as quickly as possible so that we can prevent further weight loss.”
Better Diets Lead to Better Outcomes
Leneweaver noted that “many times, patients will continue to rely on oral supplements as their primary source of nutrition over the long term. They may be missing out on several health benefits as a result.”
Research shows that high-quality diets matter in this patient group, she said. They’re associated with “decreased symptoms during treatment, reduced head and neck cancer risk, and reduced risk of those chronic nutrition impact symptoms,” Leneweaver said.
Diets before and after cancer diagnosis can make a difference. A 2019 study examined patient diets prior to diagnosis of head and neck cancer. It found that patients with better diet quality were less likely to experience overall nutrition impact symptoms (OR 0.45). However, “studies have found that the majority of our patients with head and neck cancer have an inadequate diet prior to diagnosis,” Leneweaver said.
As for postdiagnosis nutrition, a 2022 study linked healthier diets in patients with head and neck cancer to 93% lower 3-year risk of all-cause mortality and 85% lower risk of cancer-specific mortality.
What’s in a High-Quality Diet?
Regarding specific food recommendations, Leneweaver prefers the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) nutrition guidelines over the US Department of Agriculture’s Dietary Guidelines for Americans. The AICR “more clearly recommends plant-based diet with at least two-thirds of each meal coming from a variety of plant sources” and recommends avoiding alcohol entirely and limiting red meat, she said.
Leneweaver said she recognizes that dietary change can be gradual.
“It’s not going to happen overnight,” she said. “We know that lifestyle change takes a lot of work.”
Basic interventions can be effective, she said: “This can be just as simple as recommending a plant-based diet to your patient or recommending they eat the rainbow. And I don’t mean Skittles, I mean actual plants. If you just mention these couple of things to the patients, this can really go a long way, especially if they’re hearing that consistent messaging.”
Team-Based Follow-Up Is Key
Leneweaver emphasized the importance of following up over time even if patients do not initially accept referrals to nutritional services. Dieticians ideally see patients before or during initial treatment and then weekly during radiation therapy. Posttreatment follow-up continues “until they’re nutritionally stable. This can be anywhere from weekly to monthly.”
Leneweaver emphasized collaborating with other team members. For example, she works with a speech pathologist at joint visits, either weekly or monthly, “so that they can get off of that feeding tube or get back to a solid consistency diet, typically before that 3-month PET scan.”
It is also important to understand barriers to healthy eating in the veteran population, including transportation challenges and poor access to healthy food, Leneweaver said.
“Make sure you’re utilizing your social worker, your psychologist, other resources, and food pantries, if you have them.”
Even when the most ideal choices are not available, she said, “if they only have access to canned vegetables, I’d much rather them eat that than have nothing.”
No disclosures for Leneweaver were provided.
PHOENIX — Patients with head and neck cancer face high rates of malnutrition during treatment, and oral supplements are often recommended. But they are not the entire answer, a dietician told colleagues at the Association of Veterans Affairs (VA) Hematology/Oncology annual meeting.
“Patients should consume the most liberal diet possible throughout treatment,” said advanced practice oncology dietician Brittany Leneweaver, RD, CSO, CES, at the VA Washington DC Healthcare System. “This means not solely relying on oral nutrition supplements like Ensure if possible.”
While Leneweaver said many patients will need supplements, she stressed these products “are meant to supplement the diet and not be the sole source of nutrition, ideally.” Encouraging the intake of whole foods “is really key to make the transition back to solid foods after they’re done with treatment. This makes it so much easier when they’re already swallowing those thicker textures, rather than just liquid the entire time.”
Malnutrition: Common and Damaging
As Leneweaver noted, malnutrition is common in patients with head and neck cancer, and can lead to “increased treatment toxicity, increased risk of infection, decreased survival, increased surgical complication, delayed healing, decreased physical function, and decreased quality of life.”
Malnutrition data in patients with head and neck cancer in the US is sparse. However, a 2024 study found malnutrition in 20% of patients undergoing head and neck cancer surgery and linked the condition to increased length of stay (β, 5.20 additional days), higher costs (β, $15,722) higher odds of potentially preventable complications (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.04), and lower odds of discharge to home (aOR, 0.34).
Leneweaver said her role involves addressing “nutrition impact symptoms” that reduce veteran food intake such as difficulty swallowing, taste disorders, dry mouth, and inflammation of the mucus membranes.
“I can’t tell you how much time I spend just talking to the patient about their medication regimens, making sure they have antiemetics on board, letting the radiation oncologist know, ‘Hey, it’s probably time for medicine,’” she said. “We’re constantly looking at side effects and addressing to alert the team as quickly as possible so that we can prevent further weight loss.”
Better Diets Lead to Better Outcomes
Leneweaver noted that “many times, patients will continue to rely on oral supplements as their primary source of nutrition over the long term. They may be missing out on several health benefits as a result.”
Research shows that high-quality diets matter in this patient group, she said. They’re associated with “decreased symptoms during treatment, reduced head and neck cancer risk, and reduced risk of those chronic nutrition impact symptoms,” Leneweaver said.
Diets before and after cancer diagnosis can make a difference. A 2019 study examined patient diets prior to diagnosis of head and neck cancer. It found that patients with better diet quality were less likely to experience overall nutrition impact symptoms (OR 0.45). However, “studies have found that the majority of our patients with head and neck cancer have an inadequate diet prior to diagnosis,” Leneweaver said.
As for postdiagnosis nutrition, a 2022 study linked healthier diets in patients with head and neck cancer to 93% lower 3-year risk of all-cause mortality and 85% lower risk of cancer-specific mortality.
What’s in a High-Quality Diet?
Regarding specific food recommendations, Leneweaver prefers the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) nutrition guidelines over the US Department of Agriculture’s Dietary Guidelines for Americans. The AICR “more clearly recommends plant-based diet with at least two-thirds of each meal coming from a variety of plant sources” and recommends avoiding alcohol entirely and limiting red meat, she said.
Leneweaver said she recognizes that dietary change can be gradual.
“It’s not going to happen overnight,” she said. “We know that lifestyle change takes a lot of work.”
Basic interventions can be effective, she said: “This can be just as simple as recommending a plant-based diet to your patient or recommending they eat the rainbow. And I don’t mean Skittles, I mean actual plants. If you just mention these couple of things to the patients, this can really go a long way, especially if they’re hearing that consistent messaging.”
Team-Based Follow-Up Is Key
Leneweaver emphasized the importance of following up over time even if patients do not initially accept referrals to nutritional services. Dieticians ideally see patients before or during initial treatment and then weekly during radiation therapy. Posttreatment follow-up continues “until they’re nutritionally stable. This can be anywhere from weekly to monthly.”
Leneweaver emphasized collaborating with other team members. For example, she works with a speech pathologist at joint visits, either weekly or monthly, “so that they can get off of that feeding tube or get back to a solid consistency diet, typically before that 3-month PET scan.”
It is also important to understand barriers to healthy eating in the veteran population, including transportation challenges and poor access to healthy food, Leneweaver said.
“Make sure you’re utilizing your social worker, your psychologist, other resources, and food pantries, if you have them.”
Even when the most ideal choices are not available, she said, “if they only have access to canned vegetables, I’d much rather them eat that than have nothing.”
No disclosures for Leneweaver were provided.
PHOENIX — Patients with head and neck cancer face high rates of malnutrition during treatment, and oral supplements are often recommended. But they are not the entire answer, a dietician told colleagues at the Association of Veterans Affairs (VA) Hematology/Oncology annual meeting.
“Patients should consume the most liberal diet possible throughout treatment,” said advanced practice oncology dietician Brittany Leneweaver, RD, CSO, CES, at the VA Washington DC Healthcare System. “This means not solely relying on oral nutrition supplements like Ensure if possible.”
While Leneweaver said many patients will need supplements, she stressed these products “are meant to supplement the diet and not be the sole source of nutrition, ideally.” Encouraging the intake of whole foods “is really key to make the transition back to solid foods after they’re done with treatment. This makes it so much easier when they’re already swallowing those thicker textures, rather than just liquid the entire time.”
Malnutrition: Common and Damaging
As Leneweaver noted, malnutrition is common in patients with head and neck cancer, and can lead to “increased treatment toxicity, increased risk of infection, decreased survival, increased surgical complication, delayed healing, decreased physical function, and decreased quality of life.”
Malnutrition data in patients with head and neck cancer in the US is sparse. However, a 2024 study found malnutrition in 20% of patients undergoing head and neck cancer surgery and linked the condition to increased length of stay (β, 5.20 additional days), higher costs (β, $15,722) higher odds of potentially preventable complications (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.04), and lower odds of discharge to home (aOR, 0.34).
Leneweaver said her role involves addressing “nutrition impact symptoms” that reduce veteran food intake such as difficulty swallowing, taste disorders, dry mouth, and inflammation of the mucus membranes.
“I can’t tell you how much time I spend just talking to the patient about their medication regimens, making sure they have antiemetics on board, letting the radiation oncologist know, ‘Hey, it’s probably time for medicine,’” she said. “We’re constantly looking at side effects and addressing to alert the team as quickly as possible so that we can prevent further weight loss.”
Better Diets Lead to Better Outcomes
Leneweaver noted that “many times, patients will continue to rely on oral supplements as their primary source of nutrition over the long term. They may be missing out on several health benefits as a result.”
Research shows that high-quality diets matter in this patient group, she said. They’re associated with “decreased symptoms during treatment, reduced head and neck cancer risk, and reduced risk of those chronic nutrition impact symptoms,” Leneweaver said.
Diets before and after cancer diagnosis can make a difference. A 2019 study examined patient diets prior to diagnosis of head and neck cancer. It found that patients with better diet quality were less likely to experience overall nutrition impact symptoms (OR 0.45). However, “studies have found that the majority of our patients with head and neck cancer have an inadequate diet prior to diagnosis,” Leneweaver said.
As for postdiagnosis nutrition, a 2022 study linked healthier diets in patients with head and neck cancer to 93% lower 3-year risk of all-cause mortality and 85% lower risk of cancer-specific mortality.
What’s in a High-Quality Diet?
Regarding specific food recommendations, Leneweaver prefers the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) nutrition guidelines over the US Department of Agriculture’s Dietary Guidelines for Americans. The AICR “more clearly recommends plant-based diet with at least two-thirds of each meal coming from a variety of plant sources” and recommends avoiding alcohol entirely and limiting red meat, she said.
Leneweaver said she recognizes that dietary change can be gradual.
“It’s not going to happen overnight,” she said. “We know that lifestyle change takes a lot of work.”
Basic interventions can be effective, she said: “This can be just as simple as recommending a plant-based diet to your patient or recommending they eat the rainbow. And I don’t mean Skittles, I mean actual plants. If you just mention these couple of things to the patients, this can really go a long way, especially if they’re hearing that consistent messaging.”
Team-Based Follow-Up Is Key
Leneweaver emphasized the importance of following up over time even if patients do not initially accept referrals to nutritional services. Dieticians ideally see patients before or during initial treatment and then weekly during radiation therapy. Posttreatment follow-up continues “until they’re nutritionally stable. This can be anywhere from weekly to monthly.”
Leneweaver emphasized collaborating with other team members. For example, she works with a speech pathologist at joint visits, either weekly or monthly, “so that they can get off of that feeding tube or get back to a solid consistency diet, typically before that 3-month PET scan.”
It is also important to understand barriers to healthy eating in the veteran population, including transportation challenges and poor access to healthy food, Leneweaver said.
“Make sure you’re utilizing your social worker, your psychologist, other resources, and food pantries, if you have them.”
Even when the most ideal choices are not available, she said, “if they only have access to canned vegetables, I’d much rather them eat that than have nothing.”
No disclosures for Leneweaver were provided.
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
PHOENIX – Veterans are especially vulnerable to disordered eating because of their military backgrounds, a dietician warned US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) oncology clinicians at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. In fact, an estimated 15% to 25% of veterans meet diagnostic criteria for eating disorders.
“Their experience in the military probably has really shaped the way that they see weight and the stigma behind it,” said Emily Fasciana, MS, RDN, LDN, a registered dietician with the VA based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
When cancer appears, the risk of eating disorders goes up even more, she said. “If we don’t catch eating disorders early on, severe medical problems can occur. In the cancer population, they’re going through enough medical problems as it is.”
Here are things to know about eating disorders in oncology.
Military Life Can Produce a ‘Perfect Storm’ of Risk Factors
Tightly controlled eating environments and food deprivation are often routine in military life. Along with trauma, these can create a “perfect storm of risk factors for eating disorders,” Fasciana said.
During service, for example, “people often will eat as much as they can when they can, sometimes followed by days of not being able to eat,” she said. These are very much like disordered eating behaviors such as binge eating and restricting, and they can place veterans at greater risk.”
She described how service members can develop specific eating patterns during service, such as “midrats” – midnight rations – “meals served during midnight shifts that were the best meal served all day long that they had access to.”
“When I hear veterans who wake up in the middle of the night, and they’re eating, I ask: ‘Did they practice something similar during their military experience?’ They associate that time of the day with enjoyable comfort foods, and that’s what they go to now.”
Vets Can be Haunted by Stigma of Excess Weight
“Making weight” – meeting weight standards – is routine in the military. The pressure to remain under a certain level can have lasting effects on how veterans think about extra pounds, said Kaitlin Ohde, PhD, a clinical health psychologist with the VA Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle.
“I’ve heard some veterans tell me about getting kicked out of positions because of not being able to make weight. Then they carry this throughout their life, which is really sad,” Ohde said. “When they gain weight during treatment, sometimes it can be really bothersome for them.”
Regular weigh-ins can trouble patients, she said, so it’s important to explain to them why they’re getting on scales: “I’m getting your weight today because I want to see if this medication is doing XYZ.”
She advised colleagues to “make sure they explicitly know why we’re doing it [measuring weight], and how the things we’re using to treat them can impact their weight. This piece of the puzzle sometimes falls off the radar.”
Eating Disorders Can be Catastrophic in Cancer
Untreated eating disorders cause severe medical complications such as malnutrition, hormone dysregulation, low bone density or fractures, bradycardia, gastroparesis, and even anemia, Fasciana said.
There’s a New Category of Eating Disorder
Fasciana highlighted a condition that is underrecognized in oncology: Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), which refers to patients who stay away from certain foods but not because they’re worried about body image or weight gain. “Patients with ARFID are clinically distinct from those who have anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder,” she noted.
ARFID diagnosis requires food avoidance that leads to at least 1 of these consequences: significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on supplements or tube feeding, or psychosocial impairment.
“Veterans might have a gagging or retching reflex at the sight or smell of certain foods,” Fasciana explained. “They might have difficulty being in the presence of another person eating a nonpreferred food.”
Some cancer patients may be averse to foods of certain temperatures. “You might need to assess why they don’t like the temperature of that food. Why are those foods something that you can’t go to? Are they hurting your teeth? What are they doing to you?”
ARFID patients may also experience social withdrawal around eating. “With a lot of our head and neck cancer patients, especially those with oral cancers and those on feeding tubes, they might feel embarrassed to be around people while eating,” Fasciana said.
She highlighted a 2021 report about 4 cancer survivors with upper abdominal cancers who developed new-onset eating disorders with malnutrition resembling ARFID.
The patients experienced malabsorption, dumping syndrome, and excessive weight loss for 12 months postoperatively without classic body-image concerns. “This is a case example of how eating disorders can evolve in the oncology population,” Fasciana said.
The report said that none of the patients “returned to a healthy weight and/or healthy eating despite extensive team input… The outcomes were poor; 1 patient died, another required admission to a specialist eating disorder admission with a subsequent relapsing-remitting course, and the remaining 2 had complicated chronic courses.”
Treatment: Start With Screening, Then Reframe Thinking
Fasciana highlighted several screening tools, such as SCOFF, BREDS, and one for ARFID.
“Any screen is going to be better than no screen at all, and any question is going to be better than no question at all,” Fasciana said.
She cautioned that “veterans are not going to be so forthcoming about some of their struggles due to stigma and shame because of their past experiences in the military.”
As for therapy, psychological care may not be required, Ohde said. And it’s especially important to “listen to your patients about what they’re going through, and give them space to share.”
For those who could be helped by psychotherapy, she said, “sometimes I introduce it as therapy that can be really brief. Maybe you just need to talk to someone for a few sessions or just get some support around coping with this.”
One strategy is to focus on bringing enjoyment back to eating, she said. For some patients, “eating becomes a chore,” a task performed without joy, alone in a hospital room.
Fasciana emphasized asking questions over time, perhaps through multiple follow-ups, without expecting answers immediately. And she coaxes patients to consider what they hold dear. “I try to get them to think about the meaning that losing or gaining weight has for them, what their values are, and what really matters to them. I link it back to health, healing, and longevity of life.”
Fasciana and Ohde reported they had no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Veterans are especially vulnerable to disordered eating because of their military backgrounds, a dietician warned US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) oncology clinicians at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. In fact, an estimated 15% to 25% of veterans meet diagnostic criteria for eating disorders.
“Their experience in the military probably has really shaped the way that they see weight and the stigma behind it,” said Emily Fasciana, MS, RDN, LDN, a registered dietician with the VA based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
When cancer appears, the risk of eating disorders goes up even more, she said. “If we don’t catch eating disorders early on, severe medical problems can occur. In the cancer population, they’re going through enough medical problems as it is.”
Here are things to know about eating disorders in oncology.
Military Life Can Produce a ‘Perfect Storm’ of Risk Factors
Tightly controlled eating environments and food deprivation are often routine in military life. Along with trauma, these can create a “perfect storm of risk factors for eating disorders,” Fasciana said.
During service, for example, “people often will eat as much as they can when they can, sometimes followed by days of not being able to eat,” she said. These are very much like disordered eating behaviors such as binge eating and restricting, and they can place veterans at greater risk.”
She described how service members can develop specific eating patterns during service, such as “midrats” – midnight rations – “meals served during midnight shifts that were the best meal served all day long that they had access to.”
“When I hear veterans who wake up in the middle of the night, and they’re eating, I ask: ‘Did they practice something similar during their military experience?’ They associate that time of the day with enjoyable comfort foods, and that’s what they go to now.”
Vets Can be Haunted by Stigma of Excess Weight
“Making weight” – meeting weight standards – is routine in the military. The pressure to remain under a certain level can have lasting effects on how veterans think about extra pounds, said Kaitlin Ohde, PhD, a clinical health psychologist with the VA Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle.
“I’ve heard some veterans tell me about getting kicked out of positions because of not being able to make weight. Then they carry this throughout their life, which is really sad,” Ohde said. “When they gain weight during treatment, sometimes it can be really bothersome for them.”
Regular weigh-ins can trouble patients, she said, so it’s important to explain to them why they’re getting on scales: “I’m getting your weight today because I want to see if this medication is doing XYZ.”
She advised colleagues to “make sure they explicitly know why we’re doing it [measuring weight], and how the things we’re using to treat them can impact their weight. This piece of the puzzle sometimes falls off the radar.”
Eating Disorders Can be Catastrophic in Cancer
Untreated eating disorders cause severe medical complications such as malnutrition, hormone dysregulation, low bone density or fractures, bradycardia, gastroparesis, and even anemia, Fasciana said.
There’s a New Category of Eating Disorder
Fasciana highlighted a condition that is underrecognized in oncology: Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), which refers to patients who stay away from certain foods but not because they’re worried about body image or weight gain. “Patients with ARFID are clinically distinct from those who have anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder,” she noted.
ARFID diagnosis requires food avoidance that leads to at least 1 of these consequences: significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on supplements or tube feeding, or psychosocial impairment.
“Veterans might have a gagging or retching reflex at the sight or smell of certain foods,” Fasciana explained. “They might have difficulty being in the presence of another person eating a nonpreferred food.”
Some cancer patients may be averse to foods of certain temperatures. “You might need to assess why they don’t like the temperature of that food. Why are those foods something that you can’t go to? Are they hurting your teeth? What are they doing to you?”
ARFID patients may also experience social withdrawal around eating. “With a lot of our head and neck cancer patients, especially those with oral cancers and those on feeding tubes, they might feel embarrassed to be around people while eating,” Fasciana said.
She highlighted a 2021 report about 4 cancer survivors with upper abdominal cancers who developed new-onset eating disorders with malnutrition resembling ARFID.
The patients experienced malabsorption, dumping syndrome, and excessive weight loss for 12 months postoperatively without classic body-image concerns. “This is a case example of how eating disorders can evolve in the oncology population,” Fasciana said.
The report said that none of the patients “returned to a healthy weight and/or healthy eating despite extensive team input… The outcomes were poor; 1 patient died, another required admission to a specialist eating disorder admission with a subsequent relapsing-remitting course, and the remaining 2 had complicated chronic courses.”
Treatment: Start With Screening, Then Reframe Thinking
Fasciana highlighted several screening tools, such as SCOFF, BREDS, and one for ARFID.
“Any screen is going to be better than no screen at all, and any question is going to be better than no question at all,” Fasciana said.
She cautioned that “veterans are not going to be so forthcoming about some of their struggles due to stigma and shame because of their past experiences in the military.”
As for therapy, psychological care may not be required, Ohde said. And it’s especially important to “listen to your patients about what they’re going through, and give them space to share.”
For those who could be helped by psychotherapy, she said, “sometimes I introduce it as therapy that can be really brief. Maybe you just need to talk to someone for a few sessions or just get some support around coping with this.”
One strategy is to focus on bringing enjoyment back to eating, she said. For some patients, “eating becomes a chore,” a task performed without joy, alone in a hospital room.
Fasciana emphasized asking questions over time, perhaps through multiple follow-ups, without expecting answers immediately. And she coaxes patients to consider what they hold dear. “I try to get them to think about the meaning that losing or gaining weight has for them, what their values are, and what really matters to them. I link it back to health, healing, and longevity of life.”
Fasciana and Ohde reported they had no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Veterans are especially vulnerable to disordered eating because of their military backgrounds, a dietician warned US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) oncology clinicians at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. In fact, an estimated 15% to 25% of veterans meet diagnostic criteria for eating disorders.
“Their experience in the military probably has really shaped the way that they see weight and the stigma behind it,” said Emily Fasciana, MS, RDN, LDN, a registered dietician with the VA based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
When cancer appears, the risk of eating disorders goes up even more, she said. “If we don’t catch eating disorders early on, severe medical problems can occur. In the cancer population, they’re going through enough medical problems as it is.”
Here are things to know about eating disorders in oncology.
Military Life Can Produce a ‘Perfect Storm’ of Risk Factors
Tightly controlled eating environments and food deprivation are often routine in military life. Along with trauma, these can create a “perfect storm of risk factors for eating disorders,” Fasciana said.
During service, for example, “people often will eat as much as they can when they can, sometimes followed by days of not being able to eat,” she said. These are very much like disordered eating behaviors such as binge eating and restricting, and they can place veterans at greater risk.”
She described how service members can develop specific eating patterns during service, such as “midrats” – midnight rations – “meals served during midnight shifts that were the best meal served all day long that they had access to.”
“When I hear veterans who wake up in the middle of the night, and they’re eating, I ask: ‘Did they practice something similar during their military experience?’ They associate that time of the day with enjoyable comfort foods, and that’s what they go to now.”
Vets Can be Haunted by Stigma of Excess Weight
“Making weight” – meeting weight standards – is routine in the military. The pressure to remain under a certain level can have lasting effects on how veterans think about extra pounds, said Kaitlin Ohde, PhD, a clinical health psychologist with the VA Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle.
“I’ve heard some veterans tell me about getting kicked out of positions because of not being able to make weight. Then they carry this throughout their life, which is really sad,” Ohde said. “When they gain weight during treatment, sometimes it can be really bothersome for them.”
Regular weigh-ins can trouble patients, she said, so it’s important to explain to them why they’re getting on scales: “I’m getting your weight today because I want to see if this medication is doing XYZ.”
She advised colleagues to “make sure they explicitly know why we’re doing it [measuring weight], and how the things we’re using to treat them can impact their weight. This piece of the puzzle sometimes falls off the radar.”
Eating Disorders Can be Catastrophic in Cancer
Untreated eating disorders cause severe medical complications such as malnutrition, hormone dysregulation, low bone density or fractures, bradycardia, gastroparesis, and even anemia, Fasciana said.
There’s a New Category of Eating Disorder
Fasciana highlighted a condition that is underrecognized in oncology: Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), which refers to patients who stay away from certain foods but not because they’re worried about body image or weight gain. “Patients with ARFID are clinically distinct from those who have anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder,” she noted.
ARFID diagnosis requires food avoidance that leads to at least 1 of these consequences: significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on supplements or tube feeding, or psychosocial impairment.
“Veterans might have a gagging or retching reflex at the sight or smell of certain foods,” Fasciana explained. “They might have difficulty being in the presence of another person eating a nonpreferred food.”
Some cancer patients may be averse to foods of certain temperatures. “You might need to assess why they don’t like the temperature of that food. Why are those foods something that you can’t go to? Are they hurting your teeth? What are they doing to you?”
ARFID patients may also experience social withdrawal around eating. “With a lot of our head and neck cancer patients, especially those with oral cancers and those on feeding tubes, they might feel embarrassed to be around people while eating,” Fasciana said.
She highlighted a 2021 report about 4 cancer survivors with upper abdominal cancers who developed new-onset eating disorders with malnutrition resembling ARFID.
The patients experienced malabsorption, dumping syndrome, and excessive weight loss for 12 months postoperatively without classic body-image concerns. “This is a case example of how eating disorders can evolve in the oncology population,” Fasciana said.
The report said that none of the patients “returned to a healthy weight and/or healthy eating despite extensive team input… The outcomes were poor; 1 patient died, another required admission to a specialist eating disorder admission with a subsequent relapsing-remitting course, and the remaining 2 had complicated chronic courses.”
Treatment: Start With Screening, Then Reframe Thinking
Fasciana highlighted several screening tools, such as SCOFF, BREDS, and one for ARFID.
“Any screen is going to be better than no screen at all, and any question is going to be better than no question at all,” Fasciana said.
She cautioned that “veterans are not going to be so forthcoming about some of their struggles due to stigma and shame because of their past experiences in the military.”
As for therapy, psychological care may not be required, Ohde said. And it’s especially important to “listen to your patients about what they’re going through, and give them space to share.”
For those who could be helped by psychotherapy, she said, “sometimes I introduce it as therapy that can be really brief. Maybe you just need to talk to someone for a few sessions or just get some support around coping with this.”
One strategy is to focus on bringing enjoyment back to eating, she said. For some patients, “eating becomes a chore,” a task performed without joy, alone in a hospital room.
Fasciana emphasized asking questions over time, perhaps through multiple follow-ups, without expecting answers immediately. And she coaxes patients to consider what they hold dear. “I try to get them to think about the meaning that losing or gaining weight has for them, what their values are, and what really matters to them. I link it back to health, healing, and longevity of life.”
Fasciana and Ohde reported they had no disclosures.
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
PHOENIX – Medications used in oncology clinical trials pose unique challenges in areas such as labeling, packaging, and administration, a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacist cautioned colleagues, and placebos have special needs too.
Even basic safety protections can be lacking when a drug is investigational, said Emily Hennes, PharmD, BCOP, clinical pharmacy specialist for research at William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
“All of the safety features that we have come to know and love in dispensing commercial drugs are absent. There’s no Tall Man lettering, there's no color differentiation, and there's no barcoding, because these are not registered drugs," she said.
A 2017 report found that 81% of pharmacists surveyed indicated some level of concern regarding the safety risk in using investigational drugs. At the same time, Hennes noted, the Joint Commission has mandated that pharmacists must control the storage, dispensing, labeling, and distribution of investigational medications.
Here are things to know about the use of investigational cancer drugs:
Drug Interactions Are Common
Hennes highlighted a 2023 study of medication reconciliation of 501 patients in 79 clinical trials that found alarming levels of drug interactions:
• 360 clinically relevant drug-drug interactions were identified among 189 patients, including 158 therapies that were prohibited by protocols. Of these, 57.7% involved cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolism.
• Reconciliation revealed that 35.2% of medications were not otherwise known or documented.
• A median of 2 previously unknown therapies per patient was discovered in 74% of patients.
• Alternative medicine products such as supplements and over-the-counter drugs were implicated in 60% of identified drug interactions.
• Only 41% of oncologists discussed alternative medicine use with patients, which Hennes attributed to “lack of familiarity with many alternative medicine products or insufficient training.”
To make things more complicated, “We sometimes don’t know the full pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of an investigational agent,” she said.
Naming and Labeling May Not Be Standard
Investigational products may not have genetic names and instead have an alphanumeric identifier such as INV54826 that can be quite similar to other products, she said. Investigational drugs may even go through name changes, forcing pharmacists to be alerted to protect patients.
In addition, labeling may not be standardized. Drugs may arrive unlabeled, with the wrong volume and size, and lack of barcoding. In some cases, pharmacists choose to put new, patient-friendly labels on these products, Hennes said.
Information Distribution is Key
“Something that comes up in our practice quite a bit is that there’s no standard drug reference regarding investigational drugs,” Hennes said. “Finding ways to get key information to staff at the point of care is really critical to make sure we’re able to safely treat our patients.”
Precautions May Be Needed to Maintain Blinding Protocols
Hennes explained that pharmacists must use opaque brown bag covers to maintain blinding when parenteral products have distinctive colors. Lines may have to be covered too, which can create challenges during administration.
“Pumps aren’t meant to run lines that are covered,” she said, which can lead to jams. “If you don’t do education with your point of care staff, it can cause a lot of confusion.”
It’s also important for blinding purposes to keep an eye on how long it takes to prepare a treatment, she said. A study’s integrity, for example, could be violated if a complex investigational product takes an hour to equilibrate to room temperature and 20-30 minutes to prepare, while a placebo only requires “drawing a few mils of saline out of a bag and labeling it.”
Education for Patients Can Be Useful
Hennes urged colleagues to remind patients to save investigational medication at the end of each cycle and return it to the clinic site for accountability.
She also suggested creating treatment calendars/reminders for patients and discussing
Hennes reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Medications used in oncology clinical trials pose unique challenges in areas such as labeling, packaging, and administration, a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacist cautioned colleagues, and placebos have special needs too.
Even basic safety protections can be lacking when a drug is investigational, said Emily Hennes, PharmD, BCOP, clinical pharmacy specialist for research at William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
“All of the safety features that we have come to know and love in dispensing commercial drugs are absent. There’s no Tall Man lettering, there's no color differentiation, and there's no barcoding, because these are not registered drugs," she said.
A 2017 report found that 81% of pharmacists surveyed indicated some level of concern regarding the safety risk in using investigational drugs. At the same time, Hennes noted, the Joint Commission has mandated that pharmacists must control the storage, dispensing, labeling, and distribution of investigational medications.
Here are things to know about the use of investigational cancer drugs:
Drug Interactions Are Common
Hennes highlighted a 2023 study of medication reconciliation of 501 patients in 79 clinical trials that found alarming levels of drug interactions:
• 360 clinically relevant drug-drug interactions were identified among 189 patients, including 158 therapies that were prohibited by protocols. Of these, 57.7% involved cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolism.
• Reconciliation revealed that 35.2% of medications were not otherwise known or documented.
• A median of 2 previously unknown therapies per patient was discovered in 74% of patients.
• Alternative medicine products such as supplements and over-the-counter drugs were implicated in 60% of identified drug interactions.
• Only 41% of oncologists discussed alternative medicine use with patients, which Hennes attributed to “lack of familiarity with many alternative medicine products or insufficient training.”
To make things more complicated, “We sometimes don’t know the full pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of an investigational agent,” she said.
Naming and Labeling May Not Be Standard
Investigational products may not have genetic names and instead have an alphanumeric identifier such as INV54826 that can be quite similar to other products, she said. Investigational drugs may even go through name changes, forcing pharmacists to be alerted to protect patients.
In addition, labeling may not be standardized. Drugs may arrive unlabeled, with the wrong volume and size, and lack of barcoding. In some cases, pharmacists choose to put new, patient-friendly labels on these products, Hennes said.
Information Distribution is Key
“Something that comes up in our practice quite a bit is that there’s no standard drug reference regarding investigational drugs,” Hennes said. “Finding ways to get key information to staff at the point of care is really critical to make sure we’re able to safely treat our patients.”
Precautions May Be Needed to Maintain Blinding Protocols
Hennes explained that pharmacists must use opaque brown bag covers to maintain blinding when parenteral products have distinctive colors. Lines may have to be covered too, which can create challenges during administration.
“Pumps aren’t meant to run lines that are covered,” she said, which can lead to jams. “If you don’t do education with your point of care staff, it can cause a lot of confusion.”
It’s also important for blinding purposes to keep an eye on how long it takes to prepare a treatment, she said. A study’s integrity, for example, could be violated if a complex investigational product takes an hour to equilibrate to room temperature and 20-30 minutes to prepare, while a placebo only requires “drawing a few mils of saline out of a bag and labeling it.”
Education for Patients Can Be Useful
Hennes urged colleagues to remind patients to save investigational medication at the end of each cycle and return it to the clinic site for accountability.
She also suggested creating treatment calendars/reminders for patients and discussing
Hennes reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Medications used in oncology clinical trials pose unique challenges in areas such as labeling, packaging, and administration, a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacist cautioned colleagues, and placebos have special needs too.
Even basic safety protections can be lacking when a drug is investigational, said Emily Hennes, PharmD, BCOP, clinical pharmacy specialist for research at William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
“All of the safety features that we have come to know and love in dispensing commercial drugs are absent. There’s no Tall Man lettering, there's no color differentiation, and there's no barcoding, because these are not registered drugs," she said.
A 2017 report found that 81% of pharmacists surveyed indicated some level of concern regarding the safety risk in using investigational drugs. At the same time, Hennes noted, the Joint Commission has mandated that pharmacists must control the storage, dispensing, labeling, and distribution of investigational medications.
Here are things to know about the use of investigational cancer drugs:
Drug Interactions Are Common
Hennes highlighted a 2023 study of medication reconciliation of 501 patients in 79 clinical trials that found alarming levels of drug interactions:
• 360 clinically relevant drug-drug interactions were identified among 189 patients, including 158 therapies that were prohibited by protocols. Of these, 57.7% involved cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolism.
• Reconciliation revealed that 35.2% of medications were not otherwise known or documented.
• A median of 2 previously unknown therapies per patient was discovered in 74% of patients.
• Alternative medicine products such as supplements and over-the-counter drugs were implicated in 60% of identified drug interactions.
• Only 41% of oncologists discussed alternative medicine use with patients, which Hennes attributed to “lack of familiarity with many alternative medicine products or insufficient training.”
To make things more complicated, “We sometimes don’t know the full pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of an investigational agent,” she said.
Naming and Labeling May Not Be Standard
Investigational products may not have genetic names and instead have an alphanumeric identifier such as INV54826 that can be quite similar to other products, she said. Investigational drugs may even go through name changes, forcing pharmacists to be alerted to protect patients.
In addition, labeling may not be standardized. Drugs may arrive unlabeled, with the wrong volume and size, and lack of barcoding. In some cases, pharmacists choose to put new, patient-friendly labels on these products, Hennes said.
Information Distribution is Key
“Something that comes up in our practice quite a bit is that there’s no standard drug reference regarding investigational drugs,” Hennes said. “Finding ways to get key information to staff at the point of care is really critical to make sure we’re able to safely treat our patients.”
Precautions May Be Needed to Maintain Blinding Protocols
Hennes explained that pharmacists must use opaque brown bag covers to maintain blinding when parenteral products have distinctive colors. Lines may have to be covered too, which can create challenges during administration.
“Pumps aren’t meant to run lines that are covered,” she said, which can lead to jams. “If you don’t do education with your point of care staff, it can cause a lot of confusion.”
It’s also important for blinding purposes to keep an eye on how long it takes to prepare a treatment, she said. A study’s integrity, for example, could be violated if a complex investigational product takes an hour to equilibrate to room temperature and 20-30 minutes to prepare, while a placebo only requires “drawing a few mils of saline out of a bag and labeling it.”
Education for Patients Can Be Useful
Hennes urged colleagues to remind patients to save investigational medication at the end of each cycle and return it to the clinic site for accountability.
She also suggested creating treatment calendars/reminders for patients and discussing
Hennes reported no disclosures.
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty