User login
Daycare Providers’ Little Helper
It is no secret that we have a daycare problem in this country. Twenty percent of families spend more than $36,000 for child care annually. Three quarters of a single parent’s income is spent on infant care. The result is that more than $122 billion is syphoned out of our economy in lost productivity and income.
How we got into this situation is less clear. Women who once were stay-at-home moms have moved into the workplace. Families are more mobile and grandparents who had been a source of childcare may live hours away. And, when they are nearby grandparents may themselves been forced to remain employed for economic reasons.
Despite the increase demand the market has failed to respond with more daycare providers because with a median hourly wage of less than $15.00 it is difficult to attract applicants from a pool of potential employees that is already in great demand.
And, let’s be honest, long hours cooped up inside with infants and toddlers isn’t the right job for everyone. For the most successful, although maybe not financially, providing daycare is truly a labor of love. There are high school and community college courses taught on child development and day care management. Experienced providers can be a source of tips-of-the trade to those just starting out. But, when there are three infants crying, two diapers to be changed, and a toddler heading toward a tantrum, two experienced providers may not be enough to calm the turbulent waters.
A recent article in my local newspaper provided stark evidence of how serious our daycare situation has become. Although the daycare owner denies the allegation, the Department of Health and Human Service told the parents that the investigation currently supports their complaints that the children had been given melatonin gummies without their permission. Final action is pending but it is likely the daycare will lose its license. Not surprisingly the parents have already removed their children.
Curious about whether this situation was an isolated event, it didn’t take Google too long to find evidence of other daycares in which children had been given sleep-related medications without their parents’ permission. In May 2024 a daycare provider and three of her employees in Manchester, New Hampshire, were arrested and charged with endangering the welfare of a child after allegedly spiking their charges food with melatonin. Lest you think drugging infants in daycare is just a New England thing, my research found a news story dating back to 2003 that reported on several cases in which daycare providers had been administering diphenhydramine without parents permission. In one instance there was a fatal outcome. While melatonin does not pose a health risk on a par with diphenhydramine, the issue is the fact that the parents were not consulted.
I suspect that these two incidents in Maine and New Hampshire are not isolated events and melatonin has replaced diphenhydramine as the daycare provider’s “little helper” nationwide. It’s not clear how we as pediatricians can help police this practice, other than suggesting to parents that they initiate dialogues about napping strategies with their daycare providers. Not with an accusatory tone but more of a sharing about what tricks each party uses to make napping happen. It may be that the daycare provider has some valuable and sound advice that the parents can adapt to their home situation. However, if the daycare provider’s explanation for why the child naps well doesn’t sound right or the child is unusually drowsy after daycare visits they should share their concerns with us a pediatric health care advisors.
Dr Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
It is no secret that we have a daycare problem in this country. Twenty percent of families spend more than $36,000 for child care annually. Three quarters of a single parent’s income is spent on infant care. The result is that more than $122 billion is syphoned out of our economy in lost productivity and income.
How we got into this situation is less clear. Women who once were stay-at-home moms have moved into the workplace. Families are more mobile and grandparents who had been a source of childcare may live hours away. And, when they are nearby grandparents may themselves been forced to remain employed for economic reasons.
Despite the increase demand the market has failed to respond with more daycare providers because with a median hourly wage of less than $15.00 it is difficult to attract applicants from a pool of potential employees that is already in great demand.
And, let’s be honest, long hours cooped up inside with infants and toddlers isn’t the right job for everyone. For the most successful, although maybe not financially, providing daycare is truly a labor of love. There are high school and community college courses taught on child development and day care management. Experienced providers can be a source of tips-of-the trade to those just starting out. But, when there are three infants crying, two diapers to be changed, and a toddler heading toward a tantrum, two experienced providers may not be enough to calm the turbulent waters.
A recent article in my local newspaper provided stark evidence of how serious our daycare situation has become. Although the daycare owner denies the allegation, the Department of Health and Human Service told the parents that the investigation currently supports their complaints that the children had been given melatonin gummies without their permission. Final action is pending but it is likely the daycare will lose its license. Not surprisingly the parents have already removed their children.
Curious about whether this situation was an isolated event, it didn’t take Google too long to find evidence of other daycares in which children had been given sleep-related medications without their parents’ permission. In May 2024 a daycare provider and three of her employees in Manchester, New Hampshire, were arrested and charged with endangering the welfare of a child after allegedly spiking their charges food with melatonin. Lest you think drugging infants in daycare is just a New England thing, my research found a news story dating back to 2003 that reported on several cases in which daycare providers had been administering diphenhydramine without parents permission. In one instance there was a fatal outcome. While melatonin does not pose a health risk on a par with diphenhydramine, the issue is the fact that the parents were not consulted.
I suspect that these two incidents in Maine and New Hampshire are not isolated events and melatonin has replaced diphenhydramine as the daycare provider’s “little helper” nationwide. It’s not clear how we as pediatricians can help police this practice, other than suggesting to parents that they initiate dialogues about napping strategies with their daycare providers. Not with an accusatory tone but more of a sharing about what tricks each party uses to make napping happen. It may be that the daycare provider has some valuable and sound advice that the parents can adapt to their home situation. However, if the daycare provider’s explanation for why the child naps well doesn’t sound right or the child is unusually drowsy after daycare visits they should share their concerns with us a pediatric health care advisors.
Dr Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
It is no secret that we have a daycare problem in this country. Twenty percent of families spend more than $36,000 for child care annually. Three quarters of a single parent’s income is spent on infant care. The result is that more than $122 billion is syphoned out of our economy in lost productivity and income.
How we got into this situation is less clear. Women who once were stay-at-home moms have moved into the workplace. Families are more mobile and grandparents who had been a source of childcare may live hours away. And, when they are nearby grandparents may themselves been forced to remain employed for economic reasons.
Despite the increase demand the market has failed to respond with more daycare providers because with a median hourly wage of less than $15.00 it is difficult to attract applicants from a pool of potential employees that is already in great demand.
And, let’s be honest, long hours cooped up inside with infants and toddlers isn’t the right job for everyone. For the most successful, although maybe not financially, providing daycare is truly a labor of love. There are high school and community college courses taught on child development and day care management. Experienced providers can be a source of tips-of-the trade to those just starting out. But, when there are three infants crying, two diapers to be changed, and a toddler heading toward a tantrum, two experienced providers may not be enough to calm the turbulent waters.
A recent article in my local newspaper provided stark evidence of how serious our daycare situation has become. Although the daycare owner denies the allegation, the Department of Health and Human Service told the parents that the investigation currently supports their complaints that the children had been given melatonin gummies without their permission. Final action is pending but it is likely the daycare will lose its license. Not surprisingly the parents have already removed their children.
Curious about whether this situation was an isolated event, it didn’t take Google too long to find evidence of other daycares in which children had been given sleep-related medications without their parents’ permission. In May 2024 a daycare provider and three of her employees in Manchester, New Hampshire, were arrested and charged with endangering the welfare of a child after allegedly spiking their charges food with melatonin. Lest you think drugging infants in daycare is just a New England thing, my research found a news story dating back to 2003 that reported on several cases in which daycare providers had been administering diphenhydramine without parents permission. In one instance there was a fatal outcome. While melatonin does not pose a health risk on a par with diphenhydramine, the issue is the fact that the parents were not consulted.
I suspect that these two incidents in Maine and New Hampshire are not isolated events and melatonin has replaced diphenhydramine as the daycare provider’s “little helper” nationwide. It’s not clear how we as pediatricians can help police this practice, other than suggesting to parents that they initiate dialogues about napping strategies with their daycare providers. Not with an accusatory tone but more of a sharing about what tricks each party uses to make napping happen. It may be that the daycare provider has some valuable and sound advice that the parents can adapt to their home situation. However, if the daycare provider’s explanation for why the child naps well doesn’t sound right or the child is unusually drowsy after daycare visits they should share their concerns with us a pediatric health care advisors.
Dr Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Implementation Research: Simple Text Reminders Help Increase Vaccine Uptake
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I would like to briefly discuss a very interesting paper that appeared in Nature:“Megastudy Shows That Reminders Boost Vaccination but Adding Free Rides Does Not.”
Obviously, the paper has a provocative title. This is really an excellent example of what one might call implementation research, or quite frankly, what might work and what might not work in terms of having a very pragmatic goal. In this case, it was how do we get people to receive vaccinations.
This specific study looked at individuals who were scheduled to receive or were candidates to receive COVID-19 booster vaccinations. The question came up: If you gave them free rides to the location — this is obviously a high-risk population — would that increase the vaccination rate vs the other item that they were looking at here, which was potentially texting them to remind them?
The study very importantly and relevantly demonstrated, quite nicely, that offering free rides did not make a difference, but sending texts to remind them increased the 30-day vaccination rate in this population by 21%.
Again, it was a very pragmatic question that the trial addressed, and one might use this information in the future to increase the vaccination rate of a population where it is critical to do so. This type of research, which involves looking at very pragmatic questions and answering what is the optimal and most cost-effective way of doing it, should be encouraged.
I encourage you to look at this paper if you’re interested in this topic.
Markman, Professor of Medical Oncology and Therapeutics Research, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center; President, Medicine & Science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, Phoenix, has disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I would like to briefly discuss a very interesting paper that appeared in Nature:“Megastudy Shows That Reminders Boost Vaccination but Adding Free Rides Does Not.”
Obviously, the paper has a provocative title. This is really an excellent example of what one might call implementation research, or quite frankly, what might work and what might not work in terms of having a very pragmatic goal. In this case, it was how do we get people to receive vaccinations.
This specific study looked at individuals who were scheduled to receive or were candidates to receive COVID-19 booster vaccinations. The question came up: If you gave them free rides to the location — this is obviously a high-risk population — would that increase the vaccination rate vs the other item that they were looking at here, which was potentially texting them to remind them?
The study very importantly and relevantly demonstrated, quite nicely, that offering free rides did not make a difference, but sending texts to remind them increased the 30-day vaccination rate in this population by 21%.
Again, it was a very pragmatic question that the trial addressed, and one might use this information in the future to increase the vaccination rate of a population where it is critical to do so. This type of research, which involves looking at very pragmatic questions and answering what is the optimal and most cost-effective way of doing it, should be encouraged.
I encourage you to look at this paper if you’re interested in this topic.
Markman, Professor of Medical Oncology and Therapeutics Research, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center; President, Medicine & Science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, Phoenix, has disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I would like to briefly discuss a very interesting paper that appeared in Nature:“Megastudy Shows That Reminders Boost Vaccination but Adding Free Rides Does Not.”
Obviously, the paper has a provocative title. This is really an excellent example of what one might call implementation research, or quite frankly, what might work and what might not work in terms of having a very pragmatic goal. In this case, it was how do we get people to receive vaccinations.
This specific study looked at individuals who were scheduled to receive or were candidates to receive COVID-19 booster vaccinations. The question came up: If you gave them free rides to the location — this is obviously a high-risk population — would that increase the vaccination rate vs the other item that they were looking at here, which was potentially texting them to remind them?
The study very importantly and relevantly demonstrated, quite nicely, that offering free rides did not make a difference, but sending texts to remind them increased the 30-day vaccination rate in this population by 21%.
Again, it was a very pragmatic question that the trial addressed, and one might use this information in the future to increase the vaccination rate of a population where it is critical to do so. This type of research, which involves looking at very pragmatic questions and answering what is the optimal and most cost-effective way of doing it, should be encouraged.
I encourage you to look at this paper if you’re interested in this topic.
Markman, Professor of Medical Oncology and Therapeutics Research, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center; President, Medicine & Science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, Phoenix, has disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sports Injuries of the Hip in Primary Care
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.
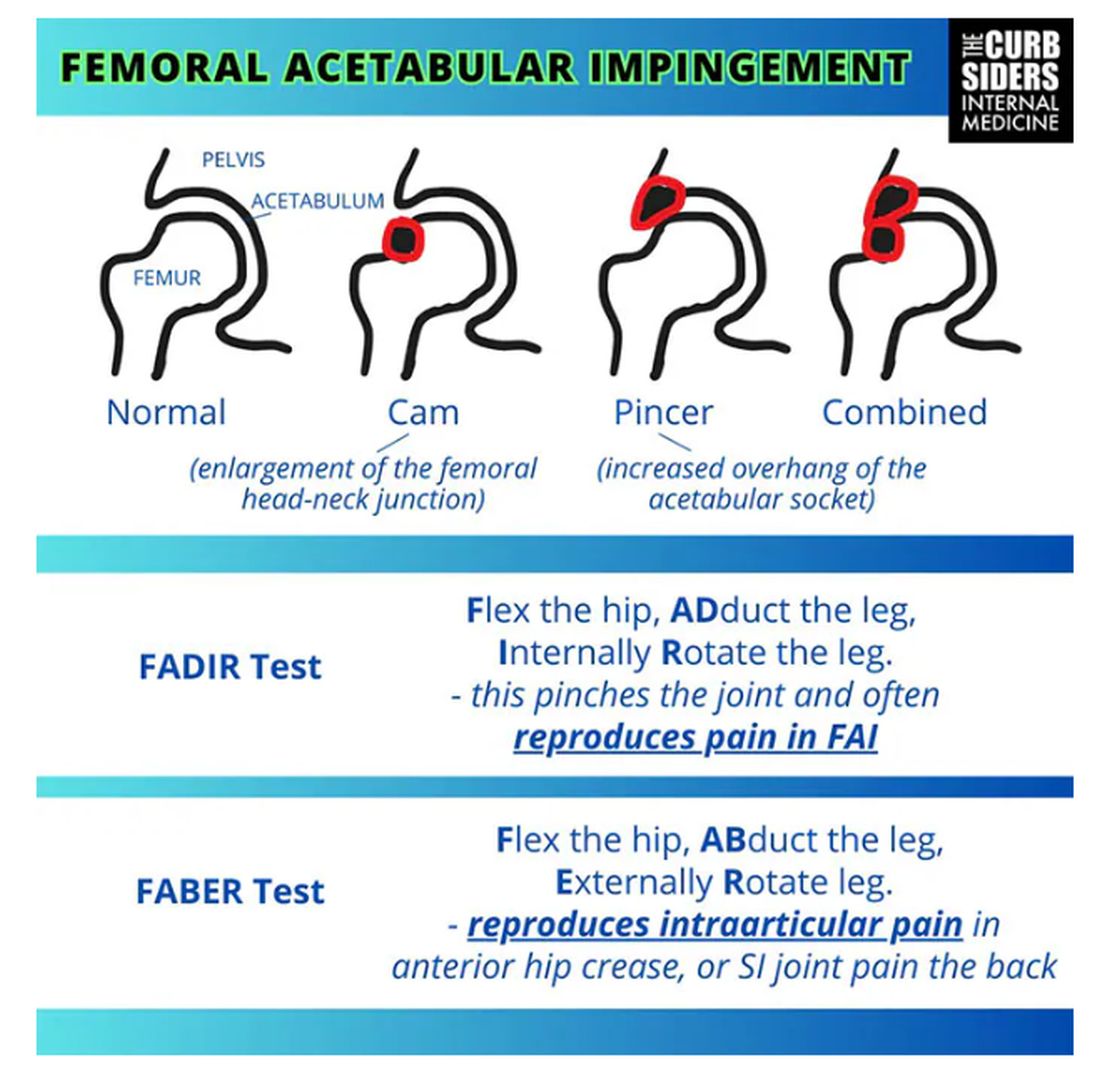
Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.
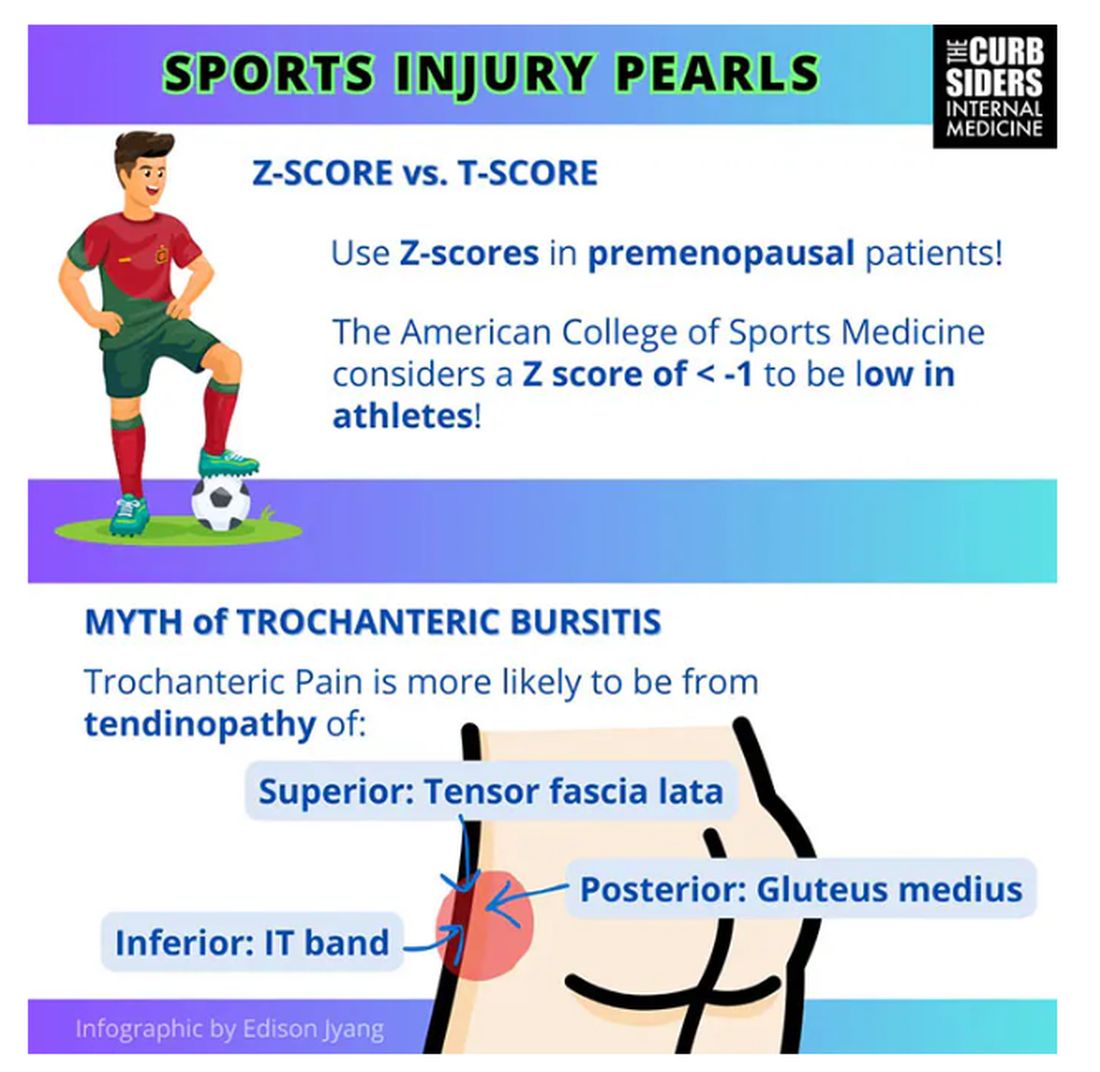
Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.

Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.

Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.

Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.

Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ADHD Myths
In the second half of the school year, you may find that there is a surge of families coming to appointments with concerns about school performance, wondering if their child has ADHD. We expect you are very familiar with this condition, both diagnosing and treating it. So this month we will offer “mythbusters” for ADHD: Responding to common misperceptions about ADHD with a summary of what the research has demonstrated as emerging facts, what is clearly fiction and what falls into the gray space between.
Demographics
A CDC survey of parents from 2022 indicates that 11.4% of children aged 3-17 have ever been diagnosed with ADHD in the United States. This is more than double the ADHD global prevalence of 5%, suggesting that there is overdiagnosis of this condition in this country. Boys are almost twice as likely to be diagnosed (14.5%) as girls (8%), and White children were more likely to be diagnosed than were Black and Hispanic children. The prevalence of ADHD diagnosis decreases as family income increases, and the condition is more frequently diagnosed in 12- to 17-year-olds than in children 11 and younger. The great majority of youth with an ADHD diagnosis (78%) have at least one co-occurring psychiatric condition. Of the children diagnosed with ADHD, slightly over half receive medication treatment (53.6%) whereas nearly a third (30.1%) receive no ADHD-specific treatment.
The Multimodal Treatment of ADHD Study (MTA), a large (600 children, aged 7-9 years), multicenter, longitudinal study of treatment outcomes for medication as well as behavioral and combination therapies demonstrated in every site that medication alone and combination therapy were significantly superior to intensive behavioral treatment alone and to routine community care in the reduction of ADHD symptoms. Of note, problems commonly associated with ADHD (parent-child conflict, anxiety symptoms, poor academic performance, and limited social skills) improved only with the combination treatment. This suggests that while core ADHD symptoms require medication, associated problems will also require behavioral treatment.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has a useful resource guide (healthychildren.org) highlighting the possible symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that should be investigated when considering this diagnosis. It is a clinical diagnosis, but screening instruments (such as the Vanderbilt) can be very helpful to identifying symptoms that should be present in more than one setting (home and school). While a child with ADHD can appear calm and focused when receiving direct one-to-one attention (as during a pediatrician’s appointment), symptoms may flourish in less structured or supervised settings. Sometimes parents are keen reporters of a child’s behaviors, but some loving (and exhausted) parents may overreact to a normal degree of inattention or disobedience. This can be especially true when a parent has a more detail-oriented temperament than the child, or with younger children and first-time parents. It is important to consider ADHD when you hear about social difficulties as well as academic ones, where there is a family history of ADHD or when a child is more impulsive, hyperactive, or inattentive than you would expect given their age and developmental stage. Confirm your clinical exam with teacher and parent reports. If the reports don’t line up or there are persistent learning problems in school, consider neuropsychological testing to root out a learning disability.
Myth 1: “ADHD never starts in adolescence; you can’t diagnose it after elementary school.”
Diagnostic criteria used to require that symptoms were present before the age of 7 (DSM 3). But current criteria allow for diagnosis before 12 years of age or after. While the consensus is that ADHD is present in childhood, its symptoms are often not apparent. This is because normal development in much younger children is marked by higher levels of activity, distractibility, and impulsivity. Also, children with inattentive-type ADHD may not be apparent to adults if they are performing adequately in school. These youth often do not present for assessment until the challenges of a busy course load make their inattention and consequent inefficiency apparent, in high school or even college. Certainly, when a teenager presents complaining of trouble performing at school, it is critical to rule out an overburdened schedule, anxiety or mood disorder, poor sleep habits or sleep disorder, and substance use disorders, all of which are more common in adolescence. But inattentive-type ADHD that was previously missed is also a possibility worth investigating.
Myth 2: “Most children outgrow ADHD; it’s best to find natural solutions and wait it out.”
Early epidemiological studies suggested that as many as 30% of ADHD cases remitted by adulthood, but more recent data has adjusted that number down substantially, closer to 9%. Interestingly, it appears that 10% of patients will experience sustained symptoms, 9% will experience recovery (sustained remission without treatment), and a large majority will have a remitting and relapsing course into adulthood.1
This emerging evidence suggests that ADHD is almost always a lifelong condition. Untreated, it can threaten healthy development (including social skills and self-esteem) and day-to-day function (academic, social and athletic performance and even vulnerability to accidents) in ways that can be profound. The MTA Study has powerfully demonstrated the efficacy of pharmacological treatment and of specific behavioral treatments for ADHD and associated problems.
Myth 3: “You should exhaust natural cures first before trying medications.”
There has been a large amount of research into a variety of “natural” treatments for ADHD: special diets, supplements, increased exercise, and interventions like neurofeedback. While high-dose omega 3 fatty acid supplementation has demonstrated mild improvement in ADHD symptoms, no “natural” treatment has come close to the efficacy of stimulant medications. Interventions such as neurofeedback are expensive and time-consuming without any demonstrated efficacy. That said, improving a child’s routines around sleep, nutrition, and regular exercise are broadly useful strategies to improve any child’s (or adult’s) energy, impulse control, attention, motivation, and capacity to manage adversity and stress. Start any treatment by addressing sleep and exercise, including moderating time spent on screens, to support healthy function. But only medication will achieve symptom remission if your patient has underlying ADHD.
Myth 4: “All medications are equally effective in ADHD.”
It is well-established that stimulants are more effective than non-stimulants in the treatment of ADHD symptoms, with an effect size that is almost double that of non-stimulants.2
Amphetamine-based medications are slightly more effective than methylphenidate-based medications, but they are also generally less well-tolerated. Individual patients commonly have a better response to one class than the other, but you will need a trial to determine which one. It is reasonable to start a patient with an extended formulation of one class, based on your assessment of their vulnerability to side effects or a family history of medication response. Non-stimulants are of use when stimulants are not tolerated (ie, use of atomoxetine with patients who have comorbid anxiety), or to target specific symptoms, such as guanfacine or clonidine for hyperactivity.
Myth 5: “You can’t treat ADHD in substance abusing teens, stimulant medications are addictive.”
ADHD itself (not medications) increases the risk for addiction; those with ADHD are almost twice as likely to develop a substance use disorder, with highest risk for marijuana, alcohol, and nicotine abuse.3
This may be a function of limited impulse control or increased sensitivity in the ADHD brain to a drug’s addictive potential. Importantly, there is growing evidence that youth whose ADHD is treated pharmacologically are at lower risk for addiction than their peers with untreated ADHD.4
Those youth who have both ADHD and addiction are more likely to stay engaged in treatment for addiction when their ADHD is effectively treated, and there are medication formulations (lisdexamfetamine) that are safe in addiction (cannot be absorbed nasally or intravenously). It is important for you to talk about the heightened vulnerability to addiction with your ADHD patients and their parents, and the value of effective treatment in preventing this complication.
Myth 6: “ADHD is usually behavioral. Help parents to set rules, expectations, and limits instead of medicating the problem.”
Bad parenting does not cause ADHD. ADHD is marked by difficulties with impulse control, hyperactivity, and sustaining attention with matters that are not intrinsically engaging. “Behavioral issues” are patterns of behavior children learn to seek rewards or avoid negative consequences. Youth with ADHD can develop behavioral problems, but these are usually driven by negative feedback about their activity level, forgetfulness, or impulse control, which they are not able to change. This can lead to frustration and irritability, poor self-esteem, and even hopelessness — in parents and children both!
While parents are not the source of ADHD symptoms, there is a great deal of parent education and support that can be powerfully effective for these families. Parents benefit from learning strategies that can help their children to shift their attention, plan ahead, and manage frustration, especially for times when their children are unmedicated (vacations and bedtime). It is worth noting that ADHD is among the most heritable of youth psychiatric illnesses, so it is not uncommon for a parent of a child with ADHD to have similar symptoms. If the parents’ ADHD is untreated, they may be more impulsive themselves. They may also be extra sensitive to the qualities they dislike in themselves, inadvertently adding to their children’s sense of shame. ADHD is very treatable, and those with it can learn executive function skills and organizational strategies that can equip them to manage residual symptoms. Parents will benefit from strategies to understand their children and to help them learn adaptive skills in a realistic way. Your discussions with parents could help the families in your practice make adjustments that can translate into big differences in their child’s healthiest development.
Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Sibley MH et al. MTA Cooperative Group. Variable Patterns of Remission From ADHD in the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2022 Feb;179(2):142-151. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.21010032.
2. Cortese S et al. Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Medications for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children, Adolescents, and Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Sep;5(9):727-738. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30269-4.
3. Lee SS et al. Prospective Association of Childhood Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Substance Use and Abuse/Dependence: A Meta-Analytic Review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2011 Apr;31(3):328-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.01.006.
4. Chorniy A, Kitashima L. Sex, Drugs, and ADHD: The Effects of ADHD Pharmacological Treatment on Teens’ Risky Behaviors. Labour Economics. 2016;43:87-105. doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2016.06.014.
In the second half of the school year, you may find that there is a surge of families coming to appointments with concerns about school performance, wondering if their child has ADHD. We expect you are very familiar with this condition, both diagnosing and treating it. So this month we will offer “mythbusters” for ADHD: Responding to common misperceptions about ADHD with a summary of what the research has demonstrated as emerging facts, what is clearly fiction and what falls into the gray space between.
Demographics
A CDC survey of parents from 2022 indicates that 11.4% of children aged 3-17 have ever been diagnosed with ADHD in the United States. This is more than double the ADHD global prevalence of 5%, suggesting that there is overdiagnosis of this condition in this country. Boys are almost twice as likely to be diagnosed (14.5%) as girls (8%), and White children were more likely to be diagnosed than were Black and Hispanic children. The prevalence of ADHD diagnosis decreases as family income increases, and the condition is more frequently diagnosed in 12- to 17-year-olds than in children 11 and younger. The great majority of youth with an ADHD diagnosis (78%) have at least one co-occurring psychiatric condition. Of the children diagnosed with ADHD, slightly over half receive medication treatment (53.6%) whereas nearly a third (30.1%) receive no ADHD-specific treatment.
The Multimodal Treatment of ADHD Study (MTA), a large (600 children, aged 7-9 years), multicenter, longitudinal study of treatment outcomes for medication as well as behavioral and combination therapies demonstrated in every site that medication alone and combination therapy were significantly superior to intensive behavioral treatment alone and to routine community care in the reduction of ADHD symptoms. Of note, problems commonly associated with ADHD (parent-child conflict, anxiety symptoms, poor academic performance, and limited social skills) improved only with the combination treatment. This suggests that while core ADHD symptoms require medication, associated problems will also require behavioral treatment.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has a useful resource guide (healthychildren.org) highlighting the possible symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that should be investigated when considering this diagnosis. It is a clinical diagnosis, but screening instruments (such as the Vanderbilt) can be very helpful to identifying symptoms that should be present in more than one setting (home and school). While a child with ADHD can appear calm and focused when receiving direct one-to-one attention (as during a pediatrician’s appointment), symptoms may flourish in less structured or supervised settings. Sometimes parents are keen reporters of a child’s behaviors, but some loving (and exhausted) parents may overreact to a normal degree of inattention or disobedience. This can be especially true when a parent has a more detail-oriented temperament than the child, or with younger children and first-time parents. It is important to consider ADHD when you hear about social difficulties as well as academic ones, where there is a family history of ADHD or when a child is more impulsive, hyperactive, or inattentive than you would expect given their age and developmental stage. Confirm your clinical exam with teacher and parent reports. If the reports don’t line up or there are persistent learning problems in school, consider neuropsychological testing to root out a learning disability.
Myth 1: “ADHD never starts in adolescence; you can’t diagnose it after elementary school.”
Diagnostic criteria used to require that symptoms were present before the age of 7 (DSM 3). But current criteria allow for diagnosis before 12 years of age or after. While the consensus is that ADHD is present in childhood, its symptoms are often not apparent. This is because normal development in much younger children is marked by higher levels of activity, distractibility, and impulsivity. Also, children with inattentive-type ADHD may not be apparent to adults if they are performing adequately in school. These youth often do not present for assessment until the challenges of a busy course load make their inattention and consequent inefficiency apparent, in high school or even college. Certainly, when a teenager presents complaining of trouble performing at school, it is critical to rule out an overburdened schedule, anxiety or mood disorder, poor sleep habits or sleep disorder, and substance use disorders, all of which are more common in adolescence. But inattentive-type ADHD that was previously missed is also a possibility worth investigating.
Myth 2: “Most children outgrow ADHD; it’s best to find natural solutions and wait it out.”
Early epidemiological studies suggested that as many as 30% of ADHD cases remitted by adulthood, but more recent data has adjusted that number down substantially, closer to 9%. Interestingly, it appears that 10% of patients will experience sustained symptoms, 9% will experience recovery (sustained remission without treatment), and a large majority will have a remitting and relapsing course into adulthood.1
This emerging evidence suggests that ADHD is almost always a lifelong condition. Untreated, it can threaten healthy development (including social skills and self-esteem) and day-to-day function (academic, social and athletic performance and even vulnerability to accidents) in ways that can be profound. The MTA Study has powerfully demonstrated the efficacy of pharmacological treatment and of specific behavioral treatments for ADHD and associated problems.
Myth 3: “You should exhaust natural cures first before trying medications.”
There has been a large amount of research into a variety of “natural” treatments for ADHD: special diets, supplements, increased exercise, and interventions like neurofeedback. While high-dose omega 3 fatty acid supplementation has demonstrated mild improvement in ADHD symptoms, no “natural” treatment has come close to the efficacy of stimulant medications. Interventions such as neurofeedback are expensive and time-consuming without any demonstrated efficacy. That said, improving a child’s routines around sleep, nutrition, and regular exercise are broadly useful strategies to improve any child’s (or adult’s) energy, impulse control, attention, motivation, and capacity to manage adversity and stress. Start any treatment by addressing sleep and exercise, including moderating time spent on screens, to support healthy function. But only medication will achieve symptom remission if your patient has underlying ADHD.
Myth 4: “All medications are equally effective in ADHD.”
It is well-established that stimulants are more effective than non-stimulants in the treatment of ADHD symptoms, with an effect size that is almost double that of non-stimulants.2
Amphetamine-based medications are slightly more effective than methylphenidate-based medications, but they are also generally less well-tolerated. Individual patients commonly have a better response to one class than the other, but you will need a trial to determine which one. It is reasonable to start a patient with an extended formulation of one class, based on your assessment of their vulnerability to side effects or a family history of medication response. Non-stimulants are of use when stimulants are not tolerated (ie, use of atomoxetine with patients who have comorbid anxiety), or to target specific symptoms, such as guanfacine or clonidine for hyperactivity.
Myth 5: “You can’t treat ADHD in substance abusing teens, stimulant medications are addictive.”
ADHD itself (not medications) increases the risk for addiction; those with ADHD are almost twice as likely to develop a substance use disorder, with highest risk for marijuana, alcohol, and nicotine abuse.3
This may be a function of limited impulse control or increased sensitivity in the ADHD brain to a drug’s addictive potential. Importantly, there is growing evidence that youth whose ADHD is treated pharmacologically are at lower risk for addiction than their peers with untreated ADHD.4
Those youth who have both ADHD and addiction are more likely to stay engaged in treatment for addiction when their ADHD is effectively treated, and there are medication formulations (lisdexamfetamine) that are safe in addiction (cannot be absorbed nasally or intravenously). It is important for you to talk about the heightened vulnerability to addiction with your ADHD patients and their parents, and the value of effective treatment in preventing this complication.
Myth 6: “ADHD is usually behavioral. Help parents to set rules, expectations, and limits instead of medicating the problem.”
Bad parenting does not cause ADHD. ADHD is marked by difficulties with impulse control, hyperactivity, and sustaining attention with matters that are not intrinsically engaging. “Behavioral issues” are patterns of behavior children learn to seek rewards or avoid negative consequences. Youth with ADHD can develop behavioral problems, but these are usually driven by negative feedback about their activity level, forgetfulness, or impulse control, which they are not able to change. This can lead to frustration and irritability, poor self-esteem, and even hopelessness — in parents and children both!
While parents are not the source of ADHD symptoms, there is a great deal of parent education and support that can be powerfully effective for these families. Parents benefit from learning strategies that can help their children to shift their attention, plan ahead, and manage frustration, especially for times when their children are unmedicated (vacations and bedtime). It is worth noting that ADHD is among the most heritable of youth psychiatric illnesses, so it is not uncommon for a parent of a child with ADHD to have similar symptoms. If the parents’ ADHD is untreated, they may be more impulsive themselves. They may also be extra sensitive to the qualities they dislike in themselves, inadvertently adding to their children’s sense of shame. ADHD is very treatable, and those with it can learn executive function skills and organizational strategies that can equip them to manage residual symptoms. Parents will benefit from strategies to understand their children and to help them learn adaptive skills in a realistic way. Your discussions with parents could help the families in your practice make adjustments that can translate into big differences in their child’s healthiest development.
Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Sibley MH et al. MTA Cooperative Group. Variable Patterns of Remission From ADHD in the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2022 Feb;179(2):142-151. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.21010032.
2. Cortese S et al. Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Medications for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children, Adolescents, and Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Sep;5(9):727-738. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30269-4.
3. Lee SS et al. Prospective Association of Childhood Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Substance Use and Abuse/Dependence: A Meta-Analytic Review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2011 Apr;31(3):328-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.01.006.
4. Chorniy A, Kitashima L. Sex, Drugs, and ADHD: The Effects of ADHD Pharmacological Treatment on Teens’ Risky Behaviors. Labour Economics. 2016;43:87-105. doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2016.06.014.
In the second half of the school year, you may find that there is a surge of families coming to appointments with concerns about school performance, wondering if their child has ADHD. We expect you are very familiar with this condition, both diagnosing and treating it. So this month we will offer “mythbusters” for ADHD: Responding to common misperceptions about ADHD with a summary of what the research has demonstrated as emerging facts, what is clearly fiction and what falls into the gray space between.
Demographics
A CDC survey of parents from 2022 indicates that 11.4% of children aged 3-17 have ever been diagnosed with ADHD in the United States. This is more than double the ADHD global prevalence of 5%, suggesting that there is overdiagnosis of this condition in this country. Boys are almost twice as likely to be diagnosed (14.5%) as girls (8%), and White children were more likely to be diagnosed than were Black and Hispanic children. The prevalence of ADHD diagnosis decreases as family income increases, and the condition is more frequently diagnosed in 12- to 17-year-olds than in children 11 and younger. The great majority of youth with an ADHD diagnosis (78%) have at least one co-occurring psychiatric condition. Of the children diagnosed with ADHD, slightly over half receive medication treatment (53.6%) whereas nearly a third (30.1%) receive no ADHD-specific treatment.
The Multimodal Treatment of ADHD Study (MTA), a large (600 children, aged 7-9 years), multicenter, longitudinal study of treatment outcomes for medication as well as behavioral and combination therapies demonstrated in every site that medication alone and combination therapy were significantly superior to intensive behavioral treatment alone and to routine community care in the reduction of ADHD symptoms. Of note, problems commonly associated with ADHD (parent-child conflict, anxiety symptoms, poor academic performance, and limited social skills) improved only with the combination treatment. This suggests that while core ADHD symptoms require medication, associated problems will also require behavioral treatment.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has a useful resource guide (healthychildren.org) highlighting the possible symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that should be investigated when considering this diagnosis. It is a clinical diagnosis, but screening instruments (such as the Vanderbilt) can be very helpful to identifying symptoms that should be present in more than one setting (home and school). While a child with ADHD can appear calm and focused when receiving direct one-to-one attention (as during a pediatrician’s appointment), symptoms may flourish in less structured or supervised settings. Sometimes parents are keen reporters of a child’s behaviors, but some loving (and exhausted) parents may overreact to a normal degree of inattention or disobedience. This can be especially true when a parent has a more detail-oriented temperament than the child, or with younger children and first-time parents. It is important to consider ADHD when you hear about social difficulties as well as academic ones, where there is a family history of ADHD or when a child is more impulsive, hyperactive, or inattentive than you would expect given their age and developmental stage. Confirm your clinical exam with teacher and parent reports. If the reports don’t line up or there are persistent learning problems in school, consider neuropsychological testing to root out a learning disability.
Myth 1: “ADHD never starts in adolescence; you can’t diagnose it after elementary school.”
Diagnostic criteria used to require that symptoms were present before the age of 7 (DSM 3). But current criteria allow for diagnosis before 12 years of age or after. While the consensus is that ADHD is present in childhood, its symptoms are often not apparent. This is because normal development in much younger children is marked by higher levels of activity, distractibility, and impulsivity. Also, children with inattentive-type ADHD may not be apparent to adults if they are performing adequately in school. These youth often do not present for assessment until the challenges of a busy course load make their inattention and consequent inefficiency apparent, in high school or even college. Certainly, when a teenager presents complaining of trouble performing at school, it is critical to rule out an overburdened schedule, anxiety or mood disorder, poor sleep habits or sleep disorder, and substance use disorders, all of which are more common in adolescence. But inattentive-type ADHD that was previously missed is also a possibility worth investigating.
Myth 2: “Most children outgrow ADHD; it’s best to find natural solutions and wait it out.”
Early epidemiological studies suggested that as many as 30% of ADHD cases remitted by adulthood, but more recent data has adjusted that number down substantially, closer to 9%. Interestingly, it appears that 10% of patients will experience sustained symptoms, 9% will experience recovery (sustained remission without treatment), and a large majority will have a remitting and relapsing course into adulthood.1
This emerging evidence suggests that ADHD is almost always a lifelong condition. Untreated, it can threaten healthy development (including social skills and self-esteem) and day-to-day function (academic, social and athletic performance and even vulnerability to accidents) in ways that can be profound. The MTA Study has powerfully demonstrated the efficacy of pharmacological treatment and of specific behavioral treatments for ADHD and associated problems.
Myth 3: “You should exhaust natural cures first before trying medications.”
There has been a large amount of research into a variety of “natural” treatments for ADHD: special diets, supplements, increased exercise, and interventions like neurofeedback. While high-dose omega 3 fatty acid supplementation has demonstrated mild improvement in ADHD symptoms, no “natural” treatment has come close to the efficacy of stimulant medications. Interventions such as neurofeedback are expensive and time-consuming without any demonstrated efficacy. That said, improving a child’s routines around sleep, nutrition, and regular exercise are broadly useful strategies to improve any child’s (or adult’s) energy, impulse control, attention, motivation, and capacity to manage adversity and stress. Start any treatment by addressing sleep and exercise, including moderating time spent on screens, to support healthy function. But only medication will achieve symptom remission if your patient has underlying ADHD.
Myth 4: “All medications are equally effective in ADHD.”
It is well-established that stimulants are more effective than non-stimulants in the treatment of ADHD symptoms, with an effect size that is almost double that of non-stimulants.2
Amphetamine-based medications are slightly more effective than methylphenidate-based medications, but they are also generally less well-tolerated. Individual patients commonly have a better response to one class than the other, but you will need a trial to determine which one. It is reasonable to start a patient with an extended formulation of one class, based on your assessment of their vulnerability to side effects or a family history of medication response. Non-stimulants are of use when stimulants are not tolerated (ie, use of atomoxetine with patients who have comorbid anxiety), or to target specific symptoms, such as guanfacine or clonidine for hyperactivity.
Myth 5: “You can’t treat ADHD in substance abusing teens, stimulant medications are addictive.”
ADHD itself (not medications) increases the risk for addiction; those with ADHD are almost twice as likely to develop a substance use disorder, with highest risk for marijuana, alcohol, and nicotine abuse.3
This may be a function of limited impulse control or increased sensitivity in the ADHD brain to a drug’s addictive potential. Importantly, there is growing evidence that youth whose ADHD is treated pharmacologically are at lower risk for addiction than their peers with untreated ADHD.4
Those youth who have both ADHD and addiction are more likely to stay engaged in treatment for addiction when their ADHD is effectively treated, and there are medication formulations (lisdexamfetamine) that are safe in addiction (cannot be absorbed nasally or intravenously). It is important for you to talk about the heightened vulnerability to addiction with your ADHD patients and their parents, and the value of effective treatment in preventing this complication.
Myth 6: “ADHD is usually behavioral. Help parents to set rules, expectations, and limits instead of medicating the problem.”
Bad parenting does not cause ADHD. ADHD is marked by difficulties with impulse control, hyperactivity, and sustaining attention with matters that are not intrinsically engaging. “Behavioral issues” are patterns of behavior children learn to seek rewards or avoid negative consequences. Youth with ADHD can develop behavioral problems, but these are usually driven by negative feedback about their activity level, forgetfulness, or impulse control, which they are not able to change. This can lead to frustration and irritability, poor self-esteem, and even hopelessness — in parents and children both!
While parents are not the source of ADHD symptoms, there is a great deal of parent education and support that can be powerfully effective for these families. Parents benefit from learning strategies that can help their children to shift their attention, plan ahead, and manage frustration, especially for times when their children are unmedicated (vacations and bedtime). It is worth noting that ADHD is among the most heritable of youth psychiatric illnesses, so it is not uncommon for a parent of a child with ADHD to have similar symptoms. If the parents’ ADHD is untreated, they may be more impulsive themselves. They may also be extra sensitive to the qualities they dislike in themselves, inadvertently adding to their children’s sense of shame. ADHD is very treatable, and those with it can learn executive function skills and organizational strategies that can equip them to manage residual symptoms. Parents will benefit from strategies to understand their children and to help them learn adaptive skills in a realistic way. Your discussions with parents could help the families in your practice make adjustments that can translate into big differences in their child’s healthiest development.
Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Sibley MH et al. MTA Cooperative Group. Variable Patterns of Remission From ADHD in the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2022 Feb;179(2):142-151. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.21010032.
2. Cortese S et al. Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Medications for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children, Adolescents, and Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018 Sep;5(9):727-738. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30269-4.
3. Lee SS et al. Prospective Association of Childhood Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Substance Use and Abuse/Dependence: A Meta-Analytic Review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2011 Apr;31(3):328-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.01.006.
4. Chorniy A, Kitashima L. Sex, Drugs, and ADHD: The Effects of ADHD Pharmacological Treatment on Teens’ Risky Behaviors. Labour Economics. 2016;43:87-105. doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2016.06.014.
Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis Diagnosis
It’s wintertime, peak season for GAS pharyngitis, and you’d think that this far into the 21st century we would have a foolproof process for diagnosing which among the many patients with pharyngitis have true GAS pharyngitis. Thinking back to the 1980s, we have come a long way from simple throat cultures for detecting GAS, e.g., numerous point of care (POC) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), waved rapid antigen detection tests (RADT), and numerous highly sensitive molecular assays, e.g. nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT). But if you think the issues surrounding management of GAS pharyngitis have been solved by these newer tests, think again.
Several good reviews1-3 are excellent resources for those wishing a refresher on GAS diagnosis/management issues. They present nitty gritty details on comparative advantages/disadvantages of the many testing options while reminding us of the nuts and bolts of GAS pharyngitis. The following are a few nuggets from these articles.
Properly collected throat specimen. A quality throat specimen involves swabbing both tonsillar pillars plus posterior pharynx without touching tongue or inner cheeks. Two swab collections increase sensitivity by almost 10% compared with a single swab. Transport media is preferred if samples will not be cultured within 24 hours. Caveat: RADT testing of a transport media-diluted sample lowers sensitivity compared with direct swab use.
Reliable GAS detection. Commercially available tests in 2025 are well studied. Culture is considered a gold standard for detecting clinically relevant GAS by CDC.4 Culture has good sensitivity (estimated 80%-90% varying among studies and by quality of specimens) and 99% specificity but requires 16-24 hours for results. RADT solves the time-delay issues and has near 100% specificity but sensitivity used to be as low as 65%, hence the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline recommendation for backup throat culture for negative tests.5 However, current RADT have sensitivities in the 85%-90% range.3,4 So a positive RADT reliably and quickly indicates GAS antigens are present. NAAT have the highest combined sensitivity and specificity, near 100% for each, and a positive reliably indicates GAS nucleic acids are present.
So why not simply always use NAAT? First, it’s a “be careful what you wish for” scenario. NAAT can, and do, detect dead remnants and colonizing GAS way more than culture.2,3 So NAAT are overly sensitive, adding an extra layer of interpretation difficulty, ie, as many as 20% of positive NAAT detections may be carriers or dead GAS. Second, NAAT often requires special instrumentation and kits are more expensive. That said, reimbursement is often higher for NAAT.
Choice based on accuracy in detecting GAS. If time delays were not a problem, culture would still seem the answer. If more rapid detection is needed, either RADT with culture back up or NAAT could be the answer. That said, consider that in the real world, throat cultures are less sensitive and RADT are less specific than indicated by some published data.6 So, the ideal answer, it seems, would be NAAT GAS detection coupled with a confirmatory biomarker of GAS infection. Such innate immune biomarkers may be on the horizon.3
But first, pretest screening. In 2025 what do we do with a positive result? Do we prescribe antibiotics? Do we think the detected GAS bacteria/antigens/nucleic acids represent the cause of the pharyngitis? Or did we just detect dead GAS or even a carrier, while a virus is the true cause? Challenges for this decision include most pharyngitis (up to 70%) being due to viruses, not GAS, plus up to 20% of GAS detections even by less sensitive culture or RADT can be carriers, plus an added 10%-20% of RADT and NAAT detections are dead GAS. Thus, with indiscriminate testing of all pharyngitis patients, the number of truly positive GAS detections that are actually “false positives” (GAS in some form is present but not causing pharyngitis) may be almost as high as for those representing true GAS pharyngitis.
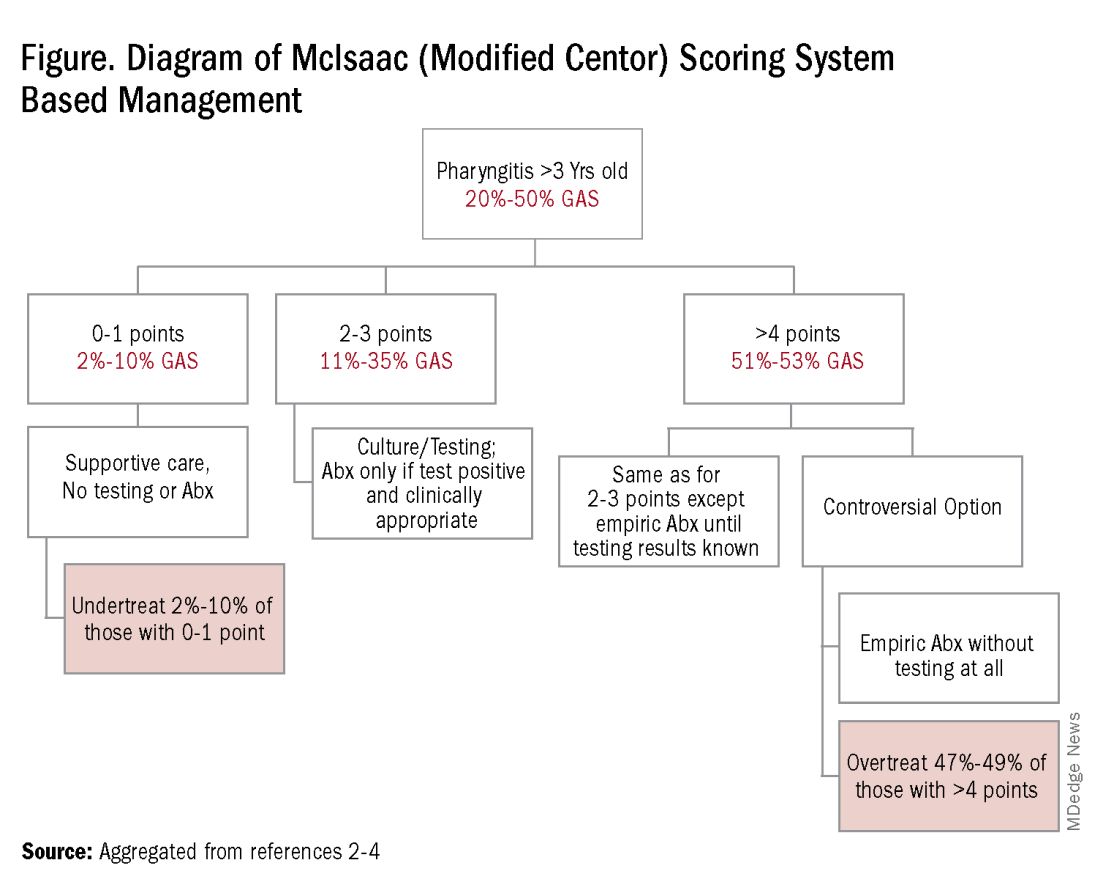
Some tool is needed to minimize testing patients who are likely to have viral pharyngitis to reduce test-positive/GAS-pharyngitis-negative scenarios. Pretest patient screening therefore is critical to increase the positive predictive value of positive GAS testing results. The history and physical can be helpful. In the simplest form of pretest screening, eliminate those younger than 3 years old* or those with viral type sign/symptoms, eg conjunctivitis, cough, coryza.7 This could cut “false” positives by as much as a half. More complete validated scoring systems are also available but remain imperfect. The most published is the McIsaac score (modified Centor score).3-5,8 (See Table and Figure.)
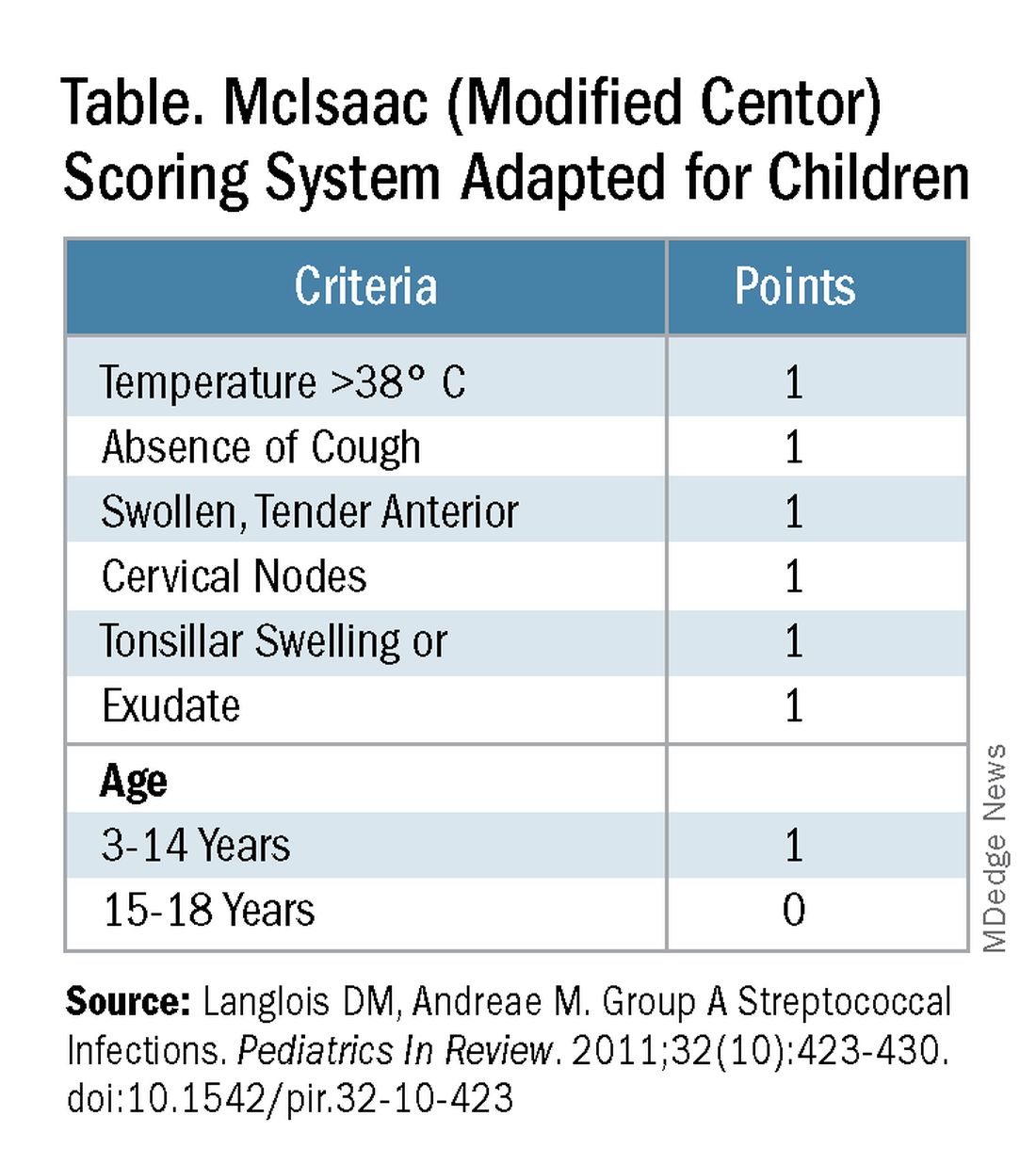
However, even with this validated scoring system, misdiagnoses and some antibiotic misuse will likely occur, particularly if the controversial option to treat a patient with a score above 4 without testing is used. For example, a 2004 study in patients older than 3 years old revealed that 45% with a score above 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis. (McIsaac et al.) A 2012 study showed similar potential overdiagnosis from using the score without testing (45% with > 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis). Of note, clinical scores of below 2 comprised up to 10% and would be neither tested nor treated. (Figure.)
Best clinical judgment. Regardless of the chosen test, we still need to interpret positive results, ie, use best clinical judgment. We know that even with pretest screening some positives tests will represent carriers or nonviable GAS. Yet true GAS pharyngitis needs antibiotic treatment to minimize nonpyogenic and pyogenic complications, plus reduce contagion/transmission risk and days of illness. Thus, we are forced to use best clinical judgment when considering if what could be GAS pharyngitis, particularly exudative pharyngitis, could actually be due to EBV, adenovirus, or gonococcus, each of which can mimic GAS findings. Differentiating these requires discussion beyond the scope of this article, but clues are often found in the history, the patient’s age, associated symptoms and distribution of tonsillopharyngeal exudate. Likewise Group C and G streptococcal pharyngitis can mimic GAS. Note: A comprehensive throat culture can identify these streptococci but requires a special order and likely a call to the laboratory.
Summary: The age-old problem persists, ie, differentiating the minority (~30%) of pharyngitis cases needing antibiotics from the majority that do not. We all wish to promptly treat true GAS pharyngitis; however our current tools remain imperfect. That said, we should strive to correctly diagnose/manage as many patients with pharyngitis as possible. I, for one, can’t wait until we get a validated biomarker that confirms GAS as the culprit in pharyngitis episodes. In the meantime, most providers likely have clinic or hospital approved pathways for managing GAS pharyngitis, many of which are at least in part based on data from sources for this discussion. If not, a firm foundation for creating one can be found in sources among the reference list below. Finally, if you think such pathways somehow interfere with patient flow, consider that a busy multi-provider private practice successfully integrated pretest screening and a pathway while maintaining patient flow and improving antibiotic stewardship.7
*Focal pharyngotonsillar GAS infection is rare in children younger than 3 years old, when GAS nasal passage infection may manifest as streptococcosis.9
Dr Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Bannerjee D, Selvarangan RS. The Evolution of Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis Testing. Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine, 2018, Sep 1.
2. Cohen JF et al. Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis in Children: New Perspectives on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2024 Apr 24;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piae0223.
3. Boyanton Jr BL et al. Current Laboratory and Point-of-Care Pharyngitis Diagnostic Testing and Knowledge Gaps. J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 23;230(Suppl 3):S182–S189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae415.
4. Group A Strep Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024, Mar 1.
5. Shulman ST et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629.
6. Rao A et al. Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis in Children in a Primary Care Setting: Impact of Point-of-Care Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1393-y.
7. Norton LE et al. Improving Guideline-Based Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing: A Quality Improvement Initiative. Pediatrics. 2018 Jul;142(1):e20172033. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2033.
8. MD+ Calc website. Centor Score (Modified/McIsaac) for Strep Pharyngitis.
9. Langlois DM, Andreae M. Group A Streptococcal Infections. Pediatr Rev. 2011 Oct;32(10):423-9; quiz 430. doi: 10.1542/pir.32-10-423.
It’s wintertime, peak season for GAS pharyngitis, and you’d think that this far into the 21st century we would have a foolproof process for diagnosing which among the many patients with pharyngitis have true GAS pharyngitis. Thinking back to the 1980s, we have come a long way from simple throat cultures for detecting GAS, e.g., numerous point of care (POC) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), waved rapid antigen detection tests (RADT), and numerous highly sensitive molecular assays, e.g. nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT). But if you think the issues surrounding management of GAS pharyngitis have been solved by these newer tests, think again.
Several good reviews1-3 are excellent resources for those wishing a refresher on GAS diagnosis/management issues. They present nitty gritty details on comparative advantages/disadvantages of the many testing options while reminding us of the nuts and bolts of GAS pharyngitis. The following are a few nuggets from these articles.
Properly collected throat specimen. A quality throat specimen involves swabbing both tonsillar pillars plus posterior pharynx without touching tongue or inner cheeks. Two swab collections increase sensitivity by almost 10% compared with a single swab. Transport media is preferred if samples will not be cultured within 24 hours. Caveat: RADT testing of a transport media-diluted sample lowers sensitivity compared with direct swab use.
Reliable GAS detection. Commercially available tests in 2025 are well studied. Culture is considered a gold standard for detecting clinically relevant GAS by CDC.4 Culture has good sensitivity (estimated 80%-90% varying among studies and by quality of specimens) and 99% specificity but requires 16-24 hours for results. RADT solves the time-delay issues and has near 100% specificity but sensitivity used to be as low as 65%, hence the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline recommendation for backup throat culture for negative tests.5 However, current RADT have sensitivities in the 85%-90% range.3,4 So a positive RADT reliably and quickly indicates GAS antigens are present. NAAT have the highest combined sensitivity and specificity, near 100% for each, and a positive reliably indicates GAS nucleic acids are present.
So why not simply always use NAAT? First, it’s a “be careful what you wish for” scenario. NAAT can, and do, detect dead remnants and colonizing GAS way more than culture.2,3 So NAAT are overly sensitive, adding an extra layer of interpretation difficulty, ie, as many as 20% of positive NAAT detections may be carriers or dead GAS. Second, NAAT often requires special instrumentation and kits are more expensive. That said, reimbursement is often higher for NAAT.
Choice based on accuracy in detecting GAS. If time delays were not a problem, culture would still seem the answer. If more rapid detection is needed, either RADT with culture back up or NAAT could be the answer. That said, consider that in the real world, throat cultures are less sensitive and RADT are less specific than indicated by some published data.6 So, the ideal answer, it seems, would be NAAT GAS detection coupled with a confirmatory biomarker of GAS infection. Such innate immune biomarkers may be on the horizon.3
But first, pretest screening. In 2025 what do we do with a positive result? Do we prescribe antibiotics? Do we think the detected GAS bacteria/antigens/nucleic acids represent the cause of the pharyngitis? Or did we just detect dead GAS or even a carrier, while a virus is the true cause? Challenges for this decision include most pharyngitis (up to 70%) being due to viruses, not GAS, plus up to 20% of GAS detections even by less sensitive culture or RADT can be carriers, plus an added 10%-20% of RADT and NAAT detections are dead GAS. Thus, with indiscriminate testing of all pharyngitis patients, the number of truly positive GAS detections that are actually “false positives” (GAS in some form is present but not causing pharyngitis) may be almost as high as for those representing true GAS pharyngitis.
Some tool is needed to minimize testing patients who are likely to have viral pharyngitis to reduce test-positive/GAS-pharyngitis-negative scenarios. Pretest patient screening therefore is critical to increase the positive predictive value of positive GAS testing results. The history and physical can be helpful. In the simplest form of pretest screening, eliminate those younger than 3 years old* or those with viral type sign/symptoms, eg conjunctivitis, cough, coryza.7 This could cut “false” positives by as much as a half. More complete validated scoring systems are also available but remain imperfect. The most published is the McIsaac score (modified Centor score).3-5,8 (See Table and Figure.)

However, even with this validated scoring system, misdiagnoses and some antibiotic misuse will likely occur, particularly if the controversial option to treat a patient with a score above 4 without testing is used. For example, a 2004 study in patients older than 3 years old revealed that 45% with a score above 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis. (McIsaac et al.) A 2012 study showed similar potential overdiagnosis from using the score without testing (45% with > 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis). Of note, clinical scores of below 2 comprised up to 10% and would be neither tested nor treated. (Figure.)

Best clinical judgment. Regardless of the chosen test, we still need to interpret positive results, ie, use best clinical judgment. We know that even with pretest screening some positives tests will represent carriers or nonviable GAS. Yet true GAS pharyngitis needs antibiotic treatment to minimize nonpyogenic and pyogenic complications, plus reduce contagion/transmission risk and days of illness. Thus, we are forced to use best clinical judgment when considering if what could be GAS pharyngitis, particularly exudative pharyngitis, could actually be due to EBV, adenovirus, or gonococcus, each of which can mimic GAS findings. Differentiating these requires discussion beyond the scope of this article, but clues are often found in the history, the patient’s age, associated symptoms and distribution of tonsillopharyngeal exudate. Likewise Group C and G streptococcal pharyngitis can mimic GAS. Note: A comprehensive throat culture can identify these streptococci but requires a special order and likely a call to the laboratory.
Summary: The age-old problem persists, ie, differentiating the minority (~30%) of pharyngitis cases needing antibiotics from the majority that do not. We all wish to promptly treat true GAS pharyngitis; however our current tools remain imperfect. That said, we should strive to correctly diagnose/manage as many patients with pharyngitis as possible. I, for one, can’t wait until we get a validated biomarker that confirms GAS as the culprit in pharyngitis episodes. In the meantime, most providers likely have clinic or hospital approved pathways for managing GAS pharyngitis, many of which are at least in part based on data from sources for this discussion. If not, a firm foundation for creating one can be found in sources among the reference list below. Finally, if you think such pathways somehow interfere with patient flow, consider that a busy multi-provider private practice successfully integrated pretest screening and a pathway while maintaining patient flow and improving antibiotic stewardship.7
*Focal pharyngotonsillar GAS infection is rare in children younger than 3 years old, when GAS nasal passage infection may manifest as streptococcosis.9
Dr Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Bannerjee D, Selvarangan RS. The Evolution of Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis Testing. Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine, 2018, Sep 1.
2. Cohen JF et al. Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis in Children: New Perspectives on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2024 Apr 24;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piae0223.
3. Boyanton Jr BL et al. Current Laboratory and Point-of-Care Pharyngitis Diagnostic Testing and Knowledge Gaps. J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 23;230(Suppl 3):S182–S189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae415.
4. Group A Strep Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024, Mar 1.
5. Shulman ST et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629.
6. Rao A et al. Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis in Children in a Primary Care Setting: Impact of Point-of-Care Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1393-y.
7. Norton LE et al. Improving Guideline-Based Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing: A Quality Improvement Initiative. Pediatrics. 2018 Jul;142(1):e20172033. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2033.
8. MD+ Calc website. Centor Score (Modified/McIsaac) for Strep Pharyngitis.
9. Langlois DM, Andreae M. Group A Streptococcal Infections. Pediatr Rev. 2011 Oct;32(10):423-9; quiz 430. doi: 10.1542/pir.32-10-423.
It’s wintertime, peak season for GAS pharyngitis, and you’d think that this far into the 21st century we would have a foolproof process for diagnosing which among the many patients with pharyngitis have true GAS pharyngitis. Thinking back to the 1980s, we have come a long way from simple throat cultures for detecting GAS, e.g., numerous point of care (POC) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), waved rapid antigen detection tests (RADT), and numerous highly sensitive molecular assays, e.g. nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT). But if you think the issues surrounding management of GAS pharyngitis have been solved by these newer tests, think again.
Several good reviews1-3 are excellent resources for those wishing a refresher on GAS diagnosis/management issues. They present nitty gritty details on comparative advantages/disadvantages of the many testing options while reminding us of the nuts and bolts of GAS pharyngitis. The following are a few nuggets from these articles.
Properly collected throat specimen. A quality throat specimen involves swabbing both tonsillar pillars plus posterior pharynx without touching tongue or inner cheeks. Two swab collections increase sensitivity by almost 10% compared with a single swab. Transport media is preferred if samples will not be cultured within 24 hours. Caveat: RADT testing of a transport media-diluted sample lowers sensitivity compared with direct swab use.
Reliable GAS detection. Commercially available tests in 2025 are well studied. Culture is considered a gold standard for detecting clinically relevant GAS by CDC.4 Culture has good sensitivity (estimated 80%-90% varying among studies and by quality of specimens) and 99% specificity but requires 16-24 hours for results. RADT solves the time-delay issues and has near 100% specificity but sensitivity used to be as low as 65%, hence the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline recommendation for backup throat culture for negative tests.5 However, current RADT have sensitivities in the 85%-90% range.3,4 So a positive RADT reliably and quickly indicates GAS antigens are present. NAAT have the highest combined sensitivity and specificity, near 100% for each, and a positive reliably indicates GAS nucleic acids are present.
So why not simply always use NAAT? First, it’s a “be careful what you wish for” scenario. NAAT can, and do, detect dead remnants and colonizing GAS way more than culture.2,3 So NAAT are overly sensitive, adding an extra layer of interpretation difficulty, ie, as many as 20% of positive NAAT detections may be carriers or dead GAS. Second, NAAT often requires special instrumentation and kits are more expensive. That said, reimbursement is often higher for NAAT.
Choice based on accuracy in detecting GAS. If time delays were not a problem, culture would still seem the answer. If more rapid detection is needed, either RADT with culture back up or NAAT could be the answer. That said, consider that in the real world, throat cultures are less sensitive and RADT are less specific than indicated by some published data.6 So, the ideal answer, it seems, would be NAAT GAS detection coupled with a confirmatory biomarker of GAS infection. Such innate immune biomarkers may be on the horizon.3
But first, pretest screening. In 2025 what do we do with a positive result? Do we prescribe antibiotics? Do we think the detected GAS bacteria/antigens/nucleic acids represent the cause of the pharyngitis? Or did we just detect dead GAS or even a carrier, while a virus is the true cause? Challenges for this decision include most pharyngitis (up to 70%) being due to viruses, not GAS, plus up to 20% of GAS detections even by less sensitive culture or RADT can be carriers, plus an added 10%-20% of RADT and NAAT detections are dead GAS. Thus, with indiscriminate testing of all pharyngitis patients, the number of truly positive GAS detections that are actually “false positives” (GAS in some form is present but not causing pharyngitis) may be almost as high as for those representing true GAS pharyngitis.
Some tool is needed to minimize testing patients who are likely to have viral pharyngitis to reduce test-positive/GAS-pharyngitis-negative scenarios. Pretest patient screening therefore is critical to increase the positive predictive value of positive GAS testing results. The history and physical can be helpful. In the simplest form of pretest screening, eliminate those younger than 3 years old* or those with viral type sign/symptoms, eg conjunctivitis, cough, coryza.7 This could cut “false” positives by as much as a half. More complete validated scoring systems are also available but remain imperfect. The most published is the McIsaac score (modified Centor score).3-5,8 (See Table and Figure.)

However, even with this validated scoring system, misdiagnoses and some antibiotic misuse will likely occur, particularly if the controversial option to treat a patient with a score above 4 without testing is used. For example, a 2004 study in patients older than 3 years old revealed that 45% with a score above 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis. (McIsaac et al.) A 2012 study showed similar potential overdiagnosis from using the score without testing (45% with > 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis). Of note, clinical scores of below 2 comprised up to 10% and would be neither tested nor treated. (Figure.)

Best clinical judgment. Regardless of the chosen test, we still need to interpret positive results, ie, use best clinical judgment. We know that even with pretest screening some positives tests will represent carriers or nonviable GAS. Yet true GAS pharyngitis needs antibiotic treatment to minimize nonpyogenic and pyogenic complications, plus reduce contagion/transmission risk and days of illness. Thus, we are forced to use best clinical judgment when considering if what could be GAS pharyngitis, particularly exudative pharyngitis, could actually be due to EBV, adenovirus, or gonococcus, each of which can mimic GAS findings. Differentiating these requires discussion beyond the scope of this article, but clues are often found in the history, the patient’s age, associated symptoms and distribution of tonsillopharyngeal exudate. Likewise Group C and G streptococcal pharyngitis can mimic GAS. Note: A comprehensive throat culture can identify these streptococci but requires a special order and likely a call to the laboratory.
Summary: The age-old problem persists, ie, differentiating the minority (~30%) of pharyngitis cases needing antibiotics from the majority that do not. We all wish to promptly treat true GAS pharyngitis; however our current tools remain imperfect. That said, we should strive to correctly diagnose/manage as many patients with pharyngitis as possible. I, for one, can’t wait until we get a validated biomarker that confirms GAS as the culprit in pharyngitis episodes. In the meantime, most providers likely have clinic or hospital approved pathways for managing GAS pharyngitis, many of which are at least in part based on data from sources for this discussion. If not, a firm foundation for creating one can be found in sources among the reference list below. Finally, if you think such pathways somehow interfere with patient flow, consider that a busy multi-provider private practice successfully integrated pretest screening and a pathway while maintaining patient flow and improving antibiotic stewardship.7
*Focal pharyngotonsillar GAS infection is rare in children younger than 3 years old, when GAS nasal passage infection may manifest as streptococcosis.9
Dr Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Bannerjee D, Selvarangan RS. The Evolution of Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis Testing. Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine, 2018, Sep 1.
2. Cohen JF et al. Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis in Children: New Perspectives on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2024 Apr 24;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piae0223.
3. Boyanton Jr BL et al. Current Laboratory and Point-of-Care Pharyngitis Diagnostic Testing and Knowledge Gaps. J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 23;230(Suppl 3):S182–S189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae415.
4. Group A Strep Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024, Mar 1.
5. Shulman ST et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629.
6. Rao A et al. Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis in Children in a Primary Care Setting: Impact of Point-of-Care Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1393-y.
7. Norton LE et al. Improving Guideline-Based Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing: A Quality Improvement Initiative. Pediatrics. 2018 Jul;142(1):e20172033. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2033.
8. MD+ Calc website. Centor Score (Modified/McIsaac) for Strep Pharyngitis.
9. Langlois DM, Andreae M. Group A Streptococcal Infections. Pediatr Rev. 2011 Oct;32(10):423-9; quiz 430. doi: 10.1542/pir.32-10-423.
Crying Tolerance
Most of the papers I review merely validate a relationship that most of us, including the investigators, have already assumed based on common sense. However, every now and then I encounter a study whose findings clearly don’t support the researchers’ initial thesis. The most recent example of this unexpected finding is a paper designed to determine whether the sound of a crying infant would have an effect on a parent’s ability to accurately mix formula.
After a cursory reading of the investigators’ plan, most of us would have assumed from our own difficulties trying to accomplish something while our infant is crying that the crying would have a negative effect on our accuracy. Especially if it was a task that required careful measurement. However, when I skipped ahead to read the paper’s conclusion I was surprised that the investigators could found no significant negative relationship.
The explanation for this counterintuitive finding became readily apparent when I read the details of the study’s design more carefully. The investigators had chosen to use a generic recording of an infant crying, not the parent’s child nor even a live generic child on site.
No one enjoys listening to a child cry. It is certainly not a pleasant sound to the human ear. We seem to be hardwired to find it irritating. But, listening to our own child cry raises an entirely different suite of emotions, particularly if the child is close enough for us to intervene.
I’m not sure exactly what made the investigators choose a generic recording, but I suspect it was less expensive. Otherwise it would have required that the parents agree to subjecting their child to some stimulus that would have predictably induced the child to cry. Fortunately, the investigators were able to regroup in the wake of this lack of common sense in their experimental design and realized that, while their data failed to show a negative association with crying, it did provide an important message. Formula mixing errors, some with potentially harmful consequences, are far too common. In a commentary accompanying this paper, a pediatrician not involved in the study observes that, in our efforts to promote breastfeeding, we have given short shrift to teaching parents about accurate and safe formula preparation.
But, let’s return to the crying piece. Why is it so difficult for parents to tolerate their own crying infant? Common sense should tell us that we know our infant is helpless. The little child is totally reliant on us to for nutrition and protection from the ever-present environmental threats to its health and safety in the environment. In short, whether we are parents, daycare providers, or the mother’s boyfriend who has been left in charge, we are totally responsible for the life of that infant, at times a heavy burden.
That example of biologic variability is just one of the reasons why so many families find it difficult to set limits and follow through with consequences. When I have written about and spoken to parents in the office about discipline, I am happy if I can convince both parents to be on the same page (literally sometimes) in how they respond to their crying child.
Helping an infant learn to put itself to sleep is usually the first challenge that requires some agreement between parents on how long they can tolerate crying. Although allowing the infant to cry itself to sleep may be the best and most efficient strategy, it isn’t going to work when two parents and/or caregivers have widely different cry tolerances. In some situations these discrepancies can be managed by having the less tolerant parent temporarily move himself/herself to a location out of earshot. Something often easier said than accomplished.
At the heart of the solution is an acceptance by both parents that differing cry intolerances are not unusual and don’t imply that one partner is a better parent. As advisors we also must accept this reality and help the family find some other solution. Nothing is gained by allowing a disagreement between parents to make an already uncomfortable situation any worse.
While we don’t give out merit badges for it, being able to tolerate one’s own child crying for brief periods of time is a gift that can be helpful in certain situations. It is not a skill listed in the curriculum of most parenting classes, but learning more about what prompts babies to cry can be very helpful. This educational approach is exemplified by a Pediatrics Patient Page in a recent issue of JAMA Pediatrics. It’s rarely hunger and most often is sleep deprivation. It’s rarely the result of an undiscovered injury or medical condition, but may be a response to an overstimulating environment.
For those of us who are advisers, one of our responsibilities is to be alert to those few individuals whose intolerance to crying is so great that they are likely to injure the child or its mother to stop the crying. The simple question at an early well-child visit should be something like “How is everyone in the house when the child starts crying” might save a life. The stereotypic example is the young boyfriend of the mother, who may suspect that he is not the biologic father. However, any parent who is feeling insecure because of a financial situation, poor physical or mental health, or fatigue may lash out to achieve quiet. Crying is one of the realities of infancy. It is our job to help parents cope with it safely.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Most of the papers I review merely validate a relationship that most of us, including the investigators, have already assumed based on common sense. However, every now and then I encounter a study whose findings clearly don’t support the researchers’ initial thesis. The most recent example of this unexpected finding is a paper designed to determine whether the sound of a crying infant would have an effect on a parent’s ability to accurately mix formula.
After a cursory reading of the investigators’ plan, most of us would have assumed from our own difficulties trying to accomplish something while our infant is crying that the crying would have a negative effect on our accuracy. Especially if it was a task that required careful measurement. However, when I skipped ahead to read the paper’s conclusion I was surprised that the investigators could found no significant negative relationship.
The explanation for this counterintuitive finding became readily apparent when I read the details of the study’s design more carefully. The investigators had chosen to use a generic recording of an infant crying, not the parent’s child nor even a live generic child on site.
No one enjoys listening to a child cry. It is certainly not a pleasant sound to the human ear. We seem to be hardwired to find it irritating. But, listening to our own child cry raises an entirely different suite of emotions, particularly if the child is close enough for us to intervene.
I’m not sure exactly what made the investigators choose a generic recording, but I suspect it was less expensive. Otherwise it would have required that the parents agree to subjecting their child to some stimulus that would have predictably induced the child to cry. Fortunately, the investigators were able to regroup in the wake of this lack of common sense in their experimental design and realized that, while their data failed to show a negative association with crying, it did provide an important message. Formula mixing errors, some with potentially harmful consequences, are far too common. In a commentary accompanying this paper, a pediatrician not involved in the study observes that, in our efforts to promote breastfeeding, we have given short shrift to teaching parents about accurate and safe formula preparation.
But, let’s return to the crying piece. Why is it so difficult for parents to tolerate their own crying infant? Common sense should tell us that we know our infant is helpless. The little child is totally reliant on us to for nutrition and protection from the ever-present environmental threats to its health and safety in the environment. In short, whether we are parents, daycare providers, or the mother’s boyfriend who has been left in charge, we are totally responsible for the life of that infant, at times a heavy burden.
That example of biologic variability is just one of the reasons why so many families find it difficult to set limits and follow through with consequences. When I have written about and spoken to parents in the office about discipline, I am happy if I can convince both parents to be on the same page (literally sometimes) in how they respond to their crying child.
Helping an infant learn to put itself to sleep is usually the first challenge that requires some agreement between parents on how long they can tolerate crying. Although allowing the infant to cry itself to sleep may be the best and most efficient strategy, it isn’t going to work when two parents and/or caregivers have widely different cry tolerances. In some situations these discrepancies can be managed by having the less tolerant parent temporarily move himself/herself to a location out of earshot. Something often easier said than accomplished.
At the heart of the solution is an acceptance by both parents that differing cry intolerances are not unusual and don’t imply that one partner is a better parent. As advisors we also must accept this reality and help the family find some other solution. Nothing is gained by allowing a disagreement between parents to make an already uncomfortable situation any worse.
While we don’t give out merit badges for it, being able to tolerate one’s own child crying for brief periods of time is a gift that can be helpful in certain situations. It is not a skill listed in the curriculum of most parenting classes, but learning more about what prompts babies to cry can be very helpful. This educational approach is exemplified by a Pediatrics Patient Page in a recent issue of JAMA Pediatrics. It’s rarely hunger and most often is sleep deprivation. It’s rarely the result of an undiscovered injury or medical condition, but may be a response to an overstimulating environment.
For those of us who are advisers, one of our responsibilities is to be alert to those few individuals whose intolerance to crying is so great that they are likely to injure the child or its mother to stop the crying. The simple question at an early well-child visit should be something like “How is everyone in the house when the child starts crying” might save a life. The stereotypic example is the young boyfriend of the mother, who may suspect that he is not the biologic father. However, any parent who is feeling insecure because of a financial situation, poor physical or mental health, or fatigue may lash out to achieve quiet. Crying is one of the realities of infancy. It is our job to help parents cope with it safely.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Most of the papers I review merely validate a relationship that most of us, including the investigators, have already assumed based on common sense. However, every now and then I encounter a study whose findings clearly don’t support the researchers’ initial thesis. The most recent example of this unexpected finding is a paper designed to determine whether the sound of a crying infant would have an effect on a parent’s ability to accurately mix formula.
After a cursory reading of the investigators’ plan, most of us would have assumed from our own difficulties trying to accomplish something while our infant is crying that the crying would have a negative effect on our accuracy. Especially if it was a task that required careful measurement. However, when I skipped ahead to read the paper’s conclusion I was surprised that the investigators could found no significant negative relationship.
The explanation for this counterintuitive finding became readily apparent when I read the details of the study’s design more carefully. The investigators had chosen to use a generic recording of an infant crying, not the parent’s child nor even a live generic child on site.
No one enjoys listening to a child cry. It is certainly not a pleasant sound to the human ear. We seem to be hardwired to find it irritating. But, listening to our own child cry raises an entirely different suite of emotions, particularly if the child is close enough for us to intervene.
I’m not sure exactly what made the investigators choose a generic recording, but I suspect it was less expensive. Otherwise it would have required that the parents agree to subjecting their child to some stimulus that would have predictably induced the child to cry. Fortunately, the investigators were able to regroup in the wake of this lack of common sense in their experimental design and realized that, while their data failed to show a negative association with crying, it did provide an important message. Formula mixing errors, some with potentially harmful consequences, are far too common. In a commentary accompanying this paper, a pediatrician not involved in the study observes that, in our efforts to promote breastfeeding, we have given short shrift to teaching parents about accurate and safe formula preparation.
But, let’s return to the crying piece. Why is it so difficult for parents to tolerate their own crying infant? Common sense should tell us that we know our infant is helpless. The little child is totally reliant on us to for nutrition and protection from the ever-present environmental threats to its health and safety in the environment. In short, whether we are parents, daycare providers, or the mother’s boyfriend who has been left in charge, we are totally responsible for the life of that infant, at times a heavy burden.
That example of biologic variability is just one of the reasons why so many families find it difficult to set limits and follow through with consequences. When I have written about and spoken to parents in the office about discipline, I am happy if I can convince both parents to be on the same page (literally sometimes) in how they respond to their crying child.
Helping an infant learn to put itself to sleep is usually the first challenge that requires some agreement between parents on how long they can tolerate crying. Although allowing the infant to cry itself to sleep may be the best and most efficient strategy, it isn’t going to work when two parents and/or caregivers have widely different cry tolerances. In some situations these discrepancies can be managed by having the less tolerant parent temporarily move himself/herself to a location out of earshot. Something often easier said than accomplished.
At the heart of the solution is an acceptance by both parents that differing cry intolerances are not unusual and don’t imply that one partner is a better parent. As advisors we also must accept this reality and help the family find some other solution. Nothing is gained by allowing a disagreement between parents to make an already uncomfortable situation any worse.
While we don’t give out merit badges for it, being able to tolerate one’s own child crying for brief periods of time is a gift that can be helpful in certain situations. It is not a skill listed in the curriculum of most parenting classes, but learning more about what prompts babies to cry can be very helpful. This educational approach is exemplified by a Pediatrics Patient Page in a recent issue of JAMA Pediatrics. It’s rarely hunger and most often is sleep deprivation. It’s rarely the result of an undiscovered injury or medical condition, but may be a response to an overstimulating environment.
For those of us who are advisers, one of our responsibilities is to be alert to those few individuals whose intolerance to crying is so great that they are likely to injure the child or its mother to stop the crying. The simple question at an early well-child visit should be something like “How is everyone in the house when the child starts crying” might save a life. The stereotypic example is the young boyfriend of the mother, who may suspect that he is not the biologic father. However, any parent who is feeling insecure because of a financial situation, poor physical or mental health, or fatigue may lash out to achieve quiet. Crying is one of the realities of infancy. It is our job to help parents cope with it safely.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Simufilam: Just Another Placebo
An Alzheimer’s drug trial failing is, unfortunately, nothing new. This one, however, had more baggage behind it than most.
Like all of these things, it was worth a try. It’s an interesting molecule with a reasonable mechanism of action.
But the trials have been raising questions for a few years, with allegations of misconduct against the drug’s co-discoverer Hoau-Yan Wang. He’s been indicted for defrauding the National Institutes of Health of $16 million in grants related to the drug. There have been concerns over doctored images and other not-so-minor issues in trying to move simufilam forward. Cassava itself agreed to pay the Securities and Exchange Commission $40 million in 2024 to settle charges about misleading investors.
Yet, like an innocent child with criminal parents, many of us hoped that the drug would work, regardless of the ethical shenanigans behind it. On the front lines we deal with a tragic disease that robs people of what makes them human and robs the families who have to live with it.
As the wheels started to come off the bus I told a friend, “it would be really sad if this drug is THE ONE and it never gets to finish trials because of everything else.”
Now we know it isn’t. Regardless of the controversy, the final data show that simufilam is just another placebo, joining the ranks of many others in the Alzheimer’s development graveyard.
Yes, there is a vague sense of jubilation behind it. I believe in fair play, and it’s good to know that those who misled investors and falsified data were wrong and will never have their day in the sun.
At the same time, however, I’m disappointed. I’m happy that the drug at least got a chance to prove itself, but when it’s all said and done, it doesn’t do anything.
I feel bad for the innocent people in the company, who had nothing to do with the scheming and were just hoping the drug would go somewhere. The majority, if not all, of them will likely lose their jobs. Like me, they have families, bills, and mortgages.
But I’m even more disappointed for the patients and families who only wanted an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, and were hoping that, regardless of its dirty laundry, simufilam would work.
They’re the ones that I, and many other neurologists, have to face every day when they ask “is there anything new out?” and we sadly shake our heads.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
An Alzheimer’s drug trial failing is, unfortunately, nothing new. This one, however, had more baggage behind it than most.
Like all of these things, it was worth a try. It’s an interesting molecule with a reasonable mechanism of action.
But the trials have been raising questions for a few years, with allegations of misconduct against the drug’s co-discoverer Hoau-Yan Wang. He’s been indicted for defrauding the National Institutes of Health of $16 million in grants related to the drug. There have been concerns over doctored images and other not-so-minor issues in trying to move simufilam forward. Cassava itself agreed to pay the Securities and Exchange Commission $40 million in 2024 to settle charges about misleading investors.
Yet, like an innocent child with criminal parents, many of us hoped that the drug would work, regardless of the ethical shenanigans behind it. On the front lines we deal with a tragic disease that robs people of what makes them human and robs the families who have to live with it.
As the wheels started to come off the bus I told a friend, “it would be really sad if this drug is THE ONE and it never gets to finish trials because of everything else.”
Now we know it isn’t. Regardless of the controversy, the final data show that simufilam is just another placebo, joining the ranks of many others in the Alzheimer’s development graveyard.
Yes, there is a vague sense of jubilation behind it. I believe in fair play, and it’s good to know that those who misled investors and falsified data were wrong and will never have their day in the sun.
At the same time, however, I’m disappointed. I’m happy that the drug at least got a chance to prove itself, but when it’s all said and done, it doesn’t do anything.
I feel bad for the innocent people in the company, who had nothing to do with the scheming and were just hoping the drug would go somewhere. The majority, if not all, of them will likely lose their jobs. Like me, they have families, bills, and mortgages.
But I’m even more disappointed for the patients and families who only wanted an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, and were hoping that, regardless of its dirty laundry, simufilam would work.
They’re the ones that I, and many other neurologists, have to face every day when they ask “is there anything new out?” and we sadly shake our heads.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
An Alzheimer’s drug trial failing is, unfortunately, nothing new. This one, however, had more baggage behind it than most.
Like all of these things, it was worth a try. It’s an interesting molecule with a reasonable mechanism of action.
But the trials have been raising questions for a few years, with allegations of misconduct against the drug’s co-discoverer Hoau-Yan Wang. He’s been indicted for defrauding the National Institutes of Health of $16 million in grants related to the drug. There have been concerns over doctored images and other not-so-minor issues in trying to move simufilam forward. Cassava itself agreed to pay the Securities and Exchange Commission $40 million in 2024 to settle charges about misleading investors.
Yet, like an innocent child with criminal parents, many of us hoped that the drug would work, regardless of the ethical shenanigans behind it. On the front lines we deal with a tragic disease that robs people of what makes them human and robs the families who have to live with it.
As the wheels started to come off the bus I told a friend, “it would be really sad if this drug is THE ONE and it never gets to finish trials because of everything else.”
Now we know it isn’t. Regardless of the controversy, the final data show that simufilam is just another placebo, joining the ranks of many others in the Alzheimer’s development graveyard.
Yes, there is a vague sense of jubilation behind it. I believe in fair play, and it’s good to know that those who misled investors and falsified data were wrong and will never have their day in the sun.
At the same time, however, I’m disappointed. I’m happy that the drug at least got a chance to prove itself, but when it’s all said and done, it doesn’t do anything.
I feel bad for the innocent people in the company, who had nothing to do with the scheming and were just hoping the drug would go somewhere. The majority, if not all, of them will likely lose their jobs. Like me, they have families, bills, and mortgages.
But I’m even more disappointed for the patients and families who only wanted an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, and were hoping that, regardless of its dirty laundry, simufilam would work.
They’re the ones that I, and many other neurologists, have to face every day when they ask “is there anything new out?” and we sadly shake our heads.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
On Second Thought: Making Sense of Blood Pressure Guidelines — What Happened in the 1930s Should Stay There
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Blood pressure. If you’re a primary care provider trying to do right by your patients, you might be understandably confused by the current mishmash of guidelines with different blood pressure targets. But as chaotic as things are, at least it’s not the 1930s, when you might hear John Hay give a lecture to the British Medical Association and say, “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.”
Yeah, he said that. But what happened in the 1930s stays in the 1930s. And now we can at least agree that we should be treating high blood pressure. But what’s the goal we should be aiming for? This is On Second Thought.
We’ve come a long way since FDR was recording blood pressures of 200 and his doctor prescribed him barbiturates and massage therapy.
That s#$# don’t fly no more. Over the past hundred years, we have become much more aggressive in treating blood pressure. Remember the Oslo study? It defined mild hypertension as a blood pressure between 150 and 180 mm Hg. Now, those numbers send people screaming to the emergency room. So, let’s acknowledge that things are substantially better than they once were. Let’s agree on that and we can start to heal this nation again.
Before we get into the numbers, when we’re treating blood pressure, let’s make a few points about measuring it. Obviously, to treat something, you have to measure it properly. Two recent trials have illustrated that these details matter a lot.
The Cuff(SZ) randomized crossover trial — and it took me a minute to realize that Cuff(SZ) meant cuff size, so bravo, Ishigami et al — showed that picking the wrong cuff size could affect BP measurements by 4.5 points if you were one size off. If you were two sizes too small, you overestimated BP by almost 20 points.
Add on here another recent study, the ARMS crossover randomized clinical trial, looking at how arm position affected BP measures. If the arm was resting on your lap or hanging by your side, that overestimated blood pressure by 4 and 6.5 points. So sometimes you have to remember the fundamentals: cuff size, arm position — it might make the difference between increasing or maintaining the patient’s meds.
But on to the main show. What numbers should we be aiming for? We no longer live in the “BP 200, the president’s going to have a stroke” world of the 1940s, and even a BP of 150 is considered quite high these days. Studies like the MRC trial, INVEST, and SPRINT have pushed BP targets ever lower. SPRINT, in particular, randomized patients to a blood pressure target under 120 systolic vs under 140 systolic, and the under-120 arm won out with fewer cardiovascular events and lower all-cause mortality.
Pretty definitive slam dunk. But the more intensive treatment came with more hypotension, syncope, and kidney injury, because there is no free lunch in medicine. And ditto with BPROAD, just published in The New England Journal of Medicine and presented at the American Heart Association annual meeting. A diabetic population randomized to 120 vs 140 as a BP target showed that more aggressive treatment was better.
Fewer cardiovascular events, like stroke, but no mortality difference, and more hypotension. So a cardiovascular benefit at the cost of more side effects. Now, like all cardiologists, my motto is “Save the heart and screw the kidney.” But if you do care about the other organs in this meat sack that we call a human body, the question you need to wrestle with is, how much do you value cardiovascular protection vs how willing are you to tolerate side effects?
Hypotension may not sound dangerous, but gravity is an unforgiving mistress. If you painstakingly compile the summary of the various BP guidelines for easy perusal, you would notice something critical: One, I have too much free time on my hands; two, the disagreements are not really all that profound.
Arguing about 120 vs 130 vs 140 is not the same as saying, “Drugs schmugs; a good massage will fix what ails you, and here are some addictive sleeping pills for good measure.” Physicians from the 1930s were a little sketchy. So much of this controversy is about how you define high-risk patients and what are the age cutoffs.
Basically, the cardiovascular guidelines say, “Treat them all and let God sort it out” because they care about cardiovascular events and are concerned about cardiovascular endpoints. Whereas general practice guidelines put more emphasis on potential side effects and admittedly tend to treat a not so high-risk population, so they have laxer targets.
A 2014 analysis from the Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration [The Lancet] had a good mathematical way of explaining this problem. Now, lowering blood pressure is obviously a good thing. That prevents heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure, and all that. Please don’t let hypertension denialism become a thing.
Let’s start with the basics. Treating high blood pressure led to a 15% to 18% decrease in cardiovascular events, pretty consistently across all risk categories, and other analyses have found that every 5-point decrease in blood pressure gives you about a 10% decrease in major cardiovascular events on the relative-risk scale.
While the benefits are pretty consistent across all groups, that difference in baseline risk translates into different absolute benefits. In the Lancet paper, when the population was divided into four different groups based on their cardiovascular risk, the absolute risk reduction in the lowest-risk group was 14 fewer cardiovascular events if you treat 1000 patients for 5 years.
With each higher-risk group, it was 20 fewer, 24 fewer, and 38 fewer. At the lowest-risk group, the number needed to treat was 71, 50, 42, and 26 fewer cardiovascular events with 5 years of treatment.
And herein lies the secret to the disagreement: If you have a high-risk patient, there is a big benefit to bringing that blood pressure down from 135 to 130. Whereas for a low-risk patient, it probably doesn’t matter as much. And the cardiovascular benefits are going to be offset by the side effects and the risks for hypotension.
Of course, there’s a simple solution to this dilemma: Just speak to the patient in front of you. Treat high blood pressure, and if your patient’s blood pressure drops or they get dizzy or have fainting spells, then just ease up on the meds. It’s not rocket science; it’s just cardiology.
Arguing about five millimeters of mercury of blood pressure is probably less important from the public health perspective than the fact that tens of millions of people in the United States are unaware that they have hypertension, and even those diagnosed are being inadequately treated.
So, let’s all do better as a medical community. Nobody should have untreated hypertension in this day and age. It’s not the 1930s.
Dr Labos, Cardiologist, Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Blood pressure. If you’re a primary care provider trying to do right by your patients, you might be understandably confused by the current mishmash of guidelines with different blood pressure targets. But as chaotic as things are, at least it’s not the 1930s, when you might hear John Hay give a lecture to the British Medical Association and say, “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.”
Yeah, he said that. But what happened in the 1930s stays in the 1930s. And now we can at least agree that we should be treating high blood pressure. But what’s the goal we should be aiming for? This is On Second Thought.
We’ve come a long way since FDR was recording blood pressures of 200 and his doctor prescribed him barbiturates and massage therapy.
That s#$# don’t fly no more. Over the past hundred years, we have become much more aggressive in treating blood pressure. Remember the Oslo study? It defined mild hypertension as a blood pressure between 150 and 180 mm Hg. Now, those numbers send people screaming to the emergency room. So, let’s acknowledge that things are substantially better than they once were. Let’s agree on that and we can start to heal this nation again.
Before we get into the numbers, when we’re treating blood pressure, let’s make a few points about measuring it. Obviously, to treat something, you have to measure it properly. Two recent trials have illustrated that these details matter a lot.
The Cuff(SZ) randomized crossover trial — and it took me a minute to realize that Cuff(SZ) meant cuff size, so bravo, Ishigami et al — showed that picking the wrong cuff size could affect BP measurements by 4.5 points if you were one size off. If you were two sizes too small, you overestimated BP by almost 20 points.
Add on here another recent study, the ARMS crossover randomized clinical trial, looking at how arm position affected BP measures. If the arm was resting on your lap or hanging by your side, that overestimated blood pressure by 4 and 6.5 points. So sometimes you have to remember the fundamentals: cuff size, arm position — it might make the difference between increasing or maintaining the patient’s meds.
But on to the main show. What numbers should we be aiming for? We no longer live in the “BP 200, the president’s going to have a stroke” world of the 1940s, and even a BP of 150 is considered quite high these days. Studies like the MRC trial, INVEST, and SPRINT have pushed BP targets ever lower. SPRINT, in particular, randomized patients to a blood pressure target under 120 systolic vs under 140 systolic, and the under-120 arm won out with fewer cardiovascular events and lower all-cause mortality.
Pretty definitive slam dunk. But the more intensive treatment came with more hypotension, syncope, and kidney injury, because there is no free lunch in medicine. And ditto with BPROAD, just published in The New England Journal of Medicine and presented at the American Heart Association annual meeting. A diabetic population randomized to 120 vs 140 as a BP target showed that more aggressive treatment was better.
Fewer cardiovascular events, like stroke, but no mortality difference, and more hypotension. So a cardiovascular benefit at the cost of more side effects. Now, like all cardiologists, my motto is “Save the heart and screw the kidney.” But if you do care about the other organs in this meat sack that we call a human body, the question you need to wrestle with is, how much do you value cardiovascular protection vs how willing are you to tolerate side effects?
Hypotension may not sound dangerous, but gravity is an unforgiving mistress. If you painstakingly compile the summary of the various BP guidelines for easy perusal, you would notice something critical: One, I have too much free time on my hands; two, the disagreements are not really all that profound.
Arguing about 120 vs 130 vs 140 is not the same as saying, “Drugs schmugs; a good massage will fix what ails you, and here are some addictive sleeping pills for good measure.” Physicians from the 1930s were a little sketchy. So much of this controversy is about how you define high-risk patients and what are the age cutoffs.
Basically, the cardiovascular guidelines say, “Treat them all and let God sort it out” because they care about cardiovascular events and are concerned about cardiovascular endpoints. Whereas general practice guidelines put more emphasis on potential side effects and admittedly tend to treat a not so high-risk population, so they have laxer targets.
A 2014 analysis from the Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration [The Lancet] had a good mathematical way of explaining this problem. Now, lowering blood pressure is obviously a good thing. That prevents heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure, and all that. Please don’t let hypertension denialism become a thing.
Let’s start with the basics. Treating high blood pressure led to a 15% to 18% decrease in cardiovascular events, pretty consistently across all risk categories, and other analyses have found that every 5-point decrease in blood pressure gives you about a 10% decrease in major cardiovascular events on the relative-risk scale.
While the benefits are pretty consistent across all groups, that difference in baseline risk translates into different absolute benefits. In the Lancet paper, when the population was divided into four different groups based on their cardiovascular risk, the absolute risk reduction in the lowest-risk group was 14 fewer cardiovascular events if you treat 1000 patients for 5 years.
With each higher-risk group, it was 20 fewer, 24 fewer, and 38 fewer. At the lowest-risk group, the number needed to treat was 71, 50, 42, and 26 fewer cardiovascular events with 5 years of treatment.
And herein lies the secret to the disagreement: If you have a high-risk patient, there is a big benefit to bringing that blood pressure down from 135 to 130. Whereas for a low-risk patient, it probably doesn’t matter as much. And the cardiovascular benefits are going to be offset by the side effects and the risks for hypotension.
Of course, there’s a simple solution to this dilemma: Just speak to the patient in front of you. Treat high blood pressure, and if your patient’s blood pressure drops or they get dizzy or have fainting spells, then just ease up on the meds. It’s not rocket science; it’s just cardiology.
Arguing about five millimeters of mercury of blood pressure is probably less important from the public health perspective than the fact that tens of millions of people in the United States are unaware that they have hypertension, and even those diagnosed are being inadequately treated.
So, let’s all do better as a medical community. Nobody should have untreated hypertension in this day and age. It’s not the 1930s.
Dr Labos, Cardiologist, Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Blood pressure. If you’re a primary care provider trying to do right by your patients, you might be understandably confused by the current mishmash of guidelines with different blood pressure targets. But as chaotic as things are, at least it’s not the 1930s, when you might hear John Hay give a lecture to the British Medical Association and say, “The greatest danger to a man with high blood pressure lies in its discovery, because then some fool is certain to try and reduce it.”
Yeah, he said that. But what happened in the 1930s stays in the 1930s. And now we can at least agree that we should be treating high blood pressure. But what’s the goal we should be aiming for? This is On Second Thought.
We’ve come a long way since FDR was recording blood pressures of 200 and his doctor prescribed him barbiturates and massage therapy.
That s#$# don’t fly no more. Over the past hundred years, we have become much more aggressive in treating blood pressure. Remember the Oslo study? It defined mild hypertension as a blood pressure between 150 and 180 mm Hg. Now, those numbers send people screaming to the emergency room. So, let’s acknowledge that things are substantially better than they once were. Let’s agree on that and we can start to heal this nation again.
Before we get into the numbers, when we’re treating blood pressure, let’s make a few points about measuring it. Obviously, to treat something, you have to measure it properly. Two recent trials have illustrated that these details matter a lot.
The Cuff(SZ) randomized crossover trial — and it took me a minute to realize that Cuff(SZ) meant cuff size, so bravo, Ishigami et al — showed that picking the wrong cuff size could affect BP measurements by 4.5 points if you were one size off. If you were two sizes too small, you overestimated BP by almost 20 points.
Add on here another recent study, the ARMS crossover randomized clinical trial, looking at how arm position affected BP measures. If the arm was resting on your lap or hanging by your side, that overestimated blood pressure by 4 and 6.5 points. So sometimes you have to remember the fundamentals: cuff size, arm position — it might make the difference between increasing or maintaining the patient’s meds.
But on to the main show. What numbers should we be aiming for? We no longer live in the “BP 200, the president’s going to have a stroke” world of the 1940s, and even a BP of 150 is considered quite high these days. Studies like the MRC trial, INVEST, and SPRINT have pushed BP targets ever lower. SPRINT, in particular, randomized patients to a blood pressure target under 120 systolic vs under 140 systolic, and the under-120 arm won out with fewer cardiovascular events and lower all-cause mortality.
Pretty definitive slam dunk. But the more intensive treatment came with more hypotension, syncope, and kidney injury, because there is no free lunch in medicine. And ditto with BPROAD, just published in The New England Journal of Medicine and presented at the American Heart Association annual meeting. A diabetic population randomized to 120 vs 140 as a BP target showed that more aggressive treatment was better.
Fewer cardiovascular events, like stroke, but no mortality difference, and more hypotension. So a cardiovascular benefit at the cost of more side effects. Now, like all cardiologists, my motto is “Save the heart and screw the kidney.” But if you do care about the other organs in this meat sack that we call a human body, the question you need to wrestle with is, how much do you value cardiovascular protection vs how willing are you to tolerate side effects?
Hypotension may not sound dangerous, but gravity is an unforgiving mistress. If you painstakingly compile the summary of the various BP guidelines for easy perusal, you would notice something critical: One, I have too much free time on my hands; two, the disagreements are not really all that profound.
Arguing about 120 vs 130 vs 140 is not the same as saying, “Drugs schmugs; a good massage will fix what ails you, and here are some addictive sleeping pills for good measure.” Physicians from the 1930s were a little sketchy. So much of this controversy is about how you define high-risk patients and what are the age cutoffs.
Basically, the cardiovascular guidelines say, “Treat them all and let God sort it out” because they care about cardiovascular events and are concerned about cardiovascular endpoints. Whereas general practice guidelines put more emphasis on potential side effects and admittedly tend to treat a not so high-risk population, so they have laxer targets.
A 2014 analysis from the Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration [The Lancet] had a good mathematical way of explaining this problem. Now, lowering blood pressure is obviously a good thing. That prevents heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure, and all that. Please don’t let hypertension denialism become a thing.
Let’s start with the basics. Treating high blood pressure led to a 15% to 18% decrease in cardiovascular events, pretty consistently across all risk categories, and other analyses have found that every 5-point decrease in blood pressure gives you about a 10% decrease in major cardiovascular events on the relative-risk scale.
While the benefits are pretty consistent across all groups, that difference in baseline risk translates into different absolute benefits. In the Lancet paper, when the population was divided into four different groups based on their cardiovascular risk, the absolute risk reduction in the lowest-risk group was 14 fewer cardiovascular events if you treat 1000 patients for 5 years.
With each higher-risk group, it was 20 fewer, 24 fewer, and 38 fewer. At the lowest-risk group, the number needed to treat was 71, 50, 42, and 26 fewer cardiovascular events with 5 years of treatment.
And herein lies the secret to the disagreement: If you have a high-risk patient, there is a big benefit to bringing that blood pressure down from 135 to 130. Whereas for a low-risk patient, it probably doesn’t matter as much. And the cardiovascular benefits are going to be offset by the side effects and the risks for hypotension.
Of course, there’s a simple solution to this dilemma: Just speak to the patient in front of you. Treat high blood pressure, and if your patient’s blood pressure drops or they get dizzy or have fainting spells, then just ease up on the meds. It’s not rocket science; it’s just cardiology.
Arguing about five millimeters of mercury of blood pressure is probably less important from the public health perspective than the fact that tens of millions of people in the United States are unaware that they have hypertension, and even those diagnosed are being inadequately treated.
So, let’s all do better as a medical community. Nobody should have untreated hypertension in this day and age. It’s not the 1930s.
Dr Labos, Cardiologist, Kirkland Medical Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical Education and Firearm-Related Deaths
For the third straight year, firearms killed more children and teens than any other cause, including motor vehicle crashes and cancer. The population-wide toll taken by guns is equally as discouraging. Finally, this elephant in the room is getting some attention from the medical community, but the voices asking for change have most recently been coming from medical students who feel that gun violence deserves to be given a larger role in their education. It’s unclear why this plea is coming from the younger end of the medical community. It may be that, unlike most of their older instructors, these 18- to 25-year-olds have grown up under the growing threat of school shootings and become uncomfortably accustomed to active shooter drills.
Should We Look to Medical School for Answers?
But, does the medical community need to take gun violence more seriously than the rest of the population? What should our response look like? To answer those questions we need to take several steps back to view the bigger picture.
Is the medical community more responsible for this current situation than any other segment of the population? Do physicians bear any more culpability than publishers who sell gun-related magazines? Since its inception pediatrics has taken on the role of advocate for children and their health and well-being. But, is there more we can and should do other than turn up the volume on our advocacy?
While still taking the longer view, let’s ask ourselves what the role of medical school should be. Not just with respect to gun violence but in producing physicians and healthcare providers. We are approaching a crisis in primary care as it loses appeal with physicians at both ends of the age continuum. It could be because it pays poorly — certainly in relation to the cost of medical school — or because the awareness that if done well primary care requires a commitment that is difficult to square with many individuals’ lifestyle expectations.
Is the traditional medical school the right place to be training primary care providers? Medical school is currently aimed at broad and deep exposure. The student will be exposed to the all the diseases to which he or she might be seeing anywhere in the world and at the same time will have learned the mechanisms down to the cellular level that lies behind that pathology. Does a primary care pediatrician practicing in a small city or suburbia need that depth of training? He or she might benefit from some breadth. But maybe it should be focused on socioeconomic and geographic population the doctor is likely to see. This is particularly true for gun-related deaths.
Returning our attention to gun violence and its relation to healthcare, let’s ask ourselves what role the traditional medical school should play. Should it be a breeding ground for gun control advocates? When physicians speak people tend to listen but our effectiveness on issues such as immunizations and gun control has not been what many have hoped for. The supply of guns available to the public in this country is staggering and certainly contributes to gun-related injuries and death. However, I’m afraid that making a significant dent in that supply, given our political history and current climate, is an issue whose ship has sailed.
On the other hand, as gun advocates are often quoted as saying, “it’s not guns that kill, it’s people.” We don’t need to go into to the fallacy of this argument, but it gives us a starting point from which a medical school might focus its efforts on addressing the fallout from gun violence. A curriculum that begins with a presentation of the grizzly statistics and moves on to research about gun-related mental health issues and the social environments that breed violence makes good sense. Recanting the depressing history of how our society got to this place, in which guns outnumber people, should be part of the undergraduate curriculum.
Addressing the specifics of gun safety and suicide prevention in general with families and individuals would be more appropriate during clinical specialty training.
How big a chunk of the curriculum should be committed to gun violence and its fallout? Some of the call for change seems to be suggesting a semester-long course. However, we must accept the reality that instructional time in medical school is a finite asset. Although gunshots are the leading cause of death in children, how effective will even the most cleverly crafted curriculum be in moving the needle on the embarrassing data?
Given what is known about the problem, a day, or at most a week would be sufficient in class time. This could include personal presentations by victims or family members. I’m sure there are some who would see that as insufficient. But I see it as realistic. For the large urban schools, observing an evening shift in the trauma unit of an ER could be a potent addition.
Beyond this, a commitment by the school to host seminars and workshops devoted to gun violence could be an important component. It might also be helpful for a school or training program to promote the habit of whenever an instructor is introducing a potentially fatal disease to the students for the first time, he or she would begin with “To put this in perspective, you should remember that xxx thousand children die of gunshot wounds every year.”
Unfortunately, like obesity, gun-related deaths and injuries are the result of our society’s failure to muster the political will to act in our best interest as a nation. The medical community is left to clean up the collateral damage. There is always more that we could do, but we must be thoughtful in how we invest our energies in the effort.
Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
For the third straight year, firearms killed more children and teens than any other cause, including motor vehicle crashes and cancer. The population-wide toll taken by guns is equally as discouraging. Finally, this elephant in the room is getting some attention from the medical community, but the voices asking for change have most recently been coming from medical students who feel that gun violence deserves to be given a larger role in their education. It’s unclear why this plea is coming from the younger end of the medical community. It may be that, unlike most of their older instructors, these 18- to 25-year-olds have grown up under the growing threat of school shootings and become uncomfortably accustomed to active shooter drills.
Should We Look to Medical School for Answers?
But, does the medical community need to take gun violence more seriously than the rest of the population? What should our response look like? To answer those questions we need to take several steps back to view the bigger picture.
Is the medical community more responsible for this current situation than any other segment of the population? Do physicians bear any more culpability than publishers who sell gun-related magazines? Since its inception pediatrics has taken on the role of advocate for children and their health and well-being. But, is there more we can and should do other than turn up the volume on our advocacy?
While still taking the longer view, let’s ask ourselves what the role of medical school should be. Not just with respect to gun violence but in producing physicians and healthcare providers. We are approaching a crisis in primary care as it loses appeal with physicians at both ends of the age continuum. It could be because it pays poorly — certainly in relation to the cost of medical school — or because the awareness that if done well primary care requires a commitment that is difficult to square with many individuals’ lifestyle expectations.
Is the traditional medical school the right place to be training primary care providers? Medical school is currently aimed at broad and deep exposure. The student will be exposed to the all the diseases to which he or she might be seeing anywhere in the world and at the same time will have learned the mechanisms down to the cellular level that lies behind that pathology. Does a primary care pediatrician practicing in a small city or suburbia need that depth of training? He or she might benefit from some breadth. But maybe it should be focused on socioeconomic and geographic population the doctor is likely to see. This is particularly true for gun-related deaths.
Returning our attention to gun violence and its relation to healthcare, let’s ask ourselves what role the traditional medical school should play. Should it be a breeding ground for gun control advocates? When physicians speak people tend to listen but our effectiveness on issues such as immunizations and gun control has not been what many have hoped for. The supply of guns available to the public in this country is staggering and certainly contributes to gun-related injuries and death. However, I’m afraid that making a significant dent in that supply, given our political history and current climate, is an issue whose ship has sailed.
On the other hand, as gun advocates are often quoted as saying, “it’s not guns that kill, it’s people.” We don’t need to go into to the fallacy of this argument, but it gives us a starting point from which a medical school might focus its efforts on addressing the fallout from gun violence. A curriculum that begins with a presentation of the grizzly statistics and moves on to research about gun-related mental health issues and the social environments that breed violence makes good sense. Recanting the depressing history of how our society got to this place, in which guns outnumber people, should be part of the undergraduate curriculum.
Addressing the specifics of gun safety and suicide prevention in general with families and individuals would be more appropriate during clinical specialty training.
How big a chunk of the curriculum should be committed to gun violence and its fallout? Some of the call for change seems to be suggesting a semester-long course. However, we must accept the reality that instructional time in medical school is a finite asset. Although gunshots are the leading cause of death in children, how effective will even the most cleverly crafted curriculum be in moving the needle on the embarrassing data?
Given what is known about the problem, a day, or at most a week would be sufficient in class time. This could include personal presentations by victims or family members. I’m sure there are some who would see that as insufficient. But I see it as realistic. For the large urban schools, observing an evening shift in the trauma unit of an ER could be a potent addition.
Beyond this, a commitment by the school to host seminars and workshops devoted to gun violence could be an important component. It might also be helpful for a school or training program to promote the habit of whenever an instructor is introducing a potentially fatal disease to the students for the first time, he or she would begin with “To put this in perspective, you should remember that xxx thousand children die of gunshot wounds every year.”
Unfortunately, like obesity, gun-related deaths and injuries are the result of our society’s failure to muster the political will to act in our best interest as a nation. The medical community is left to clean up the collateral damage. There is always more that we could do, but we must be thoughtful in how we invest our energies in the effort.
Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
For the third straight year, firearms killed more children and teens than any other cause, including motor vehicle crashes and cancer. The population-wide toll taken by guns is equally as discouraging. Finally, this elephant in the room is getting some attention from the medical community, but the voices asking for change have most recently been coming from medical students who feel that gun violence deserves to be given a larger role in their education. It’s unclear why this plea is coming from the younger end of the medical community. It may be that, unlike most of their older instructors, these 18- to 25-year-olds have grown up under the growing threat of school shootings and become uncomfortably accustomed to active shooter drills.
Should We Look to Medical School for Answers?
But, does the medical community need to take gun violence more seriously than the rest of the population? What should our response look like? To answer those questions we need to take several steps back to view the bigger picture.
Is the medical community more responsible for this current situation than any other segment of the population? Do physicians bear any more culpability than publishers who sell gun-related magazines? Since its inception pediatrics has taken on the role of advocate for children and their health and well-being. But, is there more we can and should do other than turn up the volume on our advocacy?
While still taking the longer view, let’s ask ourselves what the role of medical school should be. Not just with respect to gun violence but in producing physicians and healthcare providers. We are approaching a crisis in primary care as it loses appeal with physicians at both ends of the age continuum. It could be because it pays poorly — certainly in relation to the cost of medical school — or because the awareness that if done well primary care requires a commitment that is difficult to square with many individuals’ lifestyle expectations.
Is the traditional medical school the right place to be training primary care providers? Medical school is currently aimed at broad and deep exposure. The student will be exposed to the all the diseases to which he or she might be seeing anywhere in the world and at the same time will have learned the mechanisms down to the cellular level that lies behind that pathology. Does a primary care pediatrician practicing in a small city or suburbia need that depth of training? He or she might benefit from some breadth. But maybe it should be focused on socioeconomic and geographic population the doctor is likely to see. This is particularly true for gun-related deaths.
Returning our attention to gun violence and its relation to healthcare, let’s ask ourselves what role the traditional medical school should play. Should it be a breeding ground for gun control advocates? When physicians speak people tend to listen but our effectiveness on issues such as immunizations and gun control has not been what many have hoped for. The supply of guns available to the public in this country is staggering and certainly contributes to gun-related injuries and death. However, I’m afraid that making a significant dent in that supply, given our political history and current climate, is an issue whose ship has sailed.
On the other hand, as gun advocates are often quoted as saying, “it’s not guns that kill, it’s people.” We don’t need to go into to the fallacy of this argument, but it gives us a starting point from which a medical school might focus its efforts on addressing the fallout from gun violence. A curriculum that begins with a presentation of the grizzly statistics and moves on to research about gun-related mental health issues and the social environments that breed violence makes good sense. Recanting the depressing history of how our society got to this place, in which guns outnumber people, should be part of the undergraduate curriculum.
Addressing the specifics of gun safety and suicide prevention in general with families and individuals would be more appropriate during clinical specialty training.
How big a chunk of the curriculum should be committed to gun violence and its fallout? Some of the call for change seems to be suggesting a semester-long course. However, we must accept the reality that instructional time in medical school is a finite asset. Although gunshots are the leading cause of death in children, how effective will even the most cleverly crafted curriculum be in moving the needle on the embarrassing data?
Given what is known about the problem, a day, or at most a week would be sufficient in class time. This could include personal presentations by victims or family members. I’m sure there are some who would see that as insufficient. But I see it as realistic. For the large urban schools, observing an evening shift in the trauma unit of an ER could be a potent addition.
Beyond this, a commitment by the school to host seminars and workshops devoted to gun violence could be an important component. It might also be helpful for a school or training program to promote the habit of whenever an instructor is introducing a potentially fatal disease to the students for the first time, he or she would begin with “To put this in perspective, you should remember that xxx thousand children die of gunshot wounds every year.”
Unfortunately, like obesity, gun-related deaths and injuries are the result of our society’s failure to muster the political will to act in our best interest as a nation. The medical community is left to clean up the collateral damage. There is always more that we could do, but we must be thoughtful in how we invest our energies in the effort.
Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
A Cancer Patient’s Bittersweet Reminder
Recently, a 40-year-old woman took to Facebook to announce that she had died.
Rachel Davies, of Wales, wrote: “If you’re reading this, then it means I’m no longer here. What a life I’ve had, and surprisingly, since cancer entered my life. When I look through my photos, I’ve done and seen so much since cancer, and probably some of my best memories are from this period. In so many ways, I have to thank it for learning how to live fully. What I wish is that everyone can experience the same but without needing cancer. Get out there, experience life fully, and wear that dress!!! I’m so sad to leave my family and friends, I wish I never had to go. I’m so grateful to have had Charlie young so that I’ve watched him grow into the man he is today. I’m unbelievably proud of him. I am thankful I had the opportunity to have Kacey and Jacob in my life. Lastly, I was blessed to meet the love of my life, my husband, and my best friend. I have no regrets, I have had a wonderful life. So to all of you, don’t be sad I’ve gone. Live your life and live it well. Love, Rachel x.”
I didn’t know Ms. Davies, but am likely among many who wish I had. In a terrible situation she kept trying.
She had HER2 metastatic breast cancer, which can respond to the drug Enhertu (trastuzumab). Unfortunately, she never had the chance, because it wasn’t available to her in Wales. In the United Kingdom it’s available only in Scotland.
I’m not saying it was a cure. Statistically, it likely would have bought her another 6 months of family time. But that’s still another half year.
I’m not blaming the Welsh NHS, though they made the decision not to cover it because of cost. The jobs of such committees is a thankless one, trying to decide where the limited money goes — vaccines for many children that are proven to lessen morbidity and mortality over the course of a lifetime, or to add 6 months to the lives of comparatively fewer women with HER2 metastatic breast cancer.
I’m not blaming the company that makes Enhertu, though it was the cost that kept her from getting it. Bringing a drug to market, with all the labs and clinical research behind it, ain’t cheap. If the company can’t keep the lights on they’re not going to able to develop future pharmaceuticals to help others, though I do wonder if a better price could have been negotiated. (I’m not trying to justify the salaries of insurance CEOs — don’t even get me started on those.)
Money is always limited, and human suffering is infinite. Every health care organization, public or private, has to face that simple fact. There is no right place to draw the line, so we use the greatest good for the greatest many as our best guess.
In her last post, though, Ms. Davies didn’t dwell on any of this. She reflected on her joys and blessings, and encouraged others to live life fully. Things we should all focus on.
Thank you, Ms. Davies, for the reminder.
Allan M. Block, MD, has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Recently, a 40-year-old woman took to Facebook to announce that she had died.
Rachel Davies, of Wales, wrote: “If you’re reading this, then it means I’m no longer here. What a life I’ve had, and surprisingly, since cancer entered my life. When I look through my photos, I’ve done and seen so much since cancer, and probably some of my best memories are from this period. In so many ways, I have to thank it for learning how to live fully. What I wish is that everyone can experience the same but without needing cancer. Get out there, experience life fully, and wear that dress!!! I’m so sad to leave my family and friends, I wish I never had to go. I’m so grateful to have had Charlie young so that I’ve watched him grow into the man he is today. I’m unbelievably proud of him. I am thankful I had the opportunity to have Kacey and Jacob in my life. Lastly, I was blessed to meet the love of my life, my husband, and my best friend. I have no regrets, I have had a wonderful life. So to all of you, don’t be sad I’ve gone. Live your life and live it well. Love, Rachel x.”
I didn’t know Ms. Davies, but am likely among many who wish I had. In a terrible situation she kept trying.
She had HER2 metastatic breast cancer, which can respond to the drug Enhertu (trastuzumab). Unfortunately, she never had the chance, because it wasn’t available to her in Wales. In the United Kingdom it’s available only in Scotland.
I’m not saying it was a cure. Statistically, it likely would have bought her another 6 months of family time. But that’s still another half year.
I’m not blaming the Welsh NHS, though they made the decision not to cover it because of cost. The jobs of such committees is a thankless one, trying to decide where the limited money goes — vaccines for many children that are proven to lessen morbidity and mortality over the course of a lifetime, or to add 6 months to the lives of comparatively fewer women with HER2 metastatic breast cancer.
I’m not blaming the company that makes Enhertu, though it was the cost that kept her from getting it. Bringing a drug to market, with all the labs and clinical research behind it, ain’t cheap. If the company can’t keep the lights on they’re not going to able to develop future pharmaceuticals to help others, though I do wonder if a better price could have been negotiated. (I’m not trying to justify the salaries of insurance CEOs — don’t even get me started on those.)
Money is always limited, and human suffering is infinite. Every health care organization, public or private, has to face that simple fact. There is no right place to draw the line, so we use the greatest good for the greatest many as our best guess.
In her last post, though, Ms. Davies didn’t dwell on any of this. She reflected on her joys and blessings, and encouraged others to live life fully. Things we should all focus on.
Thank you, Ms. Davies, for the reminder.
Allan M. Block, MD, has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Recently, a 40-year-old woman took to Facebook to announce that she had died.
Rachel Davies, of Wales, wrote: “If you’re reading this, then it means I’m no longer here. What a life I’ve had, and surprisingly, since cancer entered my life. When I look through my photos, I’ve done and seen so much since cancer, and probably some of my best memories are from this period. In so many ways, I have to thank it for learning how to live fully. What I wish is that everyone can experience the same but without needing cancer. Get out there, experience life fully, and wear that dress!!! I’m so sad to leave my family and friends, I wish I never had to go. I’m so grateful to have had Charlie young so that I’ve watched him grow into the man he is today. I’m unbelievably proud of him. I am thankful I had the opportunity to have Kacey and Jacob in my life. Lastly, I was blessed to meet the love of my life, my husband, and my best friend. I have no regrets, I have had a wonderful life. So to all of you, don’t be sad I’ve gone. Live your life and live it well. Love, Rachel x.”
I didn’t know Ms. Davies, but am likely among many who wish I had. In a terrible situation she kept trying.
She had HER2 metastatic breast cancer, which can respond to the drug Enhertu (trastuzumab). Unfortunately, she never had the chance, because it wasn’t available to her in Wales. In the United Kingdom it’s available only in Scotland.
I’m not saying it was a cure. Statistically, it likely would have bought her another 6 months of family time. But that’s still another half year.
I’m not blaming the Welsh NHS, though they made the decision not to cover it because of cost. The jobs of such committees is a thankless one, trying to decide where the limited money goes — vaccines for many children that are proven to lessen morbidity and mortality over the course of a lifetime, or to add 6 months to the lives of comparatively fewer women with HER2 metastatic breast cancer.
I’m not blaming the company that makes Enhertu, though it was the cost that kept her from getting it. Bringing a drug to market, with all the labs and clinical research behind it, ain’t cheap. If the company can’t keep the lights on they’re not going to able to develop future pharmaceuticals to help others, though I do wonder if a better price could have been negotiated. (I’m not trying to justify the salaries of insurance CEOs — don’t even get me started on those.)
Money is always limited, and human suffering is infinite. Every health care organization, public or private, has to face that simple fact. There is no right place to draw the line, so we use the greatest good for the greatest many as our best guess.
In her last post, though, Ms. Davies didn’t dwell on any of this. She reflected on her joys and blessings, and encouraged others to live life fully. Things we should all focus on.
Thank you, Ms. Davies, for the reminder.
Allan M. Block, MD, has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.




