User login
Contraceptive Care Clinic Focuses on Military Readiness
SAN DIEGO — Not surprisingly, the contraception clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center near Tacoma, Wash., is popular among female soldiers seeking to avoid pregnancy. However, about half of the patients drop by for other reasons, the military pharmacist who runs the program told colleagues here at the Joint Federal Pharmacy Seminar.
“They come to suppress menstruation, to get help with pain, to get help with PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] symptoms. They're coming for a wide range of indications that we use contraception to treat,” said Sarah Abel, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist.
Regardless of the reason, Abel emphasized that contraceptives can significantly impact the ability of female soldiers to do their jobs. “If you have heavy periods and can't make it in work, or you have endometriosis and requiring a lot of doctor's appointments, or you're deployed and you get pregnant, these are all situations where contraceptive care matters,” she said. Rates of unintended pregnancy are higher in servicewomen than in the general population.
Abel, who opened the medical center’s contraceptive clinic about 10 years ago, stressed that it’s crucial to military readiness considering that the percentage of women in the American military is approaching 20%.
Thanks to a 2022 edict, military hospitals and clinics are required to offer walk-in contraceptive services with same-day access, no requirements for appointments or referrals. An announcement about the mandate noted that these contraceptive services, such as preventing unplanned pregnancy and decreasing menstrual periods, “support the overall well-being of the force and optimize personal warrior readiness.”
As Abel noted, 29 states and Washington D.C. allow pharmacists to prescribe contraception to outpatients, although the requirements vary. “Can we start practicing at the top of our license and start prescribing in the outpatient setting? Absolutely we should,” she said. “Pharmacists have a very unique opportunity to be a part of this.”
Abel also shared that setting up a contraceptive program requires patience and education. “I cannot tell you how many women have come to me who don't know the different names of their body parts, women who've had two babies that don't understand how their body works. So, I constantly find myself taking extra time to do general sexual education,” she said.
There are many lessons to impart to patients about sexual health. For example, birth control drugs and devices do not prevent transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). “So I have bowls of condoms literally everywhere because condoms are the only thing that protects against STIs,” Abel said.
In terms of devices, “we have diaphragms available and cervical caps,” she said. “The Caya diaphragm is a TRICARE-covered benefit. It’s a small purple diaphragm, one size fits most. We can prescribe it, and it is good for 2 years. Unfortunately, spermicide, which you have to use with these things, is not a TRICARE-covered benefit.”
Hormonal contraceptives are also available, with Abel recommending the continuous monophasic type for most women. “Please don't tell women they have to have their periods. They don't,” she said. “What I'm trying to do is give a woman some stability in her hormones. She can know and expect what she's going to feel like. She's not going to wake up and say, ‘Oh God, today's the day. I'm going to be like this for a week.’”
Patches are another option, and a flurry of patients have been asking about them because of recent TikTok videos promoting their use. “We have the Xulane patch, our bread and butter. They wear it on their shoulder, their hip, their butt, or their back. They leave it in place for a week at a time. And every week, they will change that patch. I usually have to walk patients through a whole month to help them understand how that works.”
Another option, the NuvaRing, is notable because it’s linked to low amounts of breakthrough bleeding Abel noted. An extended form is now available that doesn’t need to be removed during menstrual periods.
Medroxyprogesterone injections, which are linked to bone loss, and subdermal implants, which may be less effective in women over 130% of their ideal weight are also available, she said.
Finally, IUDs are an option, although when they fail, they’re linked to ectopic pregnancies.
Abel has no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — Not surprisingly, the contraception clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center near Tacoma, Wash., is popular among female soldiers seeking to avoid pregnancy. However, about half of the patients drop by for other reasons, the military pharmacist who runs the program told colleagues here at the Joint Federal Pharmacy Seminar.
“They come to suppress menstruation, to get help with pain, to get help with PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] symptoms. They're coming for a wide range of indications that we use contraception to treat,” said Sarah Abel, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist.
Regardless of the reason, Abel emphasized that contraceptives can significantly impact the ability of female soldiers to do their jobs. “If you have heavy periods and can't make it in work, or you have endometriosis and requiring a lot of doctor's appointments, or you're deployed and you get pregnant, these are all situations where contraceptive care matters,” she said. Rates of unintended pregnancy are higher in servicewomen than in the general population.
Abel, who opened the medical center’s contraceptive clinic about 10 years ago, stressed that it’s crucial to military readiness considering that the percentage of women in the American military is approaching 20%.
Thanks to a 2022 edict, military hospitals and clinics are required to offer walk-in contraceptive services with same-day access, no requirements for appointments or referrals. An announcement about the mandate noted that these contraceptive services, such as preventing unplanned pregnancy and decreasing menstrual periods, “support the overall well-being of the force and optimize personal warrior readiness.”
As Abel noted, 29 states and Washington D.C. allow pharmacists to prescribe contraception to outpatients, although the requirements vary. “Can we start practicing at the top of our license and start prescribing in the outpatient setting? Absolutely we should,” she said. “Pharmacists have a very unique opportunity to be a part of this.”
Abel also shared that setting up a contraceptive program requires patience and education. “I cannot tell you how many women have come to me who don't know the different names of their body parts, women who've had two babies that don't understand how their body works. So, I constantly find myself taking extra time to do general sexual education,” she said.
There are many lessons to impart to patients about sexual health. For example, birth control drugs and devices do not prevent transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). “So I have bowls of condoms literally everywhere because condoms are the only thing that protects against STIs,” Abel said.
In terms of devices, “we have diaphragms available and cervical caps,” she said. “The Caya diaphragm is a TRICARE-covered benefit. It’s a small purple diaphragm, one size fits most. We can prescribe it, and it is good for 2 years. Unfortunately, spermicide, which you have to use with these things, is not a TRICARE-covered benefit.”
Hormonal contraceptives are also available, with Abel recommending the continuous monophasic type for most women. “Please don't tell women they have to have their periods. They don't,” she said. “What I'm trying to do is give a woman some stability in her hormones. She can know and expect what she's going to feel like. She's not going to wake up and say, ‘Oh God, today's the day. I'm going to be like this for a week.’”
Patches are another option, and a flurry of patients have been asking about them because of recent TikTok videos promoting their use. “We have the Xulane patch, our bread and butter. They wear it on their shoulder, their hip, their butt, or their back. They leave it in place for a week at a time. And every week, they will change that patch. I usually have to walk patients through a whole month to help them understand how that works.”
Another option, the NuvaRing, is notable because it’s linked to low amounts of breakthrough bleeding Abel noted. An extended form is now available that doesn’t need to be removed during menstrual periods.
Medroxyprogesterone injections, which are linked to bone loss, and subdermal implants, which may be less effective in women over 130% of their ideal weight are also available, she said.
Finally, IUDs are an option, although when they fail, they’re linked to ectopic pregnancies.
Abel has no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — Not surprisingly, the contraception clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center near Tacoma, Wash., is popular among female soldiers seeking to avoid pregnancy. However, about half of the patients drop by for other reasons, the military pharmacist who runs the program told colleagues here at the Joint Federal Pharmacy Seminar.
“They come to suppress menstruation, to get help with pain, to get help with PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] symptoms. They're coming for a wide range of indications that we use contraception to treat,” said Sarah Abel, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist.
Regardless of the reason, Abel emphasized that contraceptives can significantly impact the ability of female soldiers to do their jobs. “If you have heavy periods and can't make it in work, or you have endometriosis and requiring a lot of doctor's appointments, or you're deployed and you get pregnant, these are all situations where contraceptive care matters,” she said. Rates of unintended pregnancy are higher in servicewomen than in the general population.
Abel, who opened the medical center’s contraceptive clinic about 10 years ago, stressed that it’s crucial to military readiness considering that the percentage of women in the American military is approaching 20%.
Thanks to a 2022 edict, military hospitals and clinics are required to offer walk-in contraceptive services with same-day access, no requirements for appointments or referrals. An announcement about the mandate noted that these contraceptive services, such as preventing unplanned pregnancy and decreasing menstrual periods, “support the overall well-being of the force and optimize personal warrior readiness.”
As Abel noted, 29 states and Washington D.C. allow pharmacists to prescribe contraception to outpatients, although the requirements vary. “Can we start practicing at the top of our license and start prescribing in the outpatient setting? Absolutely we should,” she said. “Pharmacists have a very unique opportunity to be a part of this.”
Abel also shared that setting up a contraceptive program requires patience and education. “I cannot tell you how many women have come to me who don't know the different names of their body parts, women who've had two babies that don't understand how their body works. So, I constantly find myself taking extra time to do general sexual education,” she said.
There are many lessons to impart to patients about sexual health. For example, birth control drugs and devices do not prevent transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). “So I have bowls of condoms literally everywhere because condoms are the only thing that protects against STIs,” Abel said.
In terms of devices, “we have diaphragms available and cervical caps,” she said. “The Caya diaphragm is a TRICARE-covered benefit. It’s a small purple diaphragm, one size fits most. We can prescribe it, and it is good for 2 years. Unfortunately, spermicide, which you have to use with these things, is not a TRICARE-covered benefit.”
Hormonal contraceptives are also available, with Abel recommending the continuous monophasic type for most women. “Please don't tell women they have to have their periods. They don't,” she said. “What I'm trying to do is give a woman some stability in her hormones. She can know and expect what she's going to feel like. She's not going to wake up and say, ‘Oh God, today's the day. I'm going to be like this for a week.’”
Patches are another option, and a flurry of patients have been asking about them because of recent TikTok videos promoting their use. “We have the Xulane patch, our bread and butter. They wear it on their shoulder, their hip, their butt, or their back. They leave it in place for a week at a time. And every week, they will change that patch. I usually have to walk patients through a whole month to help them understand how that works.”
Another option, the NuvaRing, is notable because it’s linked to low amounts of breakthrough bleeding Abel noted. An extended form is now available that doesn’t need to be removed during menstrual periods.
Medroxyprogesterone injections, which are linked to bone loss, and subdermal implants, which may be less effective in women over 130% of their ideal weight are also available, she said.
Finally, IUDs are an option, although when they fail, they’re linked to ectopic pregnancies.
Abel has no disclosures.
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
VA Choice Bill Defeated in the House
A U.S. House of Representatives appropriation to fund the Veterans Choice Program surprisingly went down to defeat on Monday. The VA Choice Program is set to run out of money in September, and VA officials have been calling for Congress to provide additional funding for the program. Republican leaders, hoping to expedite the bill’s passage and thinking that it was not controversial, submitted the bill in a process that required the votes of two-thirds of the representatives. The 219-186 vote fell well short of the necessary two-thirds, and voting fell largely along party lines.
Many veterans service organizations (VSOs) were critical of the bill and called on the House to make substantial changes to it. Seven VSOs signed a joint statement calling for the bill’s defeat. “As organizations who represent and support the interests of America’s 21 million veterans, and in fulfillment of our mandate to ensure that the men and women who served are able to receive the health care and benefits they need and deserve, we are calling on Members of Congress to defeat the House vote on unacceptable choice funding legislation (S. 114, with amendments),” the statement read.
AMVETS, Disabled American Veterans , Military Officers Association of America, Military Order of the Purple Heart, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Vietnam Veterans of America, and Wounded Warrior Project all signed on to the statement. The chief complaint was that the legislation “includes funding only for the ‘choice’ program which provides additional community care options, but makes no investment in VA and uses ‘savings’ from other veterans benefits or services to ‘pay’ for the ‘choice’ program.”
The bill would have allocated $2 billion for the Veterans Choice Program, taken funding for veteran housing loan fees, and would reduce the pensions for some veterans living in nursing facilities that also could be paid for under the Medicaid program.
The fate of the bill and funding for the Veterans Choice Program remains unclear. Senate and House veterans committees seem to be far apart on how to fund the program and for efforts to make more substantive changes to the program. Although House Republicans eventually may be able to pass a bill without Democrats, in the Senate, they will need the support of at least a handful of Democrats to move the bill to the President’s desk.
A U.S. House of Representatives appropriation to fund the Veterans Choice Program surprisingly went down to defeat on Monday. The VA Choice Program is set to run out of money in September, and VA officials have been calling for Congress to provide additional funding for the program. Republican leaders, hoping to expedite the bill’s passage and thinking that it was not controversial, submitted the bill in a process that required the votes of two-thirds of the representatives. The 219-186 vote fell well short of the necessary two-thirds, and voting fell largely along party lines.
Many veterans service organizations (VSOs) were critical of the bill and called on the House to make substantial changes to it. Seven VSOs signed a joint statement calling for the bill’s defeat. “As organizations who represent and support the interests of America’s 21 million veterans, and in fulfillment of our mandate to ensure that the men and women who served are able to receive the health care and benefits they need and deserve, we are calling on Members of Congress to defeat the House vote on unacceptable choice funding legislation (S. 114, with amendments),” the statement read.
AMVETS, Disabled American Veterans , Military Officers Association of America, Military Order of the Purple Heart, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Vietnam Veterans of America, and Wounded Warrior Project all signed on to the statement. The chief complaint was that the legislation “includes funding only for the ‘choice’ program which provides additional community care options, but makes no investment in VA and uses ‘savings’ from other veterans benefits or services to ‘pay’ for the ‘choice’ program.”
The bill would have allocated $2 billion for the Veterans Choice Program, taken funding for veteran housing loan fees, and would reduce the pensions for some veterans living in nursing facilities that also could be paid for under the Medicaid program.
The fate of the bill and funding for the Veterans Choice Program remains unclear. Senate and House veterans committees seem to be far apart on how to fund the program and for efforts to make more substantive changes to the program. Although House Republicans eventually may be able to pass a bill without Democrats, in the Senate, they will need the support of at least a handful of Democrats to move the bill to the President’s desk.
A U.S. House of Representatives appropriation to fund the Veterans Choice Program surprisingly went down to defeat on Monday. The VA Choice Program is set to run out of money in September, and VA officials have been calling for Congress to provide additional funding for the program. Republican leaders, hoping to expedite the bill’s passage and thinking that it was not controversial, submitted the bill in a process that required the votes of two-thirds of the representatives. The 219-186 vote fell well short of the necessary two-thirds, and voting fell largely along party lines.
Many veterans service organizations (VSOs) were critical of the bill and called on the House to make substantial changes to it. Seven VSOs signed a joint statement calling for the bill’s defeat. “As organizations who represent and support the interests of America’s 21 million veterans, and in fulfillment of our mandate to ensure that the men and women who served are able to receive the health care and benefits they need and deserve, we are calling on Members of Congress to defeat the House vote on unacceptable choice funding legislation (S. 114, with amendments),” the statement read.
AMVETS, Disabled American Veterans , Military Officers Association of America, Military Order of the Purple Heart, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Vietnam Veterans of America, and Wounded Warrior Project all signed on to the statement. The chief complaint was that the legislation “includes funding only for the ‘choice’ program which provides additional community care options, but makes no investment in VA and uses ‘savings’ from other veterans benefits or services to ‘pay’ for the ‘choice’ program.”
The bill would have allocated $2 billion for the Veterans Choice Program, taken funding for veteran housing loan fees, and would reduce the pensions for some veterans living in nursing facilities that also could be paid for under the Medicaid program.
The fate of the bill and funding for the Veterans Choice Program remains unclear. Senate and House veterans committees seem to be far apart on how to fund the program and for efforts to make more substantive changes to the program. Although House Republicans eventually may be able to pass a bill without Democrats, in the Senate, they will need the support of at least a handful of Democrats to move the bill to the President’s desk.
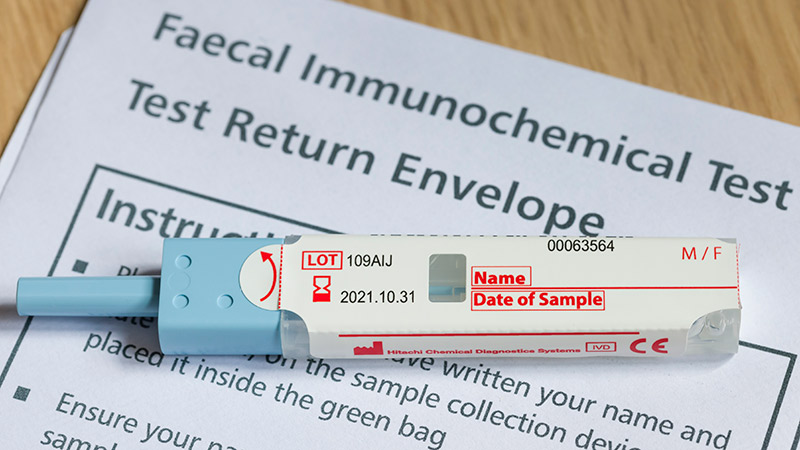
Patients With a Positive FIT Fail to Get Follow-Up Colonoscopies
Patients With a Positive FIT Fail to Get Follow-Up Colonoscopies
PHOENIX -- Patients with or without polyp removal in an index colonoscopy commonly receive follow-up surveillance with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT), yet many of these patients do not receive a recommended colonoscopy after a positive FIT.
"In this large US study, we found interval FITs are frequently performed in patients with and without prior polypectomy," said first author Natalie J. Wilson, MD, of the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis, while presenting the findings this week at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
"These findings reinforce the importance of colonoscopy following positive interval FIT, given the high risk of advanced neoplasia and colorectal cancer, regardless of polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Guideline recommendations stress the need for follow-up surveillance with a colonoscopy, particularly in patients who have had a prior polypectomy, due to the higher risk.
Reasons patients may instead turn to FIT include cost or other factors.
To determine just how often that happens, how having a previous polypectomy affects FIT results, and how adherent patients are to follow up if a FIT result is positive, Wilson and her colleagues evaluated data from nearly 4.8 million individuals in the Veterans Health Administration Corporate Data Warehouse who underwent colonoscopy between 2000 and 2004.
Of the patients, 10.9% were found to have subsequently received interval FIT within 10 years of the index colonoscopy, and of those patients, nearly half (49.9%) had received a polypectomy at the index colonoscopy.
The average time from the colonoscopy/polypectomy to the interval FIT was 5.9 years (5.6 years in the polypectomy group vs 6.2 years in the nonpolypectomy group).
Among the FIT screenings, results were positive in 17.2% of postpolypectomy patients and 14.1% of patients who no prior polypectomy, indicating a history of polypectomy to be predictive of positive interval FIT (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; P < .0001).
Notably, while a follow-up colonoscopy is considered essential following a positive FIT result -- and having a previous polypectomy should add further emergency to the matter -- the study showed only 50.4% of those who had an earlier polypectomy went on to receive the recommended follow-up colonoscopy after a positive follow-up FIT, and the rate was 49.3% among those who had not received a polypectomy (P = .001).
For those who did receive a follow-up colonoscopy after a positive FIT, the duration of time to receiving the colonoscopy was longer among those who had a prior polypectomy, at 2.9 months compared with 2.5 months in the nonpolypectomy group (P < .001).
Colonoscopy results following a positive FIT showed higher rates of detections among patients who had prior polypectomies than among those with no prior polypectomy, including tubular adenomas (54.7% vs 45.8%), tubulovillous adenomas (5.6% vs 4.7%), adenomas with high-grade dysplasia (0.8% vs 0.7%), sessile serrated lesions (3.52% vs 2.4%), advanced colorectal neoplasia (9.2% vs 7.9%), and colorectal cancer (3.3% vs 3.0%).
However, a prior polypectomy was not independently predictive of colorectal cancer (OR, 0.96; P = .65) or advanced colorectal neoplasia (OR, 0.97; P = .57) in the postcolonoscopy interval FIT.
The findings underscore that "positive results carried a high risk of advanced neoplasia or cancer, irrespective or prior polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Commenting on the study, William D. Chey, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan, noted that the study "addresses one of the biggest challenges we face as a profession, which is making sure that patients who have a positive stool test get a colonoscopy."
He noted that the low rate of just 50% of recipients of positive FITs going on to receive a colonoscopy is consistent with what is observed in other trials.
"Other data suggest that the rate might even be significantly higher -- at 70% to 80%, depending upon the population and the test," Chey told Medscape Medical News.
Reasons for the failure to receive the follow-up testing range from income restrictions (due to the high cost of a colonoscopy, especially if not covered by insurance), education, speaking a foreign language, and other factors, he said.
The relatively high rates of colon cancers detected by FIT in the study, in those with and without a prior polypectomy, along with findings from other studies "should raise questions about whether there might be a role for FIT testing in addition to colonoscopy." However, much stronger evidence would be needed, Chey noted.
In the meantime, a key issue is "how do we do a better job of making sure that individuals who have a positive FIT test get a colonoscopy," he said.
"I think a lot of this is going to come down to how it's down at the primary care level."
Chey added that in that, and any other setting, "the main message that needs to get out to people who are undergoing stool-based screening is that the stool test is only the first part of the screening process, and if it's positive, a follow-up colonoscopy must be performed.
"Otherwise, the stool-based test is of no value."
Wilson had no disclosures to report. Chey's disclosures include consulting and/or other relationships with Ardelyx, Atmo, Biomerica, Commonwealth Diagnostics International, Corprata, Dieta, Evinature, Food Marble, Gemelli, Kiwi BioScience, Modify Health, Nestle, Phathom, Redhill, Salix/Valean, Takeda, and Vibrant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX -- Patients with or without polyp removal in an index colonoscopy commonly receive follow-up surveillance with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT), yet many of these patients do not receive a recommended colonoscopy after a positive FIT.
"In this large US study, we found interval FITs are frequently performed in patients with and without prior polypectomy," said first author Natalie J. Wilson, MD, of the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis, while presenting the findings this week at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
"These findings reinforce the importance of colonoscopy following positive interval FIT, given the high risk of advanced neoplasia and colorectal cancer, regardless of polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Guideline recommendations stress the need for follow-up surveillance with a colonoscopy, particularly in patients who have had a prior polypectomy, due to the higher risk.
Reasons patients may instead turn to FIT include cost or other factors.
To determine just how often that happens, how having a previous polypectomy affects FIT results, and how adherent patients are to follow up if a FIT result is positive, Wilson and her colleagues evaluated data from nearly 4.8 million individuals in the Veterans Health Administration Corporate Data Warehouse who underwent colonoscopy between 2000 and 2004.
Of the patients, 10.9% were found to have subsequently received interval FIT within 10 years of the index colonoscopy, and of those patients, nearly half (49.9%) had received a polypectomy at the index colonoscopy.
The average time from the colonoscopy/polypectomy to the interval FIT was 5.9 years (5.6 years in the polypectomy group vs 6.2 years in the nonpolypectomy group).
Among the FIT screenings, results were positive in 17.2% of postpolypectomy patients and 14.1% of patients who no prior polypectomy, indicating a history of polypectomy to be predictive of positive interval FIT (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; P < .0001).
Notably, while a follow-up colonoscopy is considered essential following a positive FIT result -- and having a previous polypectomy should add further emergency to the matter -- the study showed only 50.4% of those who had an earlier polypectomy went on to receive the recommended follow-up colonoscopy after a positive follow-up FIT, and the rate was 49.3% among those who had not received a polypectomy (P = .001).
For those who did receive a follow-up colonoscopy after a positive FIT, the duration of time to receiving the colonoscopy was longer among those who had a prior polypectomy, at 2.9 months compared with 2.5 months in the nonpolypectomy group (P < .001).
Colonoscopy results following a positive FIT showed higher rates of detections among patients who had prior polypectomies than among those with no prior polypectomy, including tubular adenomas (54.7% vs 45.8%), tubulovillous adenomas (5.6% vs 4.7%), adenomas with high-grade dysplasia (0.8% vs 0.7%), sessile serrated lesions (3.52% vs 2.4%), advanced colorectal neoplasia (9.2% vs 7.9%), and colorectal cancer (3.3% vs 3.0%).
However, a prior polypectomy was not independently predictive of colorectal cancer (OR, 0.96; P = .65) or advanced colorectal neoplasia (OR, 0.97; P = .57) in the postcolonoscopy interval FIT.
The findings underscore that "positive results carried a high risk of advanced neoplasia or cancer, irrespective or prior polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Commenting on the study, William D. Chey, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan, noted that the study "addresses one of the biggest challenges we face as a profession, which is making sure that patients who have a positive stool test get a colonoscopy."
He noted that the low rate of just 50% of recipients of positive FITs going on to receive a colonoscopy is consistent with what is observed in other trials.
"Other data suggest that the rate might even be significantly higher -- at 70% to 80%, depending upon the population and the test," Chey told Medscape Medical News.
Reasons for the failure to receive the follow-up testing range from income restrictions (due to the high cost of a colonoscopy, especially if not covered by insurance), education, speaking a foreign language, and other factors, he said.
The relatively high rates of colon cancers detected by FIT in the study, in those with and without a prior polypectomy, along with findings from other studies "should raise questions about whether there might be a role for FIT testing in addition to colonoscopy." However, much stronger evidence would be needed, Chey noted.
In the meantime, a key issue is "how do we do a better job of making sure that individuals who have a positive FIT test get a colonoscopy," he said.
"I think a lot of this is going to come down to how it's down at the primary care level."
Chey added that in that, and any other setting, "the main message that needs to get out to people who are undergoing stool-based screening is that the stool test is only the first part of the screening process, and if it's positive, a follow-up colonoscopy must be performed.
"Otherwise, the stool-based test is of no value."
Wilson had no disclosures to report. Chey's disclosures include consulting and/or other relationships with Ardelyx, Atmo, Biomerica, Commonwealth Diagnostics International, Corprata, Dieta, Evinature, Food Marble, Gemelli, Kiwi BioScience, Modify Health, Nestle, Phathom, Redhill, Salix/Valean, Takeda, and Vibrant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHOENIX -- Patients with or without polyp removal in an index colonoscopy commonly receive follow-up surveillance with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT), yet many of these patients do not receive a recommended colonoscopy after a positive FIT.
"In this large US study, we found interval FITs are frequently performed in patients with and without prior polypectomy," said first author Natalie J. Wilson, MD, of the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis, while presenting the findings this week at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
"These findings reinforce the importance of colonoscopy following positive interval FIT, given the high risk of advanced neoplasia and colorectal cancer, regardless of polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Guideline recommendations stress the need for follow-up surveillance with a colonoscopy, particularly in patients who have had a prior polypectomy, due to the higher risk.
Reasons patients may instead turn to FIT include cost or other factors.
To determine just how often that happens, how having a previous polypectomy affects FIT results, and how adherent patients are to follow up if a FIT result is positive, Wilson and her colleagues evaluated data from nearly 4.8 million individuals in the Veterans Health Administration Corporate Data Warehouse who underwent colonoscopy between 2000 and 2004.
Of the patients, 10.9% were found to have subsequently received interval FIT within 10 years of the index colonoscopy, and of those patients, nearly half (49.9%) had received a polypectomy at the index colonoscopy.
The average time from the colonoscopy/polypectomy to the interval FIT was 5.9 years (5.6 years in the polypectomy group vs 6.2 years in the nonpolypectomy group).
Among the FIT screenings, results were positive in 17.2% of postpolypectomy patients and 14.1% of patients who no prior polypectomy, indicating a history of polypectomy to be predictive of positive interval FIT (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; P < .0001).
Notably, while a follow-up colonoscopy is considered essential following a positive FIT result -- and having a previous polypectomy should add further emergency to the matter -- the study showed only 50.4% of those who had an earlier polypectomy went on to receive the recommended follow-up colonoscopy after a positive follow-up FIT, and the rate was 49.3% among those who had not received a polypectomy (P = .001).
For those who did receive a follow-up colonoscopy after a positive FIT, the duration of time to receiving the colonoscopy was longer among those who had a prior polypectomy, at 2.9 months compared with 2.5 months in the nonpolypectomy group (P < .001).
Colonoscopy results following a positive FIT showed higher rates of detections among patients who had prior polypectomies than among those with no prior polypectomy, including tubular adenomas (54.7% vs 45.8%), tubulovillous adenomas (5.6% vs 4.7%), adenomas with high-grade dysplasia (0.8% vs 0.7%), sessile serrated lesions (3.52% vs 2.4%), advanced colorectal neoplasia (9.2% vs 7.9%), and colorectal cancer (3.3% vs 3.0%).
However, a prior polypectomy was not independently predictive of colorectal cancer (OR, 0.96; P = .65) or advanced colorectal neoplasia (OR, 0.97; P = .57) in the postcolonoscopy interval FIT.
The findings underscore that "positive results carried a high risk of advanced neoplasia or cancer, irrespective or prior polypectomy history," Wilson said.
Commenting on the study, William D. Chey, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan, noted that the study "addresses one of the biggest challenges we face as a profession, which is making sure that patients who have a positive stool test get a colonoscopy."
He noted that the low rate of just 50% of recipients of positive FITs going on to receive a colonoscopy is consistent with what is observed in other trials.
"Other data suggest that the rate might even be significantly higher -- at 70% to 80%, depending upon the population and the test," Chey told Medscape Medical News.
Reasons for the failure to receive the follow-up testing range from income restrictions (due to the high cost of a colonoscopy, especially if not covered by insurance), education, speaking a foreign language, and other factors, he said.
The relatively high rates of colon cancers detected by FIT in the study, in those with and without a prior polypectomy, along with findings from other studies "should raise questions about whether there might be a role for FIT testing in addition to colonoscopy." However, much stronger evidence would be needed, Chey noted.
In the meantime, a key issue is "how do we do a better job of making sure that individuals who have a positive FIT test get a colonoscopy," he said.
"I think a lot of this is going to come down to how it's down at the primary care level."
Chey added that in that, and any other setting, "the main message that needs to get out to people who are undergoing stool-based screening is that the stool test is only the first part of the screening process, and if it's positive, a follow-up colonoscopy must be performed.
"Otherwise, the stool-based test is of no value."
Wilson had no disclosures to report. Chey's disclosures include consulting and/or other relationships with Ardelyx, Atmo, Biomerica, Commonwealth Diagnostics International, Corprata, Dieta, Evinature, Food Marble, Gemelli, Kiwi BioScience, Modify Health, Nestle, Phathom, Redhill, Salix/Valean, Takeda, and Vibrant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients With a Positive FIT Fail to Get Follow-Up Colonoscopies
Patients With a Positive FIT Fail to Get Follow-Up Colonoscopies
The Use of Lung Cancer Screening to Increase Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Diagnosis in Veterans Affairs Primary Care
The Use of Lung Cancer Screening to Increase Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Diagnosis in Veterans Affairs Primary Care
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provide care for patients with higher rates of many diseases—diabetes, heart disease, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and stroke—compared to the nonveteran population. 1 Due to the medical complexities of these diseases, they are often misdiagnosed or not diagnosed at all.
COPD is hiding in plain sight, impacting quality of life and burdening US health care systems.2 Research has yielded new treatments and evidence-based guidelines; however, COPD remains underdiagnosed. Only 13 million of the estimated 79 million US adults with COPD aged 20 to 79 years have been formally diagnosed.3 By the time patients are diagnosed, the disease is often advanced, and therapies are less effective. In 2 large studies of patients with COPD symptoms, later diagnosis was associated with worse outcomes.4,5
Veterans have a higher prevalence of COPD (8%-19%) than nonveterans (6%), likely due to higher rates of smoking and service-related exposures, especially among veterans of post-9/11 conflicts.6,7 Veterans do not always report symptoms and PCPs may not ask about symptoms, leading to underdiagnosis.8 The combination of high likelihood and underdetection of COPD presents a challenge and a target for VA quality improvement (QI).
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against screening asymptomatic patients for COPD. However, both the USPSTF and the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Report advocate for active case finding in primary care clinics to determine whether high-risk patients, such as smokers, experience COPD symptoms and warrant spirometry. 9,10 To make early COPD diagnoses, clinicians may use questionnaires alone or in combination with handheld peak expiratory flow rate measurements.11,12 Formal spirometry, considered the gold standard for COPD diagnosis, is ordered for patients who report COPD symptoms (ie, shortness of breath with exertion) or who have both COPD symptoms and reduced peak flow rates.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found that while the combination of questionnaires and peak flows was the more effective strategy overall, questionnaires alone were also valuable for identifying patients with possible COPD.13 Implementation of either screening method in primary care practices would be challenging. In a simulation study that applied chronic disease and preventive care guidelines to hypothetical patient panels, the time required for PCPs to provide guideline-recommended chronic and preventive care in addition to acute care far exceeded 8 hours per day, even in team-based settings.14 Overburdened PCPs are therefore unlikely to accept additional tasks like COPD case finding.
Why don’t patients report their pulmonary symptoms? Patients may not recognize the symptoms as evidence of COPD. Others may be afraid of a COPD diagnosis or the stigma that is associated with it.15 Perhaps they believe COPD treatment is ineffective because of lung damage from smoking. Some patients may not want to know if they have COPD, while others reduce activity levels to avoid symptoms.16
QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PROJECT
Given the high prevalence of COPD among veterans and the potential for underdiagnosis, VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System (VANEOHS) internal medicine residents and faculty assessed the state of COPD diagnosis in its primary care clinic with a QI project in 2022. Patients in the clinic between August 1, 2015, and November 30, 2022, with an International Classification of Diseases-10 (ICD-10) COPD diagnosis code (J44) in the electronic health record were included. Of 157 included patients, 105 patients who had prior spirometry testing were excluded. Of the 52 patients with diagnosed COPD and no spirometry testing, 30 patients had computed tomography (CT) findings consistent with COPD (ie, airway thickening, emphysema, air trapping) that was performed for CT lung cancer screening (LCS).17 Twenty-three of these 30 patients were contacted by phone. All 23 were ever smokers and 13 reported COPD symptoms. The PCPs of the symptomatic patients were then contacted. Spirometry was ordered for all 13 patients and completed by 7. Three spirometry tests confirmed the COPD diagnosis. One PCP initiated inhaler therapy for a patient with newly diagnosed COPD.
All 11 PCPs of symptomatic patients were interviewed (many had > 1 symptomatic patient). They reported being unaware of patients’ COPD symptoms because the patients did not mention them, noting that screening for COPD was not a priority.
Role of Lung Cancer Screening
VA PCPs use electronic health record clinical reminders to track tests, consults, chronic disease education, cancer screenings, and routine health maintenance. A clinical reminder already exists (based on USPSTF recommendations) for LCS for patients aged 50 to 80 years who have a smoking history of 20 pack years. Patients who meet these criteria would also be considered high risk for COPD.
The VANEOHS QI project suggests that previously undiagnosed patients with findings of COPD on LCS may also have symptoms of COPD. Therefore, we wondered whether the LCS clinical reminder could serve a second purpose by prompting PCPs to ask veterans who meet LCS criteria about their COPD symptoms.
In 2022, about 13 million patients were eligible for LCS.18 Patients who qualify for LCS are at high risk for other cardiopulmonary disorders, such as COPD and coronary artery disease. Lung cancer is detected in only 1% of patients screened with CT at baseline. However, more often LCS yields evidence of additional cardiopulmonary disorders, such as emphysema or coronary artery calcifications. The International Early Lung Cancer Program (I-ELCAP) and the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial (NLST), which included > 79,000 patients, found evidence of emphysema on CT imaging in 24% and 31% of cases, respectively.19,20 In both cohorts, > 80% of patients with emphysema on CT imaging had no prior history of COPD.
In a 2022 article summarizing the potential impact of CT LCS on COPD diagnosis, Mulshine et al suggest that detection of emphysema on CT LCS provides “earlier recognition for PCPs to identify patients who would benefit from detailed symptom screening to prompt spirometry for COPD detection” and additional motivation for tobacco cessation.21 The VANEOHS QI project was developed and implemented prior to I-ELCAP or NLST reporting results but reinforces the value of CT LCS for COPD diagnosis.
Early diagnosis of COPD remains challenging because PCPs do not ask, patients do not tell, and symptoms can easily be dismissed. However, earlier diagnosis of COPD in symptomatic patients improves outcomes.3,4 To bridge this gap, VA PCPs and primary care patient aligned care teams (PACTs) need to commit to probing high-risk patients for COPD symptoms and ordering spirometry for those who are symptomatic. To accomplish this task, primary care teams need help.
The VANEOHS QI project confirmed that some patients with evidence of COPD on CT have symptoms of COPD that they did not share with their PCPs and suggests that LCS can be used as a dual action case finding method to screen both for lung cancer and COPD. We propose that patients who are eligible for LCS should also be probed for COPD symptoms at their clinic visits; for symptomatic patients, spirometry should be ordered, and COPD evidence-based management should be initiated when spirometry results are consistent with COPD. Annual probing for COPD symptoms could be considered in asymptomatic patients with ongoing tobacco use or emphysema on CT, since they may develop symptoms in the future. This new case-finding method bypasses the need for time-prohibitive questionnaires or peak flow measurements.
Future Opportunities
VA PCPs juggle many priorities and despite the simplicity of this new case finding COPD method, it may be unintentionally overlooked. PCPs often run out of time or may forget to ask patients about COPD symptoms when ordering LCS.
Future innovations to increase COPD diagnosis could include the creation of a yearly VA clinical reminder linked to the tobacco use reminder that has check boxes asking about symptoms of COPD in current and prior smokers. If patients have COPD symptoms, the reminder can prompt the ordering of spirometry. Similar reminders could be implemented to identify veterans with exposures to burn pits or other military environmental exposures who may have COPD symptoms. Another possible way to increase COPD diagnosis would be a partnership between primary care and the VA LCS program where patients receiving screening are asked about COPD symptoms during their LCS interviews and PACTs are alerted to order spirometry for symptomatic patients.
Elusive no longer! We can pull the veil back on COPD diagnosis and identify patients with possible COPD earlier in their course using their eligibility for LCS as a yearly reminder to probe them for symptoms. While not all patients who undergo LCS—even those with evidence of COPD on CT—will have COPD symptoms, symptoms may develop over time. LCS provides the possibility of 2 diagnoses from 1 test. This is an opportunity we cannot afford to miss.
- Betancourt JA, Granados PS, Pacheco GJ, et al. Exploring health outcomes for U.S. veterans compared to non-veterans from 2003 to 2019. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(5):604. doi:10.3390/healthcare90506064
- Bamonti PM, Fischer I, Moye J, Poghosyan H, Pietrzak RH. Obstructive respiratory disease in U.S. veterans: prevalence, characteristics, and health burden. J Psychiatr Res. 2024;176:140-147. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2024.05.053
- Criner RN, Han MK. COPD care in the 21st century: a public health priority. Respir Care. 2018;63(5):591-600. doi:10.4187/respcare.06276
- Larsson K, Janson C, Ställberg B, et al. Impact of COPD diagnosis timing on clinical and economic outcomes: the ARCTIC observational cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:995-1008. doi:10.2147/COPD.S195382
- Kostikas K, Price D, Gutzwiller FS, et al. Clinical impact and healthcare resource utilization associated with early versus late COPD diagnosis in patients from UK CPRD Database. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020;15:1729- 1738. doi:10.2147/COPD.S255414
- Bamonti PM, Robinson SA, Wan ES, Moy ML. Improving physiological, physical, and psychological health outcomes: a narrative review in US veterans with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Savitz DA, Woskie SR, Bello A, et al. Deployment to military bases with open burn pits and respiratory and cardiovascular disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247629. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7629
- Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
- Guirguis-Blake JM, Senger CA, Webber EM, Mularski RA, Whitlock EP. Screening for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1378-1393. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.2654
- Capriotti T, Tomy R, Morales M. COPD updates: 2023 GOLD Report for primary care providers. Clinical Advisor. May 9, 2023. Accessed May 14, 2025. https://www.clinicaladvisor.com/features/copd-updates-2023-gold-report-primary-care/
- Leidy NK, Martinez FJ, Malley KG, et al. Can CAPTURE be used to identify undiagnosed patients with mild- to- moderate COPD likely to benefit from treatment? Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1901-1912. doi:10.2147/COPD.S152226
- Jithoo A, Enright PL, Burney P, et al. Case-finding options for COPD: results from the burden of obstructive lung disease study. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(3):548-555. doi:10.1183/09031936.00132011
- Haroon SM, Jordan RE, O’Beirne-Elliman J, Adab P. Effectiveness of case finding strategies for COPD in primary care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2015;25:15056. doi:10.1038/npjpcrm.2015.56
- Porter J, Boyd C, Skandari MR, Laiteerapong N. Revisiting the time needed to provide adult primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(1)147-155. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07707-x
- Woo S, Zhou W, Larson JL. Stigma experiences in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an integrative review. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:1647- 1659. doi:10.2147/COPD.S306874
- Aaron SD, Montes de Oca M, Celli B, et al. Early diagnosis and treatment of COPD: the costs and benefits of case finding. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(8):928-937. doi:10.1164/rccm.202311-2120PP
- Kwon A, Lee C, Arafah A, Klein M, Namboodiri S, Lee C. Increasing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) diagnosis with pulmonary function testing for patients with chest imaging evidence of COPD. Poster presented at: Society of General Internal Medicine Midwest Regional Meeting; October 19-20, 2023; Chicago, IL.
- Henderson LM, Su I, Rivera MP, et al. Prevalence of lung cancer screening in the US, 2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(3):e243190. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3190
- Steiger D, Siddiqi MF, Yip R, Yankelevitz DF, Henschke CI; I-ELCAP investigators. The importance of low-dose CT screening to identify emphysema in asymptomatic participants with and without a prior diagnosis of COPD. Clin Imaging. 2021;78:136-141. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.03.012
- Pinsky PF, Lynch DA, Gierada DS. Incidental findings on low-dose CT scan lung cancer screenings and deaths from respiratory diseases. Chest. 2022;161(4):1092-1100. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.11.015
- Mulshine JL, Aldigé CR, Ambrose LF, et al. Emphysema detection in the course of lung cancer screening: optimizing a rare opportunity to impact population health. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(4):499- 503. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202207-631PS
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provide care for patients with higher rates of many diseases—diabetes, heart disease, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and stroke—compared to the nonveteran population. 1 Due to the medical complexities of these diseases, they are often misdiagnosed or not diagnosed at all.
COPD is hiding in plain sight, impacting quality of life and burdening US health care systems.2 Research has yielded new treatments and evidence-based guidelines; however, COPD remains underdiagnosed. Only 13 million of the estimated 79 million US adults with COPD aged 20 to 79 years have been formally diagnosed.3 By the time patients are diagnosed, the disease is often advanced, and therapies are less effective. In 2 large studies of patients with COPD symptoms, later diagnosis was associated with worse outcomes.4,5
Veterans have a higher prevalence of COPD (8%-19%) than nonveterans (6%), likely due to higher rates of smoking and service-related exposures, especially among veterans of post-9/11 conflicts.6,7 Veterans do not always report symptoms and PCPs may not ask about symptoms, leading to underdiagnosis.8 The combination of high likelihood and underdetection of COPD presents a challenge and a target for VA quality improvement (QI).
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against screening asymptomatic patients for COPD. However, both the USPSTF and the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Report advocate for active case finding in primary care clinics to determine whether high-risk patients, such as smokers, experience COPD symptoms and warrant spirometry. 9,10 To make early COPD diagnoses, clinicians may use questionnaires alone or in combination with handheld peak expiratory flow rate measurements.11,12 Formal spirometry, considered the gold standard for COPD diagnosis, is ordered for patients who report COPD symptoms (ie, shortness of breath with exertion) or who have both COPD symptoms and reduced peak flow rates.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found that while the combination of questionnaires and peak flows was the more effective strategy overall, questionnaires alone were also valuable for identifying patients with possible COPD.13 Implementation of either screening method in primary care practices would be challenging. In a simulation study that applied chronic disease and preventive care guidelines to hypothetical patient panels, the time required for PCPs to provide guideline-recommended chronic and preventive care in addition to acute care far exceeded 8 hours per day, even in team-based settings.14 Overburdened PCPs are therefore unlikely to accept additional tasks like COPD case finding.
Why don’t patients report their pulmonary symptoms? Patients may not recognize the symptoms as evidence of COPD. Others may be afraid of a COPD diagnosis or the stigma that is associated with it.15 Perhaps they believe COPD treatment is ineffective because of lung damage from smoking. Some patients may not want to know if they have COPD, while others reduce activity levels to avoid symptoms.16
QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PROJECT
Given the high prevalence of COPD among veterans and the potential for underdiagnosis, VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System (VANEOHS) internal medicine residents and faculty assessed the state of COPD diagnosis in its primary care clinic with a QI project in 2022. Patients in the clinic between August 1, 2015, and November 30, 2022, with an International Classification of Diseases-10 (ICD-10) COPD diagnosis code (J44) in the electronic health record were included. Of 157 included patients, 105 patients who had prior spirometry testing were excluded. Of the 52 patients with diagnosed COPD and no spirometry testing, 30 patients had computed tomography (CT) findings consistent with COPD (ie, airway thickening, emphysema, air trapping) that was performed for CT lung cancer screening (LCS).17 Twenty-three of these 30 patients were contacted by phone. All 23 were ever smokers and 13 reported COPD symptoms. The PCPs of the symptomatic patients were then contacted. Spirometry was ordered for all 13 patients and completed by 7. Three spirometry tests confirmed the COPD diagnosis. One PCP initiated inhaler therapy for a patient with newly diagnosed COPD.
All 11 PCPs of symptomatic patients were interviewed (many had > 1 symptomatic patient). They reported being unaware of patients’ COPD symptoms because the patients did not mention them, noting that screening for COPD was not a priority.
Role of Lung Cancer Screening
VA PCPs use electronic health record clinical reminders to track tests, consults, chronic disease education, cancer screenings, and routine health maintenance. A clinical reminder already exists (based on USPSTF recommendations) for LCS for patients aged 50 to 80 years who have a smoking history of 20 pack years. Patients who meet these criteria would also be considered high risk for COPD.
The VANEOHS QI project suggests that previously undiagnosed patients with findings of COPD on LCS may also have symptoms of COPD. Therefore, we wondered whether the LCS clinical reminder could serve a second purpose by prompting PCPs to ask veterans who meet LCS criteria about their COPD symptoms.
In 2022, about 13 million patients were eligible for LCS.18 Patients who qualify for LCS are at high risk for other cardiopulmonary disorders, such as COPD and coronary artery disease. Lung cancer is detected in only 1% of patients screened with CT at baseline. However, more often LCS yields evidence of additional cardiopulmonary disorders, such as emphysema or coronary artery calcifications. The International Early Lung Cancer Program (I-ELCAP) and the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial (NLST), which included > 79,000 patients, found evidence of emphysema on CT imaging in 24% and 31% of cases, respectively.19,20 In both cohorts, > 80% of patients with emphysema on CT imaging had no prior history of COPD.
In a 2022 article summarizing the potential impact of CT LCS on COPD diagnosis, Mulshine et al suggest that detection of emphysema on CT LCS provides “earlier recognition for PCPs to identify patients who would benefit from detailed symptom screening to prompt spirometry for COPD detection” and additional motivation for tobacco cessation.21 The VANEOHS QI project was developed and implemented prior to I-ELCAP or NLST reporting results but reinforces the value of CT LCS for COPD diagnosis.
Early diagnosis of COPD remains challenging because PCPs do not ask, patients do not tell, and symptoms can easily be dismissed. However, earlier diagnosis of COPD in symptomatic patients improves outcomes.3,4 To bridge this gap, VA PCPs and primary care patient aligned care teams (PACTs) need to commit to probing high-risk patients for COPD symptoms and ordering spirometry for those who are symptomatic. To accomplish this task, primary care teams need help.
The VANEOHS QI project confirmed that some patients with evidence of COPD on CT have symptoms of COPD that they did not share with their PCPs and suggests that LCS can be used as a dual action case finding method to screen both for lung cancer and COPD. We propose that patients who are eligible for LCS should also be probed for COPD symptoms at their clinic visits; for symptomatic patients, spirometry should be ordered, and COPD evidence-based management should be initiated when spirometry results are consistent with COPD. Annual probing for COPD symptoms could be considered in asymptomatic patients with ongoing tobacco use or emphysema on CT, since they may develop symptoms in the future. This new case-finding method bypasses the need for time-prohibitive questionnaires or peak flow measurements.
Future Opportunities
VA PCPs juggle many priorities and despite the simplicity of this new case finding COPD method, it may be unintentionally overlooked. PCPs often run out of time or may forget to ask patients about COPD symptoms when ordering LCS.
Future innovations to increase COPD diagnosis could include the creation of a yearly VA clinical reminder linked to the tobacco use reminder that has check boxes asking about symptoms of COPD in current and prior smokers. If patients have COPD symptoms, the reminder can prompt the ordering of spirometry. Similar reminders could be implemented to identify veterans with exposures to burn pits or other military environmental exposures who may have COPD symptoms. Another possible way to increase COPD diagnosis would be a partnership between primary care and the VA LCS program where patients receiving screening are asked about COPD symptoms during their LCS interviews and PACTs are alerted to order spirometry for symptomatic patients.
Elusive no longer! We can pull the veil back on COPD diagnosis and identify patients with possible COPD earlier in their course using their eligibility for LCS as a yearly reminder to probe them for symptoms. While not all patients who undergo LCS—even those with evidence of COPD on CT—will have COPD symptoms, symptoms may develop over time. LCS provides the possibility of 2 diagnoses from 1 test. This is an opportunity we cannot afford to miss.
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provide care for patients with higher rates of many diseases—diabetes, heart disease, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and stroke—compared to the nonveteran population. 1 Due to the medical complexities of these diseases, they are often misdiagnosed or not diagnosed at all.
COPD is hiding in plain sight, impacting quality of life and burdening US health care systems.2 Research has yielded new treatments and evidence-based guidelines; however, COPD remains underdiagnosed. Only 13 million of the estimated 79 million US adults with COPD aged 20 to 79 years have been formally diagnosed.3 By the time patients are diagnosed, the disease is often advanced, and therapies are less effective. In 2 large studies of patients with COPD symptoms, later diagnosis was associated with worse outcomes.4,5
Veterans have a higher prevalence of COPD (8%-19%) than nonveterans (6%), likely due to higher rates of smoking and service-related exposures, especially among veterans of post-9/11 conflicts.6,7 Veterans do not always report symptoms and PCPs may not ask about symptoms, leading to underdiagnosis.8 The combination of high likelihood and underdetection of COPD presents a challenge and a target for VA quality improvement (QI).
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against screening asymptomatic patients for COPD. However, both the USPSTF and the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Report advocate for active case finding in primary care clinics to determine whether high-risk patients, such as smokers, experience COPD symptoms and warrant spirometry. 9,10 To make early COPD diagnoses, clinicians may use questionnaires alone or in combination with handheld peak expiratory flow rate measurements.11,12 Formal spirometry, considered the gold standard for COPD diagnosis, is ordered for patients who report COPD symptoms (ie, shortness of breath with exertion) or who have both COPD symptoms and reduced peak flow rates.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found that while the combination of questionnaires and peak flows was the more effective strategy overall, questionnaires alone were also valuable for identifying patients with possible COPD.13 Implementation of either screening method in primary care practices would be challenging. In a simulation study that applied chronic disease and preventive care guidelines to hypothetical patient panels, the time required for PCPs to provide guideline-recommended chronic and preventive care in addition to acute care far exceeded 8 hours per day, even in team-based settings.14 Overburdened PCPs are therefore unlikely to accept additional tasks like COPD case finding.
Why don’t patients report their pulmonary symptoms? Patients may not recognize the symptoms as evidence of COPD. Others may be afraid of a COPD diagnosis or the stigma that is associated with it.15 Perhaps they believe COPD treatment is ineffective because of lung damage from smoking. Some patients may not want to know if they have COPD, while others reduce activity levels to avoid symptoms.16
QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PROJECT
Given the high prevalence of COPD among veterans and the potential for underdiagnosis, VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System (VANEOHS) internal medicine residents and faculty assessed the state of COPD diagnosis in its primary care clinic with a QI project in 2022. Patients in the clinic between August 1, 2015, and November 30, 2022, with an International Classification of Diseases-10 (ICD-10) COPD diagnosis code (J44) in the electronic health record were included. Of 157 included patients, 105 patients who had prior spirometry testing were excluded. Of the 52 patients with diagnosed COPD and no spirometry testing, 30 patients had computed tomography (CT) findings consistent with COPD (ie, airway thickening, emphysema, air trapping) that was performed for CT lung cancer screening (LCS).17 Twenty-three of these 30 patients were contacted by phone. All 23 were ever smokers and 13 reported COPD symptoms. The PCPs of the symptomatic patients were then contacted. Spirometry was ordered for all 13 patients and completed by 7. Three spirometry tests confirmed the COPD diagnosis. One PCP initiated inhaler therapy for a patient with newly diagnosed COPD.
All 11 PCPs of symptomatic patients were interviewed (many had > 1 symptomatic patient). They reported being unaware of patients’ COPD symptoms because the patients did not mention them, noting that screening for COPD was not a priority.
Role of Lung Cancer Screening
VA PCPs use electronic health record clinical reminders to track tests, consults, chronic disease education, cancer screenings, and routine health maintenance. A clinical reminder already exists (based on USPSTF recommendations) for LCS for patients aged 50 to 80 years who have a smoking history of 20 pack years. Patients who meet these criteria would also be considered high risk for COPD.
The VANEOHS QI project suggests that previously undiagnosed patients with findings of COPD on LCS may also have symptoms of COPD. Therefore, we wondered whether the LCS clinical reminder could serve a second purpose by prompting PCPs to ask veterans who meet LCS criteria about their COPD symptoms.
In 2022, about 13 million patients were eligible for LCS.18 Patients who qualify for LCS are at high risk for other cardiopulmonary disorders, such as COPD and coronary artery disease. Lung cancer is detected in only 1% of patients screened with CT at baseline. However, more often LCS yields evidence of additional cardiopulmonary disorders, such as emphysema or coronary artery calcifications. The International Early Lung Cancer Program (I-ELCAP) and the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial (NLST), which included > 79,000 patients, found evidence of emphysema on CT imaging in 24% and 31% of cases, respectively.19,20 In both cohorts, > 80% of patients with emphysema on CT imaging had no prior history of COPD.
In a 2022 article summarizing the potential impact of CT LCS on COPD diagnosis, Mulshine et al suggest that detection of emphysema on CT LCS provides “earlier recognition for PCPs to identify patients who would benefit from detailed symptom screening to prompt spirometry for COPD detection” and additional motivation for tobacco cessation.21 The VANEOHS QI project was developed and implemented prior to I-ELCAP or NLST reporting results but reinforces the value of CT LCS for COPD diagnosis.
Early diagnosis of COPD remains challenging because PCPs do not ask, patients do not tell, and symptoms can easily be dismissed. However, earlier diagnosis of COPD in symptomatic patients improves outcomes.3,4 To bridge this gap, VA PCPs and primary care patient aligned care teams (PACTs) need to commit to probing high-risk patients for COPD symptoms and ordering spirometry for those who are symptomatic. To accomplish this task, primary care teams need help.
The VANEOHS QI project confirmed that some patients with evidence of COPD on CT have symptoms of COPD that they did not share with their PCPs and suggests that LCS can be used as a dual action case finding method to screen both for lung cancer and COPD. We propose that patients who are eligible for LCS should also be probed for COPD symptoms at their clinic visits; for symptomatic patients, spirometry should be ordered, and COPD evidence-based management should be initiated when spirometry results are consistent with COPD. Annual probing for COPD symptoms could be considered in asymptomatic patients with ongoing tobacco use or emphysema on CT, since they may develop symptoms in the future. This new case-finding method bypasses the need for time-prohibitive questionnaires or peak flow measurements.
Future Opportunities
VA PCPs juggle many priorities and despite the simplicity of this new case finding COPD method, it may be unintentionally overlooked. PCPs often run out of time or may forget to ask patients about COPD symptoms when ordering LCS.
Future innovations to increase COPD diagnosis could include the creation of a yearly VA clinical reminder linked to the tobacco use reminder that has check boxes asking about symptoms of COPD in current and prior smokers. If patients have COPD symptoms, the reminder can prompt the ordering of spirometry. Similar reminders could be implemented to identify veterans with exposures to burn pits or other military environmental exposures who may have COPD symptoms. Another possible way to increase COPD diagnosis would be a partnership between primary care and the VA LCS program where patients receiving screening are asked about COPD symptoms during their LCS interviews and PACTs are alerted to order spirometry for symptomatic patients.
Elusive no longer! We can pull the veil back on COPD diagnosis and identify patients with possible COPD earlier in their course using their eligibility for LCS as a yearly reminder to probe them for symptoms. While not all patients who undergo LCS—even those with evidence of COPD on CT—will have COPD symptoms, symptoms may develop over time. LCS provides the possibility of 2 diagnoses from 1 test. This is an opportunity we cannot afford to miss.
- Betancourt JA, Granados PS, Pacheco GJ, et al. Exploring health outcomes for U.S. veterans compared to non-veterans from 2003 to 2019. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(5):604. doi:10.3390/healthcare90506064
- Bamonti PM, Fischer I, Moye J, Poghosyan H, Pietrzak RH. Obstructive respiratory disease in U.S. veterans: prevalence, characteristics, and health burden. J Psychiatr Res. 2024;176:140-147. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2024.05.053
- Criner RN, Han MK. COPD care in the 21st century: a public health priority. Respir Care. 2018;63(5):591-600. doi:10.4187/respcare.06276
- Larsson K, Janson C, Ställberg B, et al. Impact of COPD diagnosis timing on clinical and economic outcomes: the ARCTIC observational cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:995-1008. doi:10.2147/COPD.S195382
- Kostikas K, Price D, Gutzwiller FS, et al. Clinical impact and healthcare resource utilization associated with early versus late COPD diagnosis in patients from UK CPRD Database. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020;15:1729- 1738. doi:10.2147/COPD.S255414
- Bamonti PM, Robinson SA, Wan ES, Moy ML. Improving physiological, physical, and psychological health outcomes: a narrative review in US veterans with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Savitz DA, Woskie SR, Bello A, et al. Deployment to military bases with open burn pits and respiratory and cardiovascular disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247629. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7629
- Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
- Guirguis-Blake JM, Senger CA, Webber EM, Mularski RA, Whitlock EP. Screening for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1378-1393. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.2654
- Capriotti T, Tomy R, Morales M. COPD updates: 2023 GOLD Report for primary care providers. Clinical Advisor. May 9, 2023. Accessed May 14, 2025. https://www.clinicaladvisor.com/features/copd-updates-2023-gold-report-primary-care/
- Leidy NK, Martinez FJ, Malley KG, et al. Can CAPTURE be used to identify undiagnosed patients with mild- to- moderate COPD likely to benefit from treatment? Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1901-1912. doi:10.2147/COPD.S152226
- Jithoo A, Enright PL, Burney P, et al. Case-finding options for COPD: results from the burden of obstructive lung disease study. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(3):548-555. doi:10.1183/09031936.00132011
- Haroon SM, Jordan RE, O’Beirne-Elliman J, Adab P. Effectiveness of case finding strategies for COPD in primary care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2015;25:15056. doi:10.1038/npjpcrm.2015.56
- Porter J, Boyd C, Skandari MR, Laiteerapong N. Revisiting the time needed to provide adult primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(1)147-155. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07707-x
- Woo S, Zhou W, Larson JL. Stigma experiences in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an integrative review. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:1647- 1659. doi:10.2147/COPD.S306874
- Aaron SD, Montes de Oca M, Celli B, et al. Early diagnosis and treatment of COPD: the costs and benefits of case finding. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(8):928-937. doi:10.1164/rccm.202311-2120PP
- Kwon A, Lee C, Arafah A, Klein M, Namboodiri S, Lee C. Increasing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) diagnosis with pulmonary function testing for patients with chest imaging evidence of COPD. Poster presented at: Society of General Internal Medicine Midwest Regional Meeting; October 19-20, 2023; Chicago, IL.
- Henderson LM, Su I, Rivera MP, et al. Prevalence of lung cancer screening in the US, 2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(3):e243190. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3190
- Steiger D, Siddiqi MF, Yip R, Yankelevitz DF, Henschke CI; I-ELCAP investigators. The importance of low-dose CT screening to identify emphysema in asymptomatic participants with and without a prior diagnosis of COPD. Clin Imaging. 2021;78:136-141. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.03.012
- Pinsky PF, Lynch DA, Gierada DS. Incidental findings on low-dose CT scan lung cancer screenings and deaths from respiratory diseases. Chest. 2022;161(4):1092-1100. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.11.015
- Mulshine JL, Aldigé CR, Ambrose LF, et al. Emphysema detection in the course of lung cancer screening: optimizing a rare opportunity to impact population health. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(4):499- 503. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202207-631PS
- Betancourt JA, Granados PS, Pacheco GJ, et al. Exploring health outcomes for U.S. veterans compared to non-veterans from 2003 to 2019. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(5):604. doi:10.3390/healthcare90506064
- Bamonti PM, Fischer I, Moye J, Poghosyan H, Pietrzak RH. Obstructive respiratory disease in U.S. veterans: prevalence, characteristics, and health burden. J Psychiatr Res. 2024;176:140-147. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2024.05.053
- Criner RN, Han MK. COPD care in the 21st century: a public health priority. Respir Care. 2018;63(5):591-600. doi:10.4187/respcare.06276
- Larsson K, Janson C, Ställberg B, et al. Impact of COPD diagnosis timing on clinical and economic outcomes: the ARCTIC observational cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:995-1008. doi:10.2147/COPD.S195382
- Kostikas K, Price D, Gutzwiller FS, et al. Clinical impact and healthcare resource utilization associated with early versus late COPD diagnosis in patients from UK CPRD Database. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020;15:1729- 1738. doi:10.2147/COPD.S255414
- Bamonti PM, Robinson SA, Wan ES, Moy ML. Improving physiological, physical, and psychological health outcomes: a narrative review in US veterans with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Savitz DA, Woskie SR, Bello A, et al. Deployment to military bases with open burn pits and respiratory and cardiovascular disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247629. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7629
- Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
- Guirguis-Blake JM, Senger CA, Webber EM, Mularski RA, Whitlock EP. Screening for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1378-1393. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.2654
- Capriotti T, Tomy R, Morales M. COPD updates: 2023 GOLD Report for primary care providers. Clinical Advisor. May 9, 2023. Accessed May 14, 2025. https://www.clinicaladvisor.com/features/copd-updates-2023-gold-report-primary-care/
- Leidy NK, Martinez FJ, Malley KG, et al. Can CAPTURE be used to identify undiagnosed patients with mild- to- moderate COPD likely to benefit from treatment? Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1901-1912. doi:10.2147/COPD.S152226
- Jithoo A, Enright PL, Burney P, et al. Case-finding options for COPD: results from the burden of obstructive lung disease study. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(3):548-555. doi:10.1183/09031936.00132011
- Haroon SM, Jordan RE, O’Beirne-Elliman J, Adab P. Effectiveness of case finding strategies for COPD in primary care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2015;25:15056. doi:10.1038/npjpcrm.2015.56
- Porter J, Boyd C, Skandari MR, Laiteerapong N. Revisiting the time needed to provide adult primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(1)147-155. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07707-x
- Woo S, Zhou W, Larson JL. Stigma experiences in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an integrative review. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:1647- 1659. doi:10.2147/COPD.S306874
- Aaron SD, Montes de Oca M, Celli B, et al. Early diagnosis and treatment of COPD: the costs and benefits of case finding. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(8):928-937. doi:10.1164/rccm.202311-2120PP
- Kwon A, Lee C, Arafah A, Klein M, Namboodiri S, Lee C. Increasing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) diagnosis with pulmonary function testing for patients with chest imaging evidence of COPD. Poster presented at: Society of General Internal Medicine Midwest Regional Meeting; October 19-20, 2023; Chicago, IL.
- Henderson LM, Su I, Rivera MP, et al. Prevalence of lung cancer screening in the US, 2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(3):e243190. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3190
- Steiger D, Siddiqi MF, Yip R, Yankelevitz DF, Henschke CI; I-ELCAP investigators. The importance of low-dose CT screening to identify emphysema in asymptomatic participants with and without a prior diagnosis of COPD. Clin Imaging. 2021;78:136-141. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.03.012
- Pinsky PF, Lynch DA, Gierada DS. Incidental findings on low-dose CT scan lung cancer screenings and deaths from respiratory diseases. Chest. 2022;161(4):1092-1100. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.11.015
- Mulshine JL, Aldigé CR, Ambrose LF, et al. Emphysema detection in the course of lung cancer screening: optimizing a rare opportunity to impact population health. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(4):499- 503. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202207-631PS
The Use of Lung Cancer Screening to Increase Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Diagnosis in Veterans Affairs Primary Care
The Use of Lung Cancer Screening to Increase Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Diagnosis in Veterans Affairs Primary Care
When Patient-Centered Care Initiatives Align: Integrating VA Whole Health and Shared Decision-Making for Lung Cancer Screening
When Patient-Centered Care Initiatives Align: Integrating VA Whole Health and Shared Decision-Making for Lung Cancer Screening
The landmark Crossing the Quality Chasm report from the National Academy of Medicine identified patient- centered care as essential to health care quality. The report defines patientcentered care as “respectful of and responsive to individual patient preferences, needs, and values.”1 Many health care systems, including the Veterans Health Administration, are transforming to a patient-centered model of care.2 The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health System of Care initiative is a system-wide, cultural transformation. Within whole health, what matters most to the patient—including their preferences, needs, and values—is foundational to health care and meant to be essential in every clinical encounter. Whole health implementation includes a progressive rollout with health care practitioner (HCP) trainings across the VA.2
Shared decision-making (SDM) is a different but aligned patient-centered care concept. SDM is a process through which a decision or care plan, based on patients’ preferences, needs, and values, is made or developed.3-5 SDM is ideal in situations with equipoise (decisions with equivalent choices), individualized risks, and/or greater uncertainty of the net benefit, such as with lung cancer screening (LCS).3 SDM for LCS is required by the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and has been adopted by many US health care systems, including the VA.6,7 Early detection of lung cancer can reduce death by 20% at the population level.8 However, at the patient level there is wide variation in the risk of developing lung cancer and a range of potential harms.8 LCS follow-up procedures may be more invasive than with other cancer screenings. Thus, there is concern about the risk of false-positive results leading to unnecessary care or complications.8 Given this balance between benefit and harm and the differing patient value on the trade-offs of LCS, an individualized, patient-centered approach is essential when deciding whether LCS is the right choice for a specific patient.
Despite the importance of LCS SDM, observational studies have shown poor implementation in clinical encounters.9,10 HCP barriers include competing demands, limited time, lack of familiarity with and training in SDM, and beliefs biasing screening over no screening.11-13 Additionally, HCPs may assume that patients want them to make the decision. However, research has shown that patients actually want to be more involved in their health care decisions.14 One suggested strategy to overcome these barriers is aligning SDM for LCS within an organization’s broader patient-centered initiatives.15
This project sought to align the need for SDM for LCS and the broader VA whole health initiative as part of a multilevel strategy to implement SDM for LCS across Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 1.16
This article addresses HCP-level barriers. HCPs targeted are those typically involved in LCS. The VA utilizes LCS coordinators (LCSCs) in both centralized or consult models (in which LCSCs are involved in all aspects of screening) and hybrid models (in which primary care practitioners and LCSCs are both engaged in LCS tasks). The goal of this program was to generate areas of conceptual alignment between SDM and whole health as a first step in integrating these VA initiatives. This work was conducted as a foundation for an SDM for lung cancer HCP training and consultation initiative.
ALIGNMENT PROCESS
We reviewed relevant literature and resources for SDM and whole health. In reviewing the SDM literature, we included a sample of the most widely cited literature on the topic, and focused primarily on the systematic review by Bomhof-Roordink et al.4,5,17,18 This review provided a synthesis of SDM elements across SDM models and identified 53 different elements clustered into 24 components.4 The most common components were present in at least half of all SDM published models, including: make the decision, patient preferences, tailor information, deliberate, create choice awareness, and learn about the patient. Bomhof-Roordink et al provided the guiding framework for this conceptualization of SDM because that study included the available recent published SDM models.4
Second, published literature on VA whole health along with supplemental promotional and training materials were reviewed. The whole health materials included 2 sets of training slides developed for VA HCPs (available to VA employees): Implementing Whole Health in Clinical Care, which is focused on HCPs’ work with patients, and Whole Health for You and Me, which is about HCPs’ personal well-being.19 We also reviewed a publication describing the history of whole health and patient-facing online whole health tools.2,19
Each document was reviewed for key elements related to SDM, patient-centered care, and whole health. Using the 53 elements identified by Bomhof-Roordink et al, we reviewed and compared each element to the whole health materials to create the integrated model of SDM and whole health. We iteratively discussed and organized the elements until we reached consensus.
SDM and Whole Health Alignment
We created an integrated model of SDM for LCS within the context of the VA whole health initiative. This integrated model is directed at HCPs who would likely engage patients in discussions of LCS, including primary care practitioners and nurse coordinators. The model includes 3 steps for HCPs to follow that align SDM within whole health: (1) frame the conversation and partner with the patient; (2) share clinical perspective and elicit patient values; and (3) deliberate and decide together. For each step, the SDM elements, whole health elements, and integration of SDM and whole health are provided. Table 1 provides an overview of the similarities and differences between SDM and whole health. Example phrases that merge SDM and whole health for HCPs to use in patient conversations about LCS are included in Table 2.
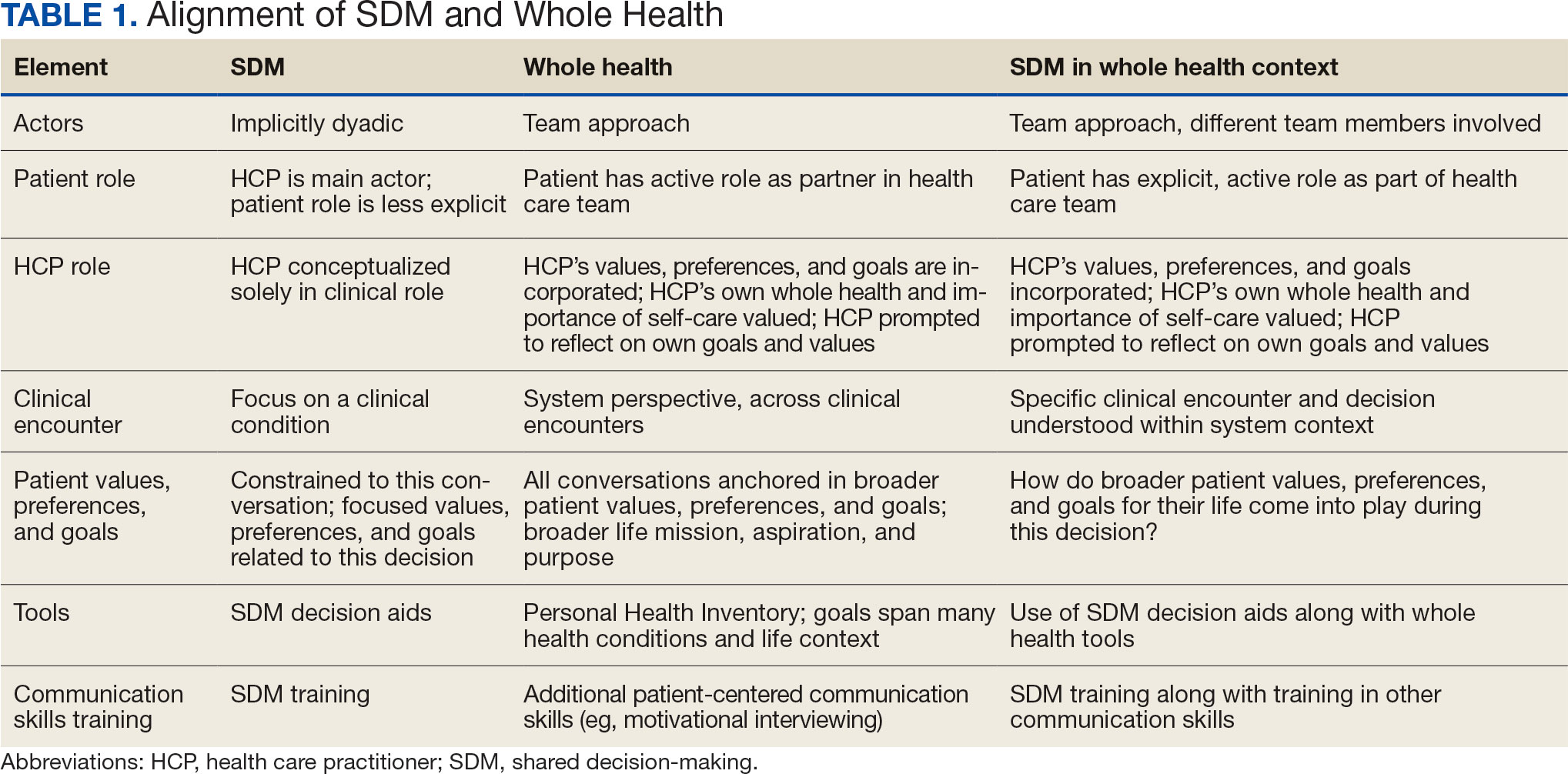

STEP 1. FRAME THE CONVERSATION AND PARTNER WITH THE PATIENT
Shared decision-making. Traditional SDM literature includes an initial step of letting patients know that there is a choice to be made between ≥ 2 clinical options.4 Ancillary elements of this first step include asking patients their preferences about the degree to which they want to be involved in SDM and about how they like to receive information (eg, verbal, written, video). These steps open the SDM conversation and ensure the patient and HCP are on the same page before moving forward. For example, the US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality SHARE model’s first step is for HCPs to communicate that choices exist and to invite the patient to be involved in decisions.20 Similarly, Elwyn’s 3-step SDM model begins with establishing that a choice exists and inviting patient input on making that choice.17
Whole health. Patients are encouraged to play an active role in their health care. Through whole health programs such as Taking Charge of My Life and Health, patients explore their values and set self-care goals.21 HCP whole health trainings teach and reinforce communication skills, including SDM, listening skills, and motivational interviewing.19
Shared decision-making/whole health integration. SDM and whole health both prioritize respect, compassion, and patients’ expertise. They focus on the patient-HCP relationship with an emphasis on fostering egalitarian interactions. HCPs frame the SDM conversation and partner with the patient so they know what to expect and who will be involved. This conversation is framed from the outset as a collaborative discussion. HCPs empower the patient to play an active role in decision-making and help them understand why their engagement is critical.
STEP 2. SHARE CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE AND ELICIT PATIENT VALUES
Shared decision-making. HCPs share clinical perspective on LCS tailored to individual patients while explicitly inviting the patient to share their preferences and values when thinking about whether to undergo LCS. HCPs give a balanced description of LCS, including the benefits and harms, tailored to the patient’s unique information needs and questions. Sharing clinical perspective also includes describing treatment options, the most common element across SDM models.4 Decision aids, which provide unbiased information and include a values clarification exercise, may be helpful in sharing clinical perspectives and clarifying patient values related to the trade-offs of LCS.22 For example, the VA National Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention developed a LCS decision aid to be used for SDM for LCS.
Whole health. The conversation shifts from “What is the matter with you?” to “What matters to you?” starting with the patient’s goals and priorities rather than disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.2 Several whole health tools exist, including the Personal Health Inventory, used to identify what matters most to patients and understand their current well-being and self-care.23 Using the inventory, the patient and their health care team develop the patient’s personal health plan.24 Additionally, whole health trains HCPs to reflect on their own attitudes and biases when providing clinical care.
Shared decision-making/whole health integration. The LCS conversation can build on other whole health-related conversations with a HCP or other team members. HCPs can reference the patient’s personal health plan for documentation of the patient’s preferences, values, and goals in the electronic medical record. During this process, HCPs can give space for patients to discuss factors in their life and experiences that impact their perspective and decision-making. For example, patient concerns could be explored here, including fear of a cancer diagnosis, stigma around smoking, and fears around the screening and/or treatment process. HCPs may ask, “What matters most to you when making this decision?” Finally, by sharing clinical information, HCPs will focus on patient values to help overcome their own biases toward a desire for LCS. HCPs, similar to the rest of the US public, tend to hold highly favorable attitudes toward cancer screening as well as misconceptions about the magnitude of benefits from screening.13
STEP 3. DELIBERATE AND DECIDE TOGETHER
Shared decision-making. Decision-making is almost always considered the last SDM step.4 In the final step, the patient and HCP discuss the options (ie, to screen or not to screen) considering the patient’s values and preferences, and patients decide with their HCP whether they will undergo LCS. Patients may decide they need more time to think about these options. As part of deliberation, HCPs assess what other information patients may need to arrive at a decision. Family members, friends, or peers may be included in making the final decision.
Whole health. In Whole health, decisions also may include the entire health care team and other individuals important to the patient (eg, family, friends). Integration across different health care settings is also considered a key whole health element. Finally, whole health focuses on long-term relationships with patients; thus, the LCS SDM process is situated within longer term relationship building and patient empowerment, both of which will facilitate partnering with the patient in future conversations about other decisions.
Shared decision-making/whole health integration. Both SDM and whole health emphasize partnership with the patient in making a final decision. There is also focus on decision-making as an ongoing process. Deciding whether LCS is the best choice might include naming and addressing emotions, voicing questions not raised, and exploring whether screening fits the patient’s goals, values, and life context. HCPs may give guidance, but patients retain the authority to make decisions. The goal is to empower patients to know that the only right decision is the one right for them and they will be supported.
Limitations
This article describes a VA practice program and was not a formal research study. Further work is needed to evaluate the presented strategies. Additionally, we did not conduct a systematic literature review and thus elements of SDM and whole health may not be exhaustive.
CONCLUSIONS
This article describes the alignment of 2 distinct VA initiatives, whole health and SDM for LCS. The goal was to reduce known barriers to SDM, such as competing demands, limited time, and lack of familiarity with and training in SDM.11-13 These concepts are well aligned. This integrated model is the first step in informing the development of a HCP training program and materials as part of a multilevel strategy that our team is using to implement SDM for LCS in VISN 1.16 The final training and materials resulting from this work were delivered to LCSCs in 3 ways: (1) a series of 3 interactive group training sessions, including didactic elements, role play, and time for open discussion; (2) 1-on-1 academic detailing; and (3) educational handouts. In academic detailing, a member of the research team trained in academic detailing met virtually with each nurse coordinator, identified that individual’s barriers to SDM, and used the training materials to highlight messages to overcome those barriers; follow-up calls provided a forum for discussing progress and overcoming additional challenges. Although this article focused specifically on whole health and SDM, the conceptual alignment process strategy can be applied to other implementations of multiple initiatives.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. The National Academies Press; 2001. doi:10.17226/10027
- Bokhour BG, Haun JN, Hyde J, Charns M, Kligler B. Transforming the Veterans Affairs to a whole health system of care: time for action and research. Med Care. 2020;58:295- 300. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001316
- Elwyn G, Frosch D, Rollnick S. Dual equipoise shared decision making: definitions for decision and behaviour support interventions. Implement Sci. 2009;4:75. doi:7510.1186/1748-5908-4-75
- Bomhof-Roordink H, Gärtner FR, Stiggelbout AM, Pieterse AH. Key components of shared decision making models: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e031763. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031763
- Charles C, Gafni A, Whelan T. Decision-making in the physician- patient encounter: revisiting the shared treatment decision-making model. Soc Sci Med. 1999;49:651-661. doi:10.1016/s0277-9536(99)00145-8
- Moyer VA; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for lung cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160:330- 338. doi:10.7326/m13-2771
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Screening for lung cancer with low dose computed tomography (LDCT). February 10, 2022. Accessed February 7, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/ncacal-decision-memo.aspx?proposed=N&ncaid=304
- Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:395-409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
- Slatore CG, Wiener RS. Pulmonary nodules: a small problem for many, severe distress for some, and how to communicate about it. Chest. 2018;153:1004-1015. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2017.10.013
- Nishi SPE, Lowenstein LM, Mendoza TR, et al. Shared decision-making for lung cancer screening: how well are we “sharing”? Chest. 2021;160:330-340. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.01.041
- Wiener RS, Koppelman E, Bolton R, et al. Patient and clinician perspectives on shared decision-making in early adopting lung cancer screening programs: a qualitative study. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33:1035-1042. doi:10.1007/s11606-018-4350-9
- Melzer AC, Golden SE, Ono SS, Datta S, Triplette M, Slatore CG. “We just never have enough time”: clinician views of lung cancer screening processes and implementation. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-262OC
- Schwartz LM, Woloshin S, Fowler FJ Jr, Welch HG. Enthusiasm for cancer screening in the United States. JAMA. 2004;291:71-78. doi:10.1001/jama.291.1.71
- Lown BA, Rosen J, Marttila J. An agenda for improving compassionate care: a survey shows about half of patients say such care is missing. Health Aff (Millwood). 2011;30:1772-1778. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0539
- Scholl I, LaRussa A, Hahlweg P, Kobrin S, Elwyn G. Organizational- and system-level characteristics that influence implementation of shared decision-making and strategies to address them - a scoping review. Implement Sci. 2018;13:40. doi:10.1186/s13012-018-0731-z
- Khanna A, Fix GM, Anderson E, et al. Towards a framework for patient-centred care coordination: a scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e066808. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-066808
- Elwyn G, Durand MA, Song J, et al. A three-talk model for shared decision making: multistage consultation process. BMJ. 2017;359:j4891. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4891
- Makoul G, Clayman ML. An integrative model of shared decision making in medical encounters. Patient Educ Couns. 2006;60:301-312. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2005.06.010
- Whole Health. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The SHARE approach. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.ahrq.gov/health-literacy/professional-training/shared-decision/index.html
- Abadi MH, Barker AM, Rao SR, Orner M, Rychener D, Bokhour BG. Examining the impact of a peer-led group program for veteran engagement and well-being. J Altern Complement Med. 2021;27:S37-S44. doi:10.1089/acm.2020.0124
- Stacey D, Lewis KB, Smith M, et al. Decision aids for people facing health treatment or screening decisions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024;1:CD001431. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001431.pub6
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Patient Centered Care and Cultural Transformation. Personal health inventory. Revised April 2019. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/docs/10-773_PHI_July2019_508.pdf
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Build your personal health plan. Updated July 24, 2024. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/phi.asp
The landmark Crossing the Quality Chasm report from the National Academy of Medicine identified patient- centered care as essential to health care quality. The report defines patientcentered care as “respectful of and responsive to individual patient preferences, needs, and values.”1 Many health care systems, including the Veterans Health Administration, are transforming to a patient-centered model of care.2 The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health System of Care initiative is a system-wide, cultural transformation. Within whole health, what matters most to the patient—including their preferences, needs, and values—is foundational to health care and meant to be essential in every clinical encounter. Whole health implementation includes a progressive rollout with health care practitioner (HCP) trainings across the VA.2
Shared decision-making (SDM) is a different but aligned patient-centered care concept. SDM is a process through which a decision or care plan, based on patients’ preferences, needs, and values, is made or developed.3-5 SDM is ideal in situations with equipoise (decisions with equivalent choices), individualized risks, and/or greater uncertainty of the net benefit, such as with lung cancer screening (LCS).3 SDM for LCS is required by the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and has been adopted by many US health care systems, including the VA.6,7 Early detection of lung cancer can reduce death by 20% at the population level.8 However, at the patient level there is wide variation in the risk of developing lung cancer and a range of potential harms.8 LCS follow-up procedures may be more invasive than with other cancer screenings. Thus, there is concern about the risk of false-positive results leading to unnecessary care or complications.8 Given this balance between benefit and harm and the differing patient value on the trade-offs of LCS, an individualized, patient-centered approach is essential when deciding whether LCS is the right choice for a specific patient.
Despite the importance of LCS SDM, observational studies have shown poor implementation in clinical encounters.9,10 HCP barriers include competing demands, limited time, lack of familiarity with and training in SDM, and beliefs biasing screening over no screening.11-13 Additionally, HCPs may assume that patients want them to make the decision. However, research has shown that patients actually want to be more involved in their health care decisions.14 One suggested strategy to overcome these barriers is aligning SDM for LCS within an organization’s broader patient-centered initiatives.15
This project sought to align the need for SDM for LCS and the broader VA whole health initiative as part of a multilevel strategy to implement SDM for LCS across Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 1.16
This article addresses HCP-level barriers. HCPs targeted are those typically involved in LCS. The VA utilizes LCS coordinators (LCSCs) in both centralized or consult models (in which LCSCs are involved in all aspects of screening) and hybrid models (in which primary care practitioners and LCSCs are both engaged in LCS tasks). The goal of this program was to generate areas of conceptual alignment between SDM and whole health as a first step in integrating these VA initiatives. This work was conducted as a foundation for an SDM for lung cancer HCP training and consultation initiative.
ALIGNMENT PROCESS
We reviewed relevant literature and resources for SDM and whole health. In reviewing the SDM literature, we included a sample of the most widely cited literature on the topic, and focused primarily on the systematic review by Bomhof-Roordink et al.4,5,17,18 This review provided a synthesis of SDM elements across SDM models and identified 53 different elements clustered into 24 components.4 The most common components were present in at least half of all SDM published models, including: make the decision, patient preferences, tailor information, deliberate, create choice awareness, and learn about the patient. Bomhof-Roordink et al provided the guiding framework for this conceptualization of SDM because that study included the available recent published SDM models.4
Second, published literature on VA whole health along with supplemental promotional and training materials were reviewed. The whole health materials included 2 sets of training slides developed for VA HCPs (available to VA employees): Implementing Whole Health in Clinical Care, which is focused on HCPs’ work with patients, and Whole Health for You and Me, which is about HCPs’ personal well-being.19 We also reviewed a publication describing the history of whole health and patient-facing online whole health tools.2,19
Each document was reviewed for key elements related to SDM, patient-centered care, and whole health. Using the 53 elements identified by Bomhof-Roordink et al, we reviewed and compared each element to the whole health materials to create the integrated model of SDM and whole health. We iteratively discussed and organized the elements until we reached consensus.
SDM and Whole Health Alignment
We created an integrated model of SDM for LCS within the context of the VA whole health initiative. This integrated model is directed at HCPs who would likely engage patients in discussions of LCS, including primary care practitioners and nurse coordinators. The model includes 3 steps for HCPs to follow that align SDM within whole health: (1) frame the conversation and partner with the patient; (2) share clinical perspective and elicit patient values; and (3) deliberate and decide together. For each step, the SDM elements, whole health elements, and integration of SDM and whole health are provided. Table 1 provides an overview of the similarities and differences between SDM and whole health. Example phrases that merge SDM and whole health for HCPs to use in patient conversations about LCS are included in Table 2.


STEP 1. FRAME THE CONVERSATION AND PARTNER WITH THE PATIENT
Shared decision-making. Traditional SDM literature includes an initial step of letting patients know that there is a choice to be made between ≥ 2 clinical options.4 Ancillary elements of this first step include asking patients their preferences about the degree to which they want to be involved in SDM and about how they like to receive information (eg, verbal, written, video). These steps open the SDM conversation and ensure the patient and HCP are on the same page before moving forward. For example, the US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality SHARE model’s first step is for HCPs to communicate that choices exist and to invite the patient to be involved in decisions.20 Similarly, Elwyn’s 3-step SDM model begins with establishing that a choice exists and inviting patient input on making that choice.17
Whole health. Patients are encouraged to play an active role in their health care. Through whole health programs such as Taking Charge of My Life and Health, patients explore their values and set self-care goals.21 HCP whole health trainings teach and reinforce communication skills, including SDM, listening skills, and motivational interviewing.19
Shared decision-making/whole health integration. SDM and whole health both prioritize respect, compassion, and patients’ expertise. They focus on the patient-HCP relationship with an emphasis on fostering egalitarian interactions. HCPs frame the SDM conversation and partner with the patient so they know what to expect and who will be involved. This conversation is framed from the outset as a collaborative discussion. HCPs empower the patient to play an active role in decision-making and help them understand why their engagement is critical.
STEP 2. SHARE CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE AND ELICIT PATIENT VALUES
Shared decision-making. HCPs share clinical perspective on LCS tailored to individual patients while explicitly inviting the patient to share their preferences and values when thinking about whether to undergo LCS. HCPs give a balanced description of LCS, including the benefits and harms, tailored to the patient’s unique information needs and questions. Sharing clinical perspective also includes describing treatment options, the most common element across SDM models.4 Decision aids, which provide unbiased information and include a values clarification exercise, may be helpful in sharing clinical perspectives and clarifying patient values related to the trade-offs of LCS.22 For example, the VA National Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention developed a LCS decision aid to be used for SDM for LCS.
Whole health. The conversation shifts from “What is the matter with you?” to “What matters to you?” starting with the patient’s goals and priorities rather than disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.2 Several whole health tools exist, including the Personal Health Inventory, used to identify what matters most to patients and understand their current well-being and self-care.23 Using the inventory, the patient and their health care team develop the patient’s personal health plan.24 Additionally, whole health trains HCPs to reflect on their own attitudes and biases when providing clinical care.
Shared decision-making/whole health integration. The LCS conversation can build on other whole health-related conversations with a HCP or other team members. HCPs can reference the patient’s personal health plan for documentation of the patient’s preferences, values, and goals in the electronic medical record. During this process, HCPs can give space for patients to discuss factors in their life and experiences that impact their perspective and decision-making. For example, patient concerns could be explored here, including fear of a cancer diagnosis, stigma around smoking, and fears around the screening and/or treatment process. HCPs may ask, “What matters most to you when making this decision?” Finally, by sharing clinical information, HCPs will focus on patient values to help overcome their own biases toward a desire for LCS. HCPs, similar to the rest of the US public, tend to hold highly favorable attitudes toward cancer screening as well as misconceptions about the magnitude of benefits from screening.13
STEP 3. DELIBERATE AND DECIDE TOGETHER
Shared decision-making. Decision-making is almost always considered the last SDM step.4 In the final step, the patient and HCP discuss the options (ie, to screen or not to screen) considering the patient’s values and preferences, and patients decide with their HCP whether they will undergo LCS. Patients may decide they need more time to think about these options. As part of deliberation, HCPs assess what other information patients may need to arrive at a decision. Family members, friends, or peers may be included in making the final decision.
Whole health. In Whole health, decisions also may include the entire health care team and other individuals important to the patient (eg, family, friends). Integration across different health care settings is also considered a key whole health element. Finally, whole health focuses on long-term relationships with patients; thus, the LCS SDM process is situated within longer term relationship building and patient empowerment, both of which will facilitate partnering with the patient in future conversations about other decisions.
Shared decision-making/whole health integration. Both SDM and whole health emphasize partnership with the patient in making a final decision. There is also focus on decision-making as an ongoing process. Deciding whether LCS is the best choice might include naming and addressing emotions, voicing questions not raised, and exploring whether screening fits the patient’s goals, values, and life context. HCPs may give guidance, but patients retain the authority to make decisions. The goal is to empower patients to know that the only right decision is the one right for them and they will be supported.
Limitations
This article describes a VA practice program and was not a formal research study. Further work is needed to evaluate the presented strategies. Additionally, we did not conduct a systematic literature review and thus elements of SDM and whole health may not be exhaustive.
CONCLUSIONS
This article describes the alignment of 2 distinct VA initiatives, whole health and SDM for LCS. The goal was to reduce known barriers to SDM, such as competing demands, limited time, and lack of familiarity with and training in SDM.11-13 These concepts are well aligned. This integrated model is the first step in informing the development of a HCP training program and materials as part of a multilevel strategy that our team is using to implement SDM for LCS in VISN 1.16 The final training and materials resulting from this work were delivered to LCSCs in 3 ways: (1) a series of 3 interactive group training sessions, including didactic elements, role play, and time for open discussion; (2) 1-on-1 academic detailing; and (3) educational handouts. In academic detailing, a member of the research team trained in academic detailing met virtually with each nurse coordinator, identified that individual’s barriers to SDM, and used the training materials to highlight messages to overcome those barriers; follow-up calls provided a forum for discussing progress and overcoming additional challenges. Although this article focused specifically on whole health and SDM, the conceptual alignment process strategy can be applied to other implementations of multiple initiatives.
The landmark Crossing the Quality Chasm report from the National Academy of Medicine identified patient- centered care as essential to health care quality. The report defines patientcentered care as “respectful of and responsive to individual patient preferences, needs, and values.”1 Many health care systems, including the Veterans Health Administration, are transforming to a patient-centered model of care.2 The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health System of Care initiative is a system-wide, cultural transformation. Within whole health, what matters most to the patient—including their preferences, needs, and values—is foundational to health care and meant to be essential in every clinical encounter. Whole health implementation includes a progressive rollout with health care practitioner (HCP) trainings across the VA.2
Shared decision-making (SDM) is a different but aligned patient-centered care concept. SDM is a process through which a decision or care plan, based on patients’ preferences, needs, and values, is made or developed.3-5 SDM is ideal in situations with equipoise (decisions with equivalent choices), individualized risks, and/or greater uncertainty of the net benefit, such as with lung cancer screening (LCS).3 SDM for LCS is required by the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and has been adopted by many US health care systems, including the VA.6,7 Early detection of lung cancer can reduce death by 20% at the population level.8 However, at the patient level there is wide variation in the risk of developing lung cancer and a range of potential harms.8 LCS follow-up procedures may be more invasive than with other cancer screenings. Thus, there is concern about the risk of false-positive results leading to unnecessary care or complications.8 Given this balance between benefit and harm and the differing patient value on the trade-offs of LCS, an individualized, patient-centered approach is essential when deciding whether LCS is the right choice for a specific patient.
Despite the importance of LCS SDM, observational studies have shown poor implementation in clinical encounters.9,10 HCP barriers include competing demands, limited time, lack of familiarity with and training in SDM, and beliefs biasing screening over no screening.11-13 Additionally, HCPs may assume that patients want them to make the decision. However, research has shown that patients actually want to be more involved in their health care decisions.14 One suggested strategy to overcome these barriers is aligning SDM for LCS within an organization’s broader patient-centered initiatives.15
This project sought to align the need for SDM for LCS and the broader VA whole health initiative as part of a multilevel strategy to implement SDM for LCS across Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 1.16
This article addresses HCP-level barriers. HCPs targeted are those typically involved in LCS. The VA utilizes LCS coordinators (LCSCs) in both centralized or consult models (in which LCSCs are involved in all aspects of screening) and hybrid models (in which primary care practitioners and LCSCs are both engaged in LCS tasks). The goal of this program was to generate areas of conceptual alignment between SDM and whole health as a first step in integrating these VA initiatives. This work was conducted as a foundation for an SDM for lung cancer HCP training and consultation initiative.
ALIGNMENT PROCESS
We reviewed relevant literature and resources for SDM and whole health. In reviewing the SDM literature, we included a sample of the most widely cited literature on the topic, and focused primarily on the systematic review by Bomhof-Roordink et al.4,5,17,18 This review provided a synthesis of SDM elements across SDM models and identified 53 different elements clustered into 24 components.4 The most common components were present in at least half of all SDM published models, including: make the decision, patient preferences, tailor information, deliberate, create choice awareness, and learn about the patient. Bomhof-Roordink et al provided the guiding framework for this conceptualization of SDM because that study included the available recent published SDM models.4
Second, published literature on VA whole health along with supplemental promotional and training materials were reviewed. The whole health materials included 2 sets of training slides developed for VA HCPs (available to VA employees): Implementing Whole Health in Clinical Care, which is focused on HCPs’ work with patients, and Whole Health for You and Me, which is about HCPs’ personal well-being.19 We also reviewed a publication describing the history of whole health and patient-facing online whole health tools.2,19
Each document was reviewed for key elements related to SDM, patient-centered care, and whole health. Using the 53 elements identified by Bomhof-Roordink et al, we reviewed and compared each element to the whole health materials to create the integrated model of SDM and whole health. We iteratively discussed and organized the elements until we reached consensus.
SDM and Whole Health Alignment
We created an integrated model of SDM for LCS within the context of the VA whole health initiative. This integrated model is directed at HCPs who would likely engage patients in discussions of LCS, including primary care practitioners and nurse coordinators. The model includes 3 steps for HCPs to follow that align SDM within whole health: (1) frame the conversation and partner with the patient; (2) share clinical perspective and elicit patient values; and (3) deliberate and decide together. For each step, the SDM elements, whole health elements, and integration of SDM and whole health are provided. Table 1 provides an overview of the similarities and differences between SDM and whole health. Example phrases that merge SDM and whole health for HCPs to use in patient conversations about LCS are included in Table 2.


STEP 1. FRAME THE CONVERSATION AND PARTNER WITH THE PATIENT
Shared decision-making. Traditional SDM literature includes an initial step of letting patients know that there is a choice to be made between ≥ 2 clinical options.4 Ancillary elements of this first step include asking patients their preferences about the degree to which they want to be involved in SDM and about how they like to receive information (eg, verbal, written, video). These steps open the SDM conversation and ensure the patient and HCP are on the same page before moving forward. For example, the US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality SHARE model’s first step is for HCPs to communicate that choices exist and to invite the patient to be involved in decisions.20 Similarly, Elwyn’s 3-step SDM model begins with establishing that a choice exists and inviting patient input on making that choice.17
Whole health. Patients are encouraged to play an active role in their health care. Through whole health programs such as Taking Charge of My Life and Health, patients explore their values and set self-care goals.21 HCP whole health trainings teach and reinforce communication skills, including SDM, listening skills, and motivational interviewing.19
Shared decision-making/whole health integration. SDM and whole health both prioritize respect, compassion, and patients’ expertise. They focus on the patient-HCP relationship with an emphasis on fostering egalitarian interactions. HCPs frame the SDM conversation and partner with the patient so they know what to expect and who will be involved. This conversation is framed from the outset as a collaborative discussion. HCPs empower the patient to play an active role in decision-making and help them understand why their engagement is critical.
STEP 2. SHARE CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE AND ELICIT PATIENT VALUES
Shared decision-making. HCPs share clinical perspective on LCS tailored to individual patients while explicitly inviting the patient to share their preferences and values when thinking about whether to undergo LCS. HCPs give a balanced description of LCS, including the benefits and harms, tailored to the patient’s unique information needs and questions. Sharing clinical perspective also includes describing treatment options, the most common element across SDM models.4 Decision aids, which provide unbiased information and include a values clarification exercise, may be helpful in sharing clinical perspectives and clarifying patient values related to the trade-offs of LCS.22 For example, the VA National Center for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention developed a LCS decision aid to be used for SDM for LCS.
Whole health. The conversation shifts from “What is the matter with you?” to “What matters to you?” starting with the patient’s goals and priorities rather than disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.2 Several whole health tools exist, including the Personal Health Inventory, used to identify what matters most to patients and understand their current well-being and self-care.23 Using the inventory, the patient and their health care team develop the patient’s personal health plan.24 Additionally, whole health trains HCPs to reflect on their own attitudes and biases when providing clinical care.
Shared decision-making/whole health integration. The LCS conversation can build on other whole health-related conversations with a HCP or other team members. HCPs can reference the patient’s personal health plan for documentation of the patient’s preferences, values, and goals in the electronic medical record. During this process, HCPs can give space for patients to discuss factors in their life and experiences that impact their perspective and decision-making. For example, patient concerns could be explored here, including fear of a cancer diagnosis, stigma around smoking, and fears around the screening and/or treatment process. HCPs may ask, “What matters most to you when making this decision?” Finally, by sharing clinical information, HCPs will focus on patient values to help overcome their own biases toward a desire for LCS. HCPs, similar to the rest of the US public, tend to hold highly favorable attitudes toward cancer screening as well as misconceptions about the magnitude of benefits from screening.13
STEP 3. DELIBERATE AND DECIDE TOGETHER
Shared decision-making. Decision-making is almost always considered the last SDM step.4 In the final step, the patient and HCP discuss the options (ie, to screen or not to screen) considering the patient’s values and preferences, and patients decide with their HCP whether they will undergo LCS. Patients may decide they need more time to think about these options. As part of deliberation, HCPs assess what other information patients may need to arrive at a decision. Family members, friends, or peers may be included in making the final decision.
Whole health. In Whole health, decisions also may include the entire health care team and other individuals important to the patient (eg, family, friends). Integration across different health care settings is also considered a key whole health element. Finally, whole health focuses on long-term relationships with patients; thus, the LCS SDM process is situated within longer term relationship building and patient empowerment, both of which will facilitate partnering with the patient in future conversations about other decisions.
Shared decision-making/whole health integration. Both SDM and whole health emphasize partnership with the patient in making a final decision. There is also focus on decision-making as an ongoing process. Deciding whether LCS is the best choice might include naming and addressing emotions, voicing questions not raised, and exploring whether screening fits the patient’s goals, values, and life context. HCPs may give guidance, but patients retain the authority to make decisions. The goal is to empower patients to know that the only right decision is the one right for them and they will be supported.
Limitations
This article describes a VA practice program and was not a formal research study. Further work is needed to evaluate the presented strategies. Additionally, we did not conduct a systematic literature review and thus elements of SDM and whole health may not be exhaustive.
CONCLUSIONS
This article describes the alignment of 2 distinct VA initiatives, whole health and SDM for LCS. The goal was to reduce known barriers to SDM, such as competing demands, limited time, and lack of familiarity with and training in SDM.11-13 These concepts are well aligned. This integrated model is the first step in informing the development of a HCP training program and materials as part of a multilevel strategy that our team is using to implement SDM for LCS in VISN 1.16 The final training and materials resulting from this work were delivered to LCSCs in 3 ways: (1) a series of 3 interactive group training sessions, including didactic elements, role play, and time for open discussion; (2) 1-on-1 academic detailing; and (3) educational handouts. In academic detailing, a member of the research team trained in academic detailing met virtually with each nurse coordinator, identified that individual’s barriers to SDM, and used the training materials to highlight messages to overcome those barriers; follow-up calls provided a forum for discussing progress and overcoming additional challenges. Although this article focused specifically on whole health and SDM, the conceptual alignment process strategy can be applied to other implementations of multiple initiatives.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. The National Academies Press; 2001. doi:10.17226/10027
- Bokhour BG, Haun JN, Hyde J, Charns M, Kligler B. Transforming the Veterans Affairs to a whole health system of care: time for action and research. Med Care. 2020;58:295- 300. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001316
- Elwyn G, Frosch D, Rollnick S. Dual equipoise shared decision making: definitions for decision and behaviour support interventions. Implement Sci. 2009;4:75. doi:7510.1186/1748-5908-4-75
- Bomhof-Roordink H, Gärtner FR, Stiggelbout AM, Pieterse AH. Key components of shared decision making models: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e031763. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031763
- Charles C, Gafni A, Whelan T. Decision-making in the physician- patient encounter: revisiting the shared treatment decision-making model. Soc Sci Med. 1999;49:651-661. doi:10.1016/s0277-9536(99)00145-8
- Moyer VA; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for lung cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160:330- 338. doi:10.7326/m13-2771
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Screening for lung cancer with low dose computed tomography (LDCT). February 10, 2022. Accessed February 7, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/ncacal-decision-memo.aspx?proposed=N&ncaid=304
- Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:395-409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
- Slatore CG, Wiener RS. Pulmonary nodules: a small problem for many, severe distress for some, and how to communicate about it. Chest. 2018;153:1004-1015. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2017.10.013
- Nishi SPE, Lowenstein LM, Mendoza TR, et al. Shared decision-making for lung cancer screening: how well are we “sharing”? Chest. 2021;160:330-340. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.01.041
- Wiener RS, Koppelman E, Bolton R, et al. Patient and clinician perspectives on shared decision-making in early adopting lung cancer screening programs: a qualitative study. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33:1035-1042. doi:10.1007/s11606-018-4350-9
- Melzer AC, Golden SE, Ono SS, Datta S, Triplette M, Slatore CG. “We just never have enough time”: clinician views of lung cancer screening processes and implementation. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-262OC
- Schwartz LM, Woloshin S, Fowler FJ Jr, Welch HG. Enthusiasm for cancer screening in the United States. JAMA. 2004;291:71-78. doi:10.1001/jama.291.1.71
- Lown BA, Rosen J, Marttila J. An agenda for improving compassionate care: a survey shows about half of patients say such care is missing. Health Aff (Millwood). 2011;30:1772-1778. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0539
- Scholl I, LaRussa A, Hahlweg P, Kobrin S, Elwyn G. Organizational- and system-level characteristics that influence implementation of shared decision-making and strategies to address them - a scoping review. Implement Sci. 2018;13:40. doi:10.1186/s13012-018-0731-z
- Khanna A, Fix GM, Anderson E, et al. Towards a framework for patient-centred care coordination: a scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e066808. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-066808
- Elwyn G, Durand MA, Song J, et al. A three-talk model for shared decision making: multistage consultation process. BMJ. 2017;359:j4891. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4891
- Makoul G, Clayman ML. An integrative model of shared decision making in medical encounters. Patient Educ Couns. 2006;60:301-312. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2005.06.010
- Whole Health. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The SHARE approach. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.ahrq.gov/health-literacy/professional-training/shared-decision/index.html
- Abadi MH, Barker AM, Rao SR, Orner M, Rychener D, Bokhour BG. Examining the impact of a peer-led group program for veteran engagement and well-being. J Altern Complement Med. 2021;27:S37-S44. doi:10.1089/acm.2020.0124
- Stacey D, Lewis KB, Smith M, et al. Decision aids for people facing health treatment or screening decisions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024;1:CD001431. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001431.pub6
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Patient Centered Care and Cultural Transformation. Personal health inventory. Revised April 2019. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/docs/10-773_PHI_July2019_508.pdf
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Build your personal health plan. Updated July 24, 2024. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/phi.asp
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. The National Academies Press; 2001. doi:10.17226/10027
- Bokhour BG, Haun JN, Hyde J, Charns M, Kligler B. Transforming the Veterans Affairs to a whole health system of care: time for action and research. Med Care. 2020;58:295- 300. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001316
- Elwyn G, Frosch D, Rollnick S. Dual equipoise shared decision making: definitions for decision and behaviour support interventions. Implement Sci. 2009;4:75. doi:7510.1186/1748-5908-4-75
- Bomhof-Roordink H, Gärtner FR, Stiggelbout AM, Pieterse AH. Key components of shared decision making models: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e031763. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031763
- Charles C, Gafni A, Whelan T. Decision-making in the physician- patient encounter: revisiting the shared treatment decision-making model. Soc Sci Med. 1999;49:651-661. doi:10.1016/s0277-9536(99)00145-8
- Moyer VA; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for lung cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160:330- 338. doi:10.7326/m13-2771
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Screening for lung cancer with low dose computed tomography (LDCT). February 10, 2022. Accessed February 7, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/ncacal-decision-memo.aspx?proposed=N&ncaid=304
- Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:395-409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
- Slatore CG, Wiener RS. Pulmonary nodules: a small problem for many, severe distress for some, and how to communicate about it. Chest. 2018;153:1004-1015. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2017.10.013
- Nishi SPE, Lowenstein LM, Mendoza TR, et al. Shared decision-making for lung cancer screening: how well are we “sharing”? Chest. 2021;160:330-340. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.01.041
- Wiener RS, Koppelman E, Bolton R, et al. Patient and clinician perspectives on shared decision-making in early adopting lung cancer screening programs: a qualitative study. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33:1035-1042. doi:10.1007/s11606-018-4350-9
- Melzer AC, Golden SE, Ono SS, Datta S, Triplette M, Slatore CG. “We just never have enough time”: clinician views of lung cancer screening processes and implementation. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-262OC
- Schwartz LM, Woloshin S, Fowler FJ Jr, Welch HG. Enthusiasm for cancer screening in the United States. JAMA. 2004;291:71-78. doi:10.1001/jama.291.1.71
- Lown BA, Rosen J, Marttila J. An agenda for improving compassionate care: a survey shows about half of patients say such care is missing. Health Aff (Millwood). 2011;30:1772-1778. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0539
- Scholl I, LaRussa A, Hahlweg P, Kobrin S, Elwyn G. Organizational- and system-level characteristics that influence implementation of shared decision-making and strategies to address them - a scoping review. Implement Sci. 2018;13:40. doi:10.1186/s13012-018-0731-z
- Khanna A, Fix GM, Anderson E, et al. Towards a framework for patient-centred care coordination: a scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e066808. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-066808
- Elwyn G, Durand MA, Song J, et al. A three-talk model for shared decision making: multistage consultation process. BMJ. 2017;359:j4891. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4891
- Makoul G, Clayman ML. An integrative model of shared decision making in medical encounters. Patient Educ Couns. 2006;60:301-312. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2005.06.010
- Whole Health. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The SHARE approach. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.ahrq.gov/health-literacy/professional-training/shared-decision/index.html
- Abadi MH, Barker AM, Rao SR, Orner M, Rychener D, Bokhour BG. Examining the impact of a peer-led group program for veteran engagement and well-being. J Altern Complement Med. 2021;27:S37-S44. doi:10.1089/acm.2020.0124
- Stacey D, Lewis KB, Smith M, et al. Decision aids for people facing health treatment or screening decisions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024;1:CD001431. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001431.pub6
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Patient Centered Care and Cultural Transformation. Personal health inventory. Revised April 2019. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/docs/10-773_PHI_July2019_508.pdf
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Build your personal health plan. Updated July 24, 2024. Accessed April 14, 2025. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth/phi.asp
When Patient-Centered Care Initiatives Align: Integrating VA Whole Health and Shared Decision-Making for Lung Cancer Screening
When Patient-Centered Care Initiatives Align: Integrating VA Whole Health and Shared Decision-Making for Lung Cancer Screening
PharmDs, Not MDs, RNs in VA Hiring Freeze Exemption List
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has outlined > 300,000 exemptions to the federal hiring freeze to fill essential benefits and health positions. The exempted positions are primarily medical support staff. While the exemptions include pharmacists, physicians and nurses were not included. The day after taking office for the second time, President Trump signed an Executive Order implementing a “freeze on the hiring of Federal civilian employees, to be applied throughout the executive branch” but left many of the details to individual agencies.
Set to last 90 days, the hiring freeze forced Federal agencies to develop plans to reduce the size of their workforces through efficiencies and attrition, Trump said. These agencies would also not be able to hire contractors.
Three days later, however, the VA responded “Following successful implementation of President Trump’s federal hiring freeze, the Department of Veterans Affairs announced several exemptions to the policy. These exemptions clarify the department’s ability to continue filling essential positions that provide health care and other vital services to Veterans and VA beneficiaries.”
This allowed > 304,000 jobs to be exempt from the freeze. Almost 92% of the VA’s 450,000 employees work in health care and health administration and support services. Most of the exemptions involve support staff. No physicians, mental health professionals or nursing positions are on the list. However, it does include 12,622 pharmacists and 5,975 pharmacy technicians.
The VA worked in accordance with the White House and Office of Personnel Management to develop the updated guidance, Acting Veterans Affairs Secretary Todd Hunter said. In a Jan. 21 memo, Hunter wrote: "Positions critical to delivering care to veterans in the Veteran[s] Health Administration ... are exempted under the category of public safety.”
According to Hunter's memo, no other vacancies that existed as of midday Monday will be filled. Candidates who received job offers before noon on Jan. 20 and have a start date on or before Feb. 8 will be onboarded, while those with a start date after Feb. 8—or one that is undetermined—will have their offers rescinded.
The first Trump Administration began the same way in 2017, initiating a freeze on Federal hiring and receiving a similar response from the VA. In 2017, the hiring of doctors and nurses continued while that freeze was in effect, but onboarding of new support and administrative staff was not. Then-Secretary of Veterans Affairs Dr. David J. Shulkin said, “VA is committed to serving veterans, but at the same time improving efficiency and reducing bureaucracy.”
The current Executive Order states it “shall not adversely impact veterans’ benefits and does not apply to positions related to public safety” (or military personnel, immigration enforcement, and national security). It also says it does not adversely impact the provision of Social Security, Medicare, or Veterans’ benefits.
“Under President Trump’s leadership, VA will always do what is necessary to provide America’s Veterans with the benefits and services they have earned. The targeted hiring-freeze exemptions announced today underscore that fact,” said VA Director of Media Affairs Morgan Ackley.
Some in Congress feel the VA should be doing more, though, and are pushing for an exemption of all VA employees. On Friday, Senate Veterans’ Affairs Committee Ranking Member Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) released a statement on the exemptions. “The latest Administration hiring freeze announcement still falls short. While I’m encouraged the President responded to our concerns by exempting certain VA personnel, only a clear, unequivocal statement to exempt all VA employees from the hiring freeze will reassure me—and veterans—they will receive the care and benefits they need and deserve. The exemptions listed yesterday provide more questions than answers and fail to include key personnel, including Veterans Benefits Administration employees. The Trump Administration is going to try to confuse the issue with a lot of vague assurances. We need a clear commitment every VA employee is exempt—effective immediately. Moreover, the Trump Administration must address the offers it has already rescinded that are now exempt.”
Blumenthal and 24 Democratic Senators also signed a letter to that effect, stressing concerns about the negative impact the hiring freeze will have on the delivery of veterans’ health care and benefits nationwide “if not quickly reversed.” Blumenthal also pressed Doug Collins (R-GA), Trump’s nominee for VA Secretary, to push back against a hiring freeze at VA, if his nomination is confirmed: “This is going to be a first test of your leadership.”
“We’ll take a look at the current levels of employees that we have and where they’re properly located,” Collins said, adding that he was “still examining” the freeze’s impact on the VA. “We will work under the Executive Order [Trump] has given us.”
Blumenthal argued that the new exemptions exclude a number of critical positions at VA. Among them include all positions at the Veterans Benefits Administration and National Cemetery Administration, which provide veterans’ claims processing, survivor benefits, GI Bill education benefits, and burial scheduling and operations; many nonclinical positions critical to VA hospital functioning, including patient advocates, food service workers, and chaplains; and positions relating to construction project management for new hospitals and clinics, new nursing homes, new cemetery construction, leases, and repairs to existing VA facilities.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has outlined > 300,000 exemptions to the federal hiring freeze to fill essential benefits and health positions. The exempted positions are primarily medical support staff. While the exemptions include pharmacists, physicians and nurses were not included. The day after taking office for the second time, President Trump signed an Executive Order implementing a “freeze on the hiring of Federal civilian employees, to be applied throughout the executive branch” but left many of the details to individual agencies.
Set to last 90 days, the hiring freeze forced Federal agencies to develop plans to reduce the size of their workforces through efficiencies and attrition, Trump said. These agencies would also not be able to hire contractors.
Three days later, however, the VA responded “Following successful implementation of President Trump’s federal hiring freeze, the Department of Veterans Affairs announced several exemptions to the policy. These exemptions clarify the department’s ability to continue filling essential positions that provide health care and other vital services to Veterans and VA beneficiaries.”
This allowed > 304,000 jobs to be exempt from the freeze. Almost 92% of the VA’s 450,000 employees work in health care and health administration and support services. Most of the exemptions involve support staff. No physicians, mental health professionals or nursing positions are on the list. However, it does include 12,622 pharmacists and 5,975 pharmacy technicians.
The VA worked in accordance with the White House and Office of Personnel Management to develop the updated guidance, Acting Veterans Affairs Secretary Todd Hunter said. In a Jan. 21 memo, Hunter wrote: "Positions critical to delivering care to veterans in the Veteran[s] Health Administration ... are exempted under the category of public safety.”
According to Hunter's memo, no other vacancies that existed as of midday Monday will be filled. Candidates who received job offers before noon on Jan. 20 and have a start date on or before Feb. 8 will be onboarded, while those with a start date after Feb. 8—or one that is undetermined—will have their offers rescinded.
The first Trump Administration began the same way in 2017, initiating a freeze on Federal hiring and receiving a similar response from the VA. In 2017, the hiring of doctors and nurses continued while that freeze was in effect, but onboarding of new support and administrative staff was not. Then-Secretary of Veterans Affairs Dr. David J. Shulkin said, “VA is committed to serving veterans, but at the same time improving efficiency and reducing bureaucracy.”
The current Executive Order states it “shall not adversely impact veterans’ benefits and does not apply to positions related to public safety” (or military personnel, immigration enforcement, and national security). It also says it does not adversely impact the provision of Social Security, Medicare, or Veterans’ benefits.
“Under President Trump’s leadership, VA will always do what is necessary to provide America’s Veterans with the benefits and services they have earned. The targeted hiring-freeze exemptions announced today underscore that fact,” said VA Director of Media Affairs Morgan Ackley.
Some in Congress feel the VA should be doing more, though, and are pushing for an exemption of all VA employees. On Friday, Senate Veterans’ Affairs Committee Ranking Member Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) released a statement on the exemptions. “The latest Administration hiring freeze announcement still falls short. While I’m encouraged the President responded to our concerns by exempting certain VA personnel, only a clear, unequivocal statement to exempt all VA employees from the hiring freeze will reassure me—and veterans—they will receive the care and benefits they need and deserve. The exemptions listed yesterday provide more questions than answers and fail to include key personnel, including Veterans Benefits Administration employees. The Trump Administration is going to try to confuse the issue with a lot of vague assurances. We need a clear commitment every VA employee is exempt—effective immediately. Moreover, the Trump Administration must address the offers it has already rescinded that are now exempt.”
Blumenthal and 24 Democratic Senators also signed a letter to that effect, stressing concerns about the negative impact the hiring freeze will have on the delivery of veterans’ health care and benefits nationwide “if not quickly reversed.” Blumenthal also pressed Doug Collins (R-GA), Trump’s nominee for VA Secretary, to push back against a hiring freeze at VA, if his nomination is confirmed: “This is going to be a first test of your leadership.”
“We’ll take a look at the current levels of employees that we have and where they’re properly located,” Collins said, adding that he was “still examining” the freeze’s impact on the VA. “We will work under the Executive Order [Trump] has given us.”
Blumenthal argued that the new exemptions exclude a number of critical positions at VA. Among them include all positions at the Veterans Benefits Administration and National Cemetery Administration, which provide veterans’ claims processing, survivor benefits, GI Bill education benefits, and burial scheduling and operations; many nonclinical positions critical to VA hospital functioning, including patient advocates, food service workers, and chaplains; and positions relating to construction project management for new hospitals and clinics, new nursing homes, new cemetery construction, leases, and repairs to existing VA facilities.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has outlined > 300,000 exemptions to the federal hiring freeze to fill essential benefits and health positions. The exempted positions are primarily medical support staff. While the exemptions include pharmacists, physicians and nurses were not included. The day after taking office for the second time, President Trump signed an Executive Order implementing a “freeze on the hiring of Federal civilian employees, to be applied throughout the executive branch” but left many of the details to individual agencies.
Set to last 90 days, the hiring freeze forced Federal agencies to develop plans to reduce the size of their workforces through efficiencies and attrition, Trump said. These agencies would also not be able to hire contractors.
Three days later, however, the VA responded “Following successful implementation of President Trump’s federal hiring freeze, the Department of Veterans Affairs announced several exemptions to the policy. These exemptions clarify the department’s ability to continue filling essential positions that provide health care and other vital services to Veterans and VA beneficiaries.”
This allowed > 304,000 jobs to be exempt from the freeze. Almost 92% of the VA’s 450,000 employees work in health care and health administration and support services. Most of the exemptions involve support staff. No physicians, mental health professionals or nursing positions are on the list. However, it does include 12,622 pharmacists and 5,975 pharmacy technicians.
The VA worked in accordance with the White House and Office of Personnel Management to develop the updated guidance, Acting Veterans Affairs Secretary Todd Hunter said. In a Jan. 21 memo, Hunter wrote: "Positions critical to delivering care to veterans in the Veteran[s] Health Administration ... are exempted under the category of public safety.”
According to Hunter's memo, no other vacancies that existed as of midday Monday will be filled. Candidates who received job offers before noon on Jan. 20 and have a start date on or before Feb. 8 will be onboarded, while those with a start date after Feb. 8—or one that is undetermined—will have their offers rescinded.
The first Trump Administration began the same way in 2017, initiating a freeze on Federal hiring and receiving a similar response from the VA. In 2017, the hiring of doctors and nurses continued while that freeze was in effect, but onboarding of new support and administrative staff was not. Then-Secretary of Veterans Affairs Dr. David J. Shulkin said, “VA is committed to serving veterans, but at the same time improving efficiency and reducing bureaucracy.”
The current Executive Order states it “shall not adversely impact veterans’ benefits and does not apply to positions related to public safety” (or military personnel, immigration enforcement, and national security). It also says it does not adversely impact the provision of Social Security, Medicare, or Veterans’ benefits.
“Under President Trump’s leadership, VA will always do what is necessary to provide America’s Veterans with the benefits and services they have earned. The targeted hiring-freeze exemptions announced today underscore that fact,” said VA Director of Media Affairs Morgan Ackley.
Some in Congress feel the VA should be doing more, though, and are pushing for an exemption of all VA employees. On Friday, Senate Veterans’ Affairs Committee Ranking Member Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) released a statement on the exemptions. “The latest Administration hiring freeze announcement still falls short. While I’m encouraged the President responded to our concerns by exempting certain VA personnel, only a clear, unequivocal statement to exempt all VA employees from the hiring freeze will reassure me—and veterans—they will receive the care and benefits they need and deserve. The exemptions listed yesterday provide more questions than answers and fail to include key personnel, including Veterans Benefits Administration employees. The Trump Administration is going to try to confuse the issue with a lot of vague assurances. We need a clear commitment every VA employee is exempt—effective immediately. Moreover, the Trump Administration must address the offers it has already rescinded that are now exempt.”
Blumenthal and 24 Democratic Senators also signed a letter to that effect, stressing concerns about the negative impact the hiring freeze will have on the delivery of veterans’ health care and benefits nationwide “if not quickly reversed.” Blumenthal also pressed Doug Collins (R-GA), Trump’s nominee for VA Secretary, to push back against a hiring freeze at VA, if his nomination is confirmed: “This is going to be a first test of your leadership.”
“We’ll take a look at the current levels of employees that we have and where they’re properly located,” Collins said, adding that he was “still examining” the freeze’s impact on the VA. “We will work under the Executive Order [Trump] has given us.”
Blumenthal argued that the new exemptions exclude a number of critical positions at VA. Among them include all positions at the Veterans Benefits Administration and National Cemetery Administration, which provide veterans’ claims processing, survivor benefits, GI Bill education benefits, and burial scheduling and operations; many nonclinical positions critical to VA hospital functioning, including patient advocates, food service workers, and chaplains; and positions relating to construction project management for new hospitals and clinics, new nursing homes, new cemetery construction, leases, and repairs to existing VA facilities.
Emergency Presentations for Vets with CRC Linked to Higher Mortality
TOPLINE: More than 28% of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients with colorectal cancer were diagnosed through emergency presentations, which were associated with a higher mortality risk. Emergency presentations increased during COVID-19 from prepandemic rates.
METHODOLOGY:
- A retrospective cohort study analyzed 9096 incident colorectal cancer cancer cases diagnosed in the Veterans Health Administration from 2017 to 2021.
- Researchers applied a validated algorithm to identify emergency presentations, defined as cancer diagnoses within 30 days following emergency care episodes or unplanned hospital admissions.
- Analysis utilized multivariable logistic regression and Cox proportional hazards models to examine associations between emergency presentations and cancer stage, treatment, and mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with emergency presentations were more likely to have advanced stage disease (odds ratio [OR], 1.70; 95% CI, 1.53-1.88) compared to those without emergency presentations.
- Emergency presentations were associated with lower likelihood of receiving cancer treatment (OR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.56-0.75) and higher mortality risk (hazard ratio [HR], 1.70; 95% CI, 1.56-1.84).
- The proportion of emergency presentations increased from 26.4% in 2017-2019 to 31.4% during the COVID-19 pandemic years 2020-2021 (P < .0001).
IN PRACTICE: " Our findings from one of the largest studies within a US population to examine emergency presentations among patients with colorectal cancer show that emergency presentations are common and an important negative predictor of cancer outcomes…Our study findings highlight the need for continued research and implementation efforts focused on measurement and mitigation of emergency presentations among patients with colorectal cancer.”
SOURCE: The study was led by the Center for Innovations in Quality, Effectiveness and Safety at Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. It was published online on December 11 in Digestive Diseases and Sciences.
LIMITATIONS: The study's findings are limited by the predominantly male veteran population with lower socioeconomic status, which may affect generalizability. The equal access health care model used by the VA and its and strong screening programs may result in emergency presentation rates that differ from the private sector.
TOPLINE: More than 28% of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients with colorectal cancer were diagnosed through emergency presentations, which were associated with a higher mortality risk. Emergency presentations increased during COVID-19 from prepandemic rates.
METHODOLOGY:
- A retrospective cohort study analyzed 9096 incident colorectal cancer cancer cases diagnosed in the Veterans Health Administration from 2017 to 2021.
- Researchers applied a validated algorithm to identify emergency presentations, defined as cancer diagnoses within 30 days following emergency care episodes or unplanned hospital admissions.
- Analysis utilized multivariable logistic regression and Cox proportional hazards models to examine associations between emergency presentations and cancer stage, treatment, and mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with emergency presentations were more likely to have advanced stage disease (odds ratio [OR], 1.70; 95% CI, 1.53-1.88) compared to those without emergency presentations.
- Emergency presentations were associated with lower likelihood of receiving cancer treatment (OR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.56-0.75) and higher mortality risk (hazard ratio [HR], 1.70; 95% CI, 1.56-1.84).
- The proportion of emergency presentations increased from 26.4% in 2017-2019 to 31.4% during the COVID-19 pandemic years 2020-2021 (P < .0001).
IN PRACTICE: " Our findings from one of the largest studies within a US population to examine emergency presentations among patients with colorectal cancer show that emergency presentations are common and an important negative predictor of cancer outcomes…Our study findings highlight the need for continued research and implementation efforts focused on measurement and mitigation of emergency presentations among patients with colorectal cancer.”
SOURCE: The study was led by the Center for Innovations in Quality, Effectiveness and Safety at Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. It was published online on December 11 in Digestive Diseases and Sciences.
LIMITATIONS: The study's findings are limited by the predominantly male veteran population with lower socioeconomic status, which may affect generalizability. The equal access health care model used by the VA and its and strong screening programs may result in emergency presentation rates that differ from the private sector.
TOPLINE: More than 28% of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients with colorectal cancer were diagnosed through emergency presentations, which were associated with a higher mortality risk. Emergency presentations increased during COVID-19 from prepandemic rates.
METHODOLOGY:
- A retrospective cohort study analyzed 9096 incident colorectal cancer cancer cases diagnosed in the Veterans Health Administration from 2017 to 2021.
- Researchers applied a validated algorithm to identify emergency presentations, defined as cancer diagnoses within 30 days following emergency care episodes or unplanned hospital admissions.
- Analysis utilized multivariable logistic regression and Cox proportional hazards models to examine associations between emergency presentations and cancer stage, treatment, and mortality.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with emergency presentations were more likely to have advanced stage disease (odds ratio [OR], 1.70; 95% CI, 1.53-1.88) compared to those without emergency presentations.
- Emergency presentations were associated with lower likelihood of receiving cancer treatment (OR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.56-0.75) and higher mortality risk (hazard ratio [HR], 1.70; 95% CI, 1.56-1.84).
- The proportion of emergency presentations increased from 26.4% in 2017-2019 to 31.4% during the COVID-19 pandemic years 2020-2021 (P < .0001).
IN PRACTICE: " Our findings from one of the largest studies within a US population to examine emergency presentations among patients with colorectal cancer show that emergency presentations are common and an important negative predictor of cancer outcomes…Our study findings highlight the need for continued research and implementation efforts focused on measurement and mitigation of emergency presentations among patients with colorectal cancer.”
SOURCE: The study was led by the Center for Innovations in Quality, Effectiveness and Safety at Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. It was published online on December 11 in Digestive Diseases and Sciences.
LIMITATIONS: The study's findings are limited by the predominantly male veteran population with lower socioeconomic status, which may affect generalizability. The equal access health care model used by the VA and its and strong screening programs may result in emergency presentation rates that differ from the private sector.
Agent Orange and Uranium Exposures Associated With Bladder Cancer Risk in Veterans
Exposure to Agent Orange and depleted urology are associated with increased risk of bladder cancer, according to a recent Urology meta-analysis. About 3200 US veterans are diagnosed with bladder cancer each year, which is the fourth most diagnosed cancer among veterans. “Identifying veterans exposed to these risk factors is crucial for implementing screening protocols and connecting them with preventive healthcare measures when possible,” the authors said.
A meta-analysis using narrative synthesis to incorporate diverse studies examined the impact of exposure to Agent Orange, depleted uranium exposure, contaminated drinking water, and other environmental contaminants. The researchers found 7 studies of Agent Orange exposure that in total showed a statistically significant increase in bladder cancer risk (hazard ratio [HR], 1.17; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01-1.36; P < .001) among 2,705,283 veterans. Six studies revealed that depleted uranium exposure caused a statistically significant association with bladder cancer as well (HR, 2.13; 95% CI, 1.31-3.48; P = .002) among 28,899 patients. Exposure to contaminated drinking water exposure in 4 studies also suggested an increased bladder cancer risk (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.97-1.61; P = .08) among 370,408 veterans.
The authors identified other factors that also contributed to increased bladder cancer risk, including smoking, occupational exposures to substances like asbestos and diesel fumes, and exposure to ionizing radiation from nuclear tests. “These findings emphasize the urgent need for enhanced clinical management strategies and preventive measures for veterans exposed to these carcinogenic agents,” the authors asserted.
The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
Exposure to Agent Orange and depleted urology are associated with increased risk of bladder cancer, according to a recent Urology meta-analysis. About 3200 US veterans are diagnosed with bladder cancer each year, which is the fourth most diagnosed cancer among veterans. “Identifying veterans exposed to these risk factors is crucial for implementing screening protocols and connecting them with preventive healthcare measures when possible,” the authors said.
A meta-analysis using narrative synthesis to incorporate diverse studies examined the impact of exposure to Agent Orange, depleted uranium exposure, contaminated drinking water, and other environmental contaminants. The researchers found 7 studies of Agent Orange exposure that in total showed a statistically significant increase in bladder cancer risk (hazard ratio [HR], 1.17; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01-1.36; P < .001) among 2,705,283 veterans. Six studies revealed that depleted uranium exposure caused a statistically significant association with bladder cancer as well (HR, 2.13; 95% CI, 1.31-3.48; P = .002) among 28,899 patients. Exposure to contaminated drinking water exposure in 4 studies also suggested an increased bladder cancer risk (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.97-1.61; P = .08) among 370,408 veterans.
The authors identified other factors that also contributed to increased bladder cancer risk, including smoking, occupational exposures to substances like asbestos and diesel fumes, and exposure to ionizing radiation from nuclear tests. “These findings emphasize the urgent need for enhanced clinical management strategies and preventive measures for veterans exposed to these carcinogenic agents,” the authors asserted.
The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
Exposure to Agent Orange and depleted urology are associated with increased risk of bladder cancer, according to a recent Urology meta-analysis. About 3200 US veterans are diagnosed with bladder cancer each year, which is the fourth most diagnosed cancer among veterans. “Identifying veterans exposed to these risk factors is crucial for implementing screening protocols and connecting them with preventive healthcare measures when possible,” the authors said.
A meta-analysis using narrative synthesis to incorporate diverse studies examined the impact of exposure to Agent Orange, depleted uranium exposure, contaminated drinking water, and other environmental contaminants. The researchers found 7 studies of Agent Orange exposure that in total showed a statistically significant increase in bladder cancer risk (hazard ratio [HR], 1.17; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01-1.36; P < .001) among 2,705,283 veterans. Six studies revealed that depleted uranium exposure caused a statistically significant association with bladder cancer as well (HR, 2.13; 95% CI, 1.31-3.48; P = .002) among 28,899 patients. Exposure to contaminated drinking water exposure in 4 studies also suggested an increased bladder cancer risk (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.97-1.61; P = .08) among 370,408 veterans.
The authors identified other factors that also contributed to increased bladder cancer risk, including smoking, occupational exposures to substances like asbestos and diesel fumes, and exposure to ionizing radiation from nuclear tests. “These findings emphasize the urgent need for enhanced clinical management strategies and preventive measures for veterans exposed to these carcinogenic agents,” the authors asserted.
The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
VA Pays Billions for Costs Shifted From Medicare
In Fiscal Year (FY) 2023, > 40% of veterans enrolled by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) received care from private practice, mainly for emergency services. Costs associated with that care have shifted from Medicare to the VA to the tune of billions of dollars, according to a recent study published in JAMA Health Forum.
The expenses are a result of the Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Integrated Outside Networks (MISSION) Act of 2018, which established the Veterans Community Care Program (VCCP) and allowed the VA to contract with private clinicians. This provided veterans enrolled in both the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and Medicare to have 2 government sources of health care financing. The VHA is billed if the veteran receives care at one of its facilities or is referred to a community facility; Medicare is billed only if the veteran is treated for a service not covered by VHA.
These shifts are concerning, according to Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, and Said Ibrahim, MD, MPH. In an accompanying editorial, they outline how the changes affect whether VHA care will have adequate funding to provide care for the additional 740,000 enrollees who have entered the system in the past 2 years.
“This has created a $12 billion medical care budget shortfall for FY 2024,” Kizer and Ibrahim argue. The resulting “substantial budgetary tumult … is adversely impacting the front lines of care delivery at individual VA facilities, leading to delays in hiring caregivers and impeding access to VA care and timely care delivery, as well as greatly straining the traditional roles of VA staff and clinicians trying to manage the challenging cross-system referral processes.”
The study calculated the number of yearly emergency department (ED) visits per 1000 veterans in Medicare overall and by VA ED visits, VA-purchased community ED visits, and Medicare-purchased community ED visits. Estimated total costs shifted from Medicare to the VA after the MISSION Act between 2016 and 2021 were then calculated.
Of the 4,960,189 VA and Medicare enrollees in 2016, 37.0% presented to the ED at least once. Of the 4,837,436 dual enrollees in 2021, 37.6% presented to the ED at least once. ED visits increased 8%, from 820 per 1000 veterans in 2016, to 886 per 1000 veterans in 2019. The COVID-19 pandemic caused a dip in ED visits in 2020 by veterans (769 per 1000), but the number rose 2021 (852 per 1000 veterans).
Between 2016 and 2021, the percentage of VA-purchased community ED visits more than doubled, from 8.0% to 21.1%, while Medicare-purchased community ED visits dropped from 65.2% to 52.6%. Patterns were similar among veterans enrolled in traditional Medicare vs Medicare Advantage (MA). The study estimated that in 2021 at least $2 billion of VA community ED spending was due to payer shift from Medicare.
The shift is “particularly concerning” among veterans enrolled in MA since insurance plans receive capitated payments regardless of actual use of VA- or Medicare-covered services. However, the study’s observational design “limited our ability to infer causality between MISSION Act implementation and payer change.”
The cost shifting is “symptomatic of the fiscally undisciplined implementation of the VCCP and the lack of financially sound policy on payment for VA-Medicare dual enrollees,” according to Drs. Kizer and Ibrahim. “Addressing this matter seems especially important in light of numerous studies showing that the quality of community care often may be inferior to VA care, as well as less timely.”
Kizer and Ibrahim point out that when a veteran who is jointly enrolled in VA and MA plans receives care from the VA, the VA incurs the cost of providing those services even though the MA plan is being paid to provide them. The VA is not allowed to recoup its costs from Medicare. Thus, the government pays twice for the care of the same person.
A recent study reported > $78 billion in duplicate VA-MA spending between 2011 and 2020, with $12 billion in FY 2020. Kizer and Ibrahim suggest the current VA-MA duplicate spending is likely to be significantly more than the reported amounts.
“[No] evidence shows that this duplicate spending yields a demonstrable health benefit for veterans, although undoubtedly it benefits the financial well-being of the MA plans,” they write.
It’s a “challenging policy and programmatic conundrum,” the co-authors say, noting that eligible veterans often have military service-related conditions that the VA is uniquely experienced in treating.
“Policies and programs need to be designed and aligned to ensure that veterans have timely access to emergency and other services and that rising community care costs do not jeopardize veterans’ choice to access and use VA services, nor compromise the nationally vital roles of the VA in graduate medical education and other health professional training, research, and emergency preparedness.”
In Fiscal Year (FY) 2023, > 40% of veterans enrolled by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) received care from private practice, mainly for emergency services. Costs associated with that care have shifted from Medicare to the VA to the tune of billions of dollars, according to a recent study published in JAMA Health Forum.
The expenses are a result of the Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Integrated Outside Networks (MISSION) Act of 2018, which established the Veterans Community Care Program (VCCP) and allowed the VA to contract with private clinicians. This provided veterans enrolled in both the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and Medicare to have 2 government sources of health care financing. The VHA is billed if the veteran receives care at one of its facilities or is referred to a community facility; Medicare is billed only if the veteran is treated for a service not covered by VHA.
These shifts are concerning, according to Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, and Said Ibrahim, MD, MPH. In an accompanying editorial, they outline how the changes affect whether VHA care will have adequate funding to provide care for the additional 740,000 enrollees who have entered the system in the past 2 years.
“This has created a $12 billion medical care budget shortfall for FY 2024,” Kizer and Ibrahim argue. The resulting “substantial budgetary tumult … is adversely impacting the front lines of care delivery at individual VA facilities, leading to delays in hiring caregivers and impeding access to VA care and timely care delivery, as well as greatly straining the traditional roles of VA staff and clinicians trying to manage the challenging cross-system referral processes.”
The study calculated the number of yearly emergency department (ED) visits per 1000 veterans in Medicare overall and by VA ED visits, VA-purchased community ED visits, and Medicare-purchased community ED visits. Estimated total costs shifted from Medicare to the VA after the MISSION Act between 2016 and 2021 were then calculated.
Of the 4,960,189 VA and Medicare enrollees in 2016, 37.0% presented to the ED at least once. Of the 4,837,436 dual enrollees in 2021, 37.6% presented to the ED at least once. ED visits increased 8%, from 820 per 1000 veterans in 2016, to 886 per 1000 veterans in 2019. The COVID-19 pandemic caused a dip in ED visits in 2020 by veterans (769 per 1000), but the number rose 2021 (852 per 1000 veterans).
Between 2016 and 2021, the percentage of VA-purchased community ED visits more than doubled, from 8.0% to 21.1%, while Medicare-purchased community ED visits dropped from 65.2% to 52.6%. Patterns were similar among veterans enrolled in traditional Medicare vs Medicare Advantage (MA). The study estimated that in 2021 at least $2 billion of VA community ED spending was due to payer shift from Medicare.
The shift is “particularly concerning” among veterans enrolled in MA since insurance plans receive capitated payments regardless of actual use of VA- or Medicare-covered services. However, the study’s observational design “limited our ability to infer causality between MISSION Act implementation and payer change.”
The cost shifting is “symptomatic of the fiscally undisciplined implementation of the VCCP and the lack of financially sound policy on payment for VA-Medicare dual enrollees,” according to Drs. Kizer and Ibrahim. “Addressing this matter seems especially important in light of numerous studies showing that the quality of community care often may be inferior to VA care, as well as less timely.”
Kizer and Ibrahim point out that when a veteran who is jointly enrolled in VA and MA plans receives care from the VA, the VA incurs the cost of providing those services even though the MA plan is being paid to provide them. The VA is not allowed to recoup its costs from Medicare. Thus, the government pays twice for the care of the same person.
A recent study reported > $78 billion in duplicate VA-MA spending between 2011 and 2020, with $12 billion in FY 2020. Kizer and Ibrahim suggest the current VA-MA duplicate spending is likely to be significantly more than the reported amounts.
“[No] evidence shows that this duplicate spending yields a demonstrable health benefit for veterans, although undoubtedly it benefits the financial well-being of the MA plans,” they write.
It’s a “challenging policy and programmatic conundrum,” the co-authors say, noting that eligible veterans often have military service-related conditions that the VA is uniquely experienced in treating.
“Policies and programs need to be designed and aligned to ensure that veterans have timely access to emergency and other services and that rising community care costs do not jeopardize veterans’ choice to access and use VA services, nor compromise the nationally vital roles of the VA in graduate medical education and other health professional training, research, and emergency preparedness.”
In Fiscal Year (FY) 2023, > 40% of veterans enrolled by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) received care from private practice, mainly for emergency services. Costs associated with that care have shifted from Medicare to the VA to the tune of billions of dollars, according to a recent study published in JAMA Health Forum.
The expenses are a result of the Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Integrated Outside Networks (MISSION) Act of 2018, which established the Veterans Community Care Program (VCCP) and allowed the VA to contract with private clinicians. This provided veterans enrolled in both the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and Medicare to have 2 government sources of health care financing. The VHA is billed if the veteran receives care at one of its facilities or is referred to a community facility; Medicare is billed only if the veteran is treated for a service not covered by VHA.
These shifts are concerning, according to Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, and Said Ibrahim, MD, MPH. In an accompanying editorial, they outline how the changes affect whether VHA care will have adequate funding to provide care for the additional 740,000 enrollees who have entered the system in the past 2 years.
“This has created a $12 billion medical care budget shortfall for FY 2024,” Kizer and Ibrahim argue. The resulting “substantial budgetary tumult … is adversely impacting the front lines of care delivery at individual VA facilities, leading to delays in hiring caregivers and impeding access to VA care and timely care delivery, as well as greatly straining the traditional roles of VA staff and clinicians trying to manage the challenging cross-system referral processes.”
The study calculated the number of yearly emergency department (ED) visits per 1000 veterans in Medicare overall and by VA ED visits, VA-purchased community ED visits, and Medicare-purchased community ED visits. Estimated total costs shifted from Medicare to the VA after the MISSION Act between 2016 and 2021 were then calculated.
Of the 4,960,189 VA and Medicare enrollees in 2016, 37.0% presented to the ED at least once. Of the 4,837,436 dual enrollees in 2021, 37.6% presented to the ED at least once. ED visits increased 8%, from 820 per 1000 veterans in 2016, to 886 per 1000 veterans in 2019. The COVID-19 pandemic caused a dip in ED visits in 2020 by veterans (769 per 1000), but the number rose 2021 (852 per 1000 veterans).
Between 2016 and 2021, the percentage of VA-purchased community ED visits more than doubled, from 8.0% to 21.1%, while Medicare-purchased community ED visits dropped from 65.2% to 52.6%. Patterns were similar among veterans enrolled in traditional Medicare vs Medicare Advantage (MA). The study estimated that in 2021 at least $2 billion of VA community ED spending was due to payer shift from Medicare.
The shift is “particularly concerning” among veterans enrolled in MA since insurance plans receive capitated payments regardless of actual use of VA- or Medicare-covered services. However, the study’s observational design “limited our ability to infer causality between MISSION Act implementation and payer change.”
The cost shifting is “symptomatic of the fiscally undisciplined implementation of the VCCP and the lack of financially sound policy on payment for VA-Medicare dual enrollees,” according to Drs. Kizer and Ibrahim. “Addressing this matter seems especially important in light of numerous studies showing that the quality of community care often may be inferior to VA care, as well as less timely.”
Kizer and Ibrahim point out that when a veteran who is jointly enrolled in VA and MA plans receives care from the VA, the VA incurs the cost of providing those services even though the MA plan is being paid to provide them. The VA is not allowed to recoup its costs from Medicare. Thus, the government pays twice for the care of the same person.
A recent study reported > $78 billion in duplicate VA-MA spending between 2011 and 2020, with $12 billion in FY 2020. Kizer and Ibrahim suggest the current VA-MA duplicate spending is likely to be significantly more than the reported amounts.
“[No] evidence shows that this duplicate spending yields a demonstrable health benefit for veterans, although undoubtedly it benefits the financial well-being of the MA plans,” they write.
It’s a “challenging policy and programmatic conundrum,” the co-authors say, noting that eligible veterans often have military service-related conditions that the VA is uniquely experienced in treating.
“Policies and programs need to be designed and aligned to ensure that veterans have timely access to emergency and other services and that rising community care costs do not jeopardize veterans’ choice to access and use VA services, nor compromise the nationally vital roles of the VA in graduate medical education and other health professional training, research, and emergency preparedness.”