User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
The Bad News Behind the Rise in Locum Tenens
I’ve worked locum tenens off and on since 1982. Flexible schedules allowed me to write several books, pursue a parallel career as a medical journalist, lead medical missions in the Philippines, and develop modest expertise as an underwater photographer.
But the recent rise in locum tenens practitioners signals trouble for medicine.
A Multibillion-Dollar Industry
Roughly 52,000 US doctors work locum tenens full or part time. In annual reports by CHG Healthcare, two thirds of healthcare facilities surveyed report using locums and more than half expect to maintain or increase their use in 2024.
Another measure of the industry’s growth is that membership of The National Association of Locum Tenens Organizations (NALTO), formed in 2001 to lead this fledgling industry, has doubled since 2019. Currently, NALTO has 148 member agencies.
Why Locums?
What used to be the preserve of older physicians transitioning to retirement is now becoming a career choice. According to the 2024 Survey of Locum Tenens Physicians and Advanced Practice Professionals by AMN Healthcare, 81% of respondents said they started taking locum tenens assignments immediately after finishing medical training or in mid-career. What entices doctors to move from place to place, repeatedly adapt to new facilities and electronic medical records, live in cheap hotels, and work without paid vacations, health insurance, or retirement benefits?
Supplemental income is one reason. But the elephant in the room is clearly burnout. Rates of burnout in practicing doctors and physicians-in-training have exceeded 50%. Burnout results in medical errors, malpractice suits, and increased healthcare costs.
A recent Doximity poll of 7590 physicians revealed that 63% would not want their children to pursue a medical career. And in a Medscape survey of 7000 physicians, a third of docs under 40 would not choose medicine again if they had a do-over. If a career in medicine brings high income and privileged status, why do so many physicians regret it and discourage their children from taking the same path?
Where Is Marcus Welby, MD?
Private practice is an endangered species that no one is trying to save. According to a 2022 AMA survey, 44% of physicians owned their practices compared with 76% of physicians in the 1980s. Even fewer younger physicians are choosing private practice. Among physicians under 45 years of age, only 32% owned their practices. Most physicians are now employees, not employers. They have lost control over their duties and work hours.
In 2022, barely 13% of physicians were in solo practice. The iconic Dr Marcus Welby of the 1970s TV series has transmuted from an idealized physician to an implausible figure. (My medical students have never heard of him.)
Hospitals and health systems have purchased many private medical groups. Private-equity companies own close to 1000 physician practices and staff up to 40% of emergency rooms. For these firms, profits are paramount.
Canary in a Coal Mine
Locum tenens offers physicians unprecedented flexibility where they work, when they work, and how much they work. It provides an escape from overwhelming and unsatisfying clinical practice. While some physicians have fled to nonclinical careers, locums physicians can practice medicine without the burdens of administration, hospital politics, and ever-increasing overhead.
The locum tenens paradox is that its successful growth indicates a deteriorating traditional healthcare model. Locum tenens is not the problem, but it’s also not the solution. At best, locums is a pair of crutches that helps the current system limp along.
Healthcare is increasingly controlled by those who prioritize profit, not patients. If physicians become nothing more than complicit cogs in a dysfunctional system, burnout will fester. The profession will fail to attract the best and the brightest, the doctor shortage will increase, and the quality of patient care will decline. Everyone will suffer.
It’s already happening.
Andrew Wilner is an associate professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported conflicts of interest from Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I’ve worked locum tenens off and on since 1982. Flexible schedules allowed me to write several books, pursue a parallel career as a medical journalist, lead medical missions in the Philippines, and develop modest expertise as an underwater photographer.
But the recent rise in locum tenens practitioners signals trouble for medicine.
A Multibillion-Dollar Industry
Roughly 52,000 US doctors work locum tenens full or part time. In annual reports by CHG Healthcare, two thirds of healthcare facilities surveyed report using locums and more than half expect to maintain or increase their use in 2024.
Another measure of the industry’s growth is that membership of The National Association of Locum Tenens Organizations (NALTO), formed in 2001 to lead this fledgling industry, has doubled since 2019. Currently, NALTO has 148 member agencies.
Why Locums?
What used to be the preserve of older physicians transitioning to retirement is now becoming a career choice. According to the 2024 Survey of Locum Tenens Physicians and Advanced Practice Professionals by AMN Healthcare, 81% of respondents said they started taking locum tenens assignments immediately after finishing medical training or in mid-career. What entices doctors to move from place to place, repeatedly adapt to new facilities and electronic medical records, live in cheap hotels, and work without paid vacations, health insurance, or retirement benefits?
Supplemental income is one reason. But the elephant in the room is clearly burnout. Rates of burnout in practicing doctors and physicians-in-training have exceeded 50%. Burnout results in medical errors, malpractice suits, and increased healthcare costs.
A recent Doximity poll of 7590 physicians revealed that 63% would not want their children to pursue a medical career. And in a Medscape survey of 7000 physicians, a third of docs under 40 would not choose medicine again if they had a do-over. If a career in medicine brings high income and privileged status, why do so many physicians regret it and discourage their children from taking the same path?
Where Is Marcus Welby, MD?
Private practice is an endangered species that no one is trying to save. According to a 2022 AMA survey, 44% of physicians owned their practices compared with 76% of physicians in the 1980s. Even fewer younger physicians are choosing private practice. Among physicians under 45 years of age, only 32% owned their practices. Most physicians are now employees, not employers. They have lost control over their duties and work hours.
In 2022, barely 13% of physicians were in solo practice. The iconic Dr Marcus Welby of the 1970s TV series has transmuted from an idealized physician to an implausible figure. (My medical students have never heard of him.)
Hospitals and health systems have purchased many private medical groups. Private-equity companies own close to 1000 physician practices and staff up to 40% of emergency rooms. For these firms, profits are paramount.
Canary in a Coal Mine
Locum tenens offers physicians unprecedented flexibility where they work, when they work, and how much they work. It provides an escape from overwhelming and unsatisfying clinical practice. While some physicians have fled to nonclinical careers, locums physicians can practice medicine without the burdens of administration, hospital politics, and ever-increasing overhead.
The locum tenens paradox is that its successful growth indicates a deteriorating traditional healthcare model. Locum tenens is not the problem, but it’s also not the solution. At best, locums is a pair of crutches that helps the current system limp along.
Healthcare is increasingly controlled by those who prioritize profit, not patients. If physicians become nothing more than complicit cogs in a dysfunctional system, burnout will fester. The profession will fail to attract the best and the brightest, the doctor shortage will increase, and the quality of patient care will decline. Everyone will suffer.
It’s already happening.
Andrew Wilner is an associate professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported conflicts of interest from Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I’ve worked locum tenens off and on since 1982. Flexible schedules allowed me to write several books, pursue a parallel career as a medical journalist, lead medical missions in the Philippines, and develop modest expertise as an underwater photographer.
But the recent rise in locum tenens practitioners signals trouble for medicine.
A Multibillion-Dollar Industry
Roughly 52,000 US doctors work locum tenens full or part time. In annual reports by CHG Healthcare, two thirds of healthcare facilities surveyed report using locums and more than half expect to maintain or increase their use in 2024.
Another measure of the industry’s growth is that membership of The National Association of Locum Tenens Organizations (NALTO), formed in 2001 to lead this fledgling industry, has doubled since 2019. Currently, NALTO has 148 member agencies.
Why Locums?
What used to be the preserve of older physicians transitioning to retirement is now becoming a career choice. According to the 2024 Survey of Locum Tenens Physicians and Advanced Practice Professionals by AMN Healthcare, 81% of respondents said they started taking locum tenens assignments immediately after finishing medical training or in mid-career. What entices doctors to move from place to place, repeatedly adapt to new facilities and electronic medical records, live in cheap hotels, and work without paid vacations, health insurance, or retirement benefits?
Supplemental income is one reason. But the elephant in the room is clearly burnout. Rates of burnout in practicing doctors and physicians-in-training have exceeded 50%. Burnout results in medical errors, malpractice suits, and increased healthcare costs.
A recent Doximity poll of 7590 physicians revealed that 63% would not want their children to pursue a medical career. And in a Medscape survey of 7000 physicians, a third of docs under 40 would not choose medicine again if they had a do-over. If a career in medicine brings high income and privileged status, why do so many physicians regret it and discourage their children from taking the same path?
Where Is Marcus Welby, MD?
Private practice is an endangered species that no one is trying to save. According to a 2022 AMA survey, 44% of physicians owned their practices compared with 76% of physicians in the 1980s. Even fewer younger physicians are choosing private practice. Among physicians under 45 years of age, only 32% owned their practices. Most physicians are now employees, not employers. They have lost control over their duties and work hours.
In 2022, barely 13% of physicians were in solo practice. The iconic Dr Marcus Welby of the 1970s TV series has transmuted from an idealized physician to an implausible figure. (My medical students have never heard of him.)
Hospitals and health systems have purchased many private medical groups. Private-equity companies own close to 1000 physician practices and staff up to 40% of emergency rooms. For these firms, profits are paramount.
Canary in a Coal Mine
Locum tenens offers physicians unprecedented flexibility where they work, when they work, and how much they work. It provides an escape from overwhelming and unsatisfying clinical practice. While some physicians have fled to nonclinical careers, locums physicians can practice medicine without the burdens of administration, hospital politics, and ever-increasing overhead.
The locum tenens paradox is that its successful growth indicates a deteriorating traditional healthcare model. Locum tenens is not the problem, but it’s also not the solution. At best, locums is a pair of crutches that helps the current system limp along.
Healthcare is increasingly controlled by those who prioritize profit, not patients. If physicians become nothing more than complicit cogs in a dysfunctional system, burnout will fester. The profession will fail to attract the best and the brightest, the doctor shortage will increase, and the quality of patient care will decline. Everyone will suffer.
It’s already happening.
Andrew Wilner is an associate professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported conflicts of interest from Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How Extreme Rainfall Amplifies Health Risks
Climate change is intensifying the variability of precipitation caused by extreme daily and overall rainfall events. Awareness of the effects of these events is crucial for understanding the complex health consequences of climate change. Physicians have often advised their patients to move to a better climate, and when they did, the recommendation was rarely based on precise scientific knowledge. However, the benefits of changing environments were often so evident that they were indisputable.
Today, advanced models, satellite imagery, and biological approaches such as environmental epigenetics are enhancing our understanding of health risks related to climate change.
Extreme Rainfall and Health
The increase in precipitation variability is linked to climate warming, which leads to higher atmospheric humidity and extreme rainfall events. These manifestations can cause rapid weather changes, increasing interactions with harmful aerosols and raising the risk for various cardiovascular and respiratory conditions. However, a full understanding of the association between rain and health has been hindered by conflicting results and methodological issues (limited geographical locations and short observation durations) in studies.
The association between rainfall intensity and health effects is likely nonlinear. Moderate precipitation can mitigate summer heat and help reduce air pollution, an effect that may lower some environmental health risks. Conversely, intense, low-frequency, short-duration rainfall events can have particularly harmful effects on health, as such events can trigger rapid weather changes, increased proliferation of pathogens, and a rise in the risk of various pollutants, potentially exacerbating health conditions.
Rain and Mortality
Using an intensity-duration-frequency model of three rainfall indices (high intensity, low frequency, short duration), a study published in October 2024 combined these with mortality data from 34 countries or regions. Researchers estimated associations between mortality (all cause, cardiovascular, and respiratory) and rainfall events with different return periods (the average time expected before an extreme event of a certain magnitude occurs again) and crucial effect modifiers, including climatic, socioeconomic, and urban environmental conditions.
The analysis included 109,954,744 deaths from all causes; 31,164,161 cardiovascular deaths; and 11,817,278 respiratory deaths. During the study period, from 1980 to 2020, a total of 50,913 rainfall events with a 1-year return period, 8362 events with a 2-year return period, and 3301 events with a 5-year return period were identified.
The most significant finding was a global positive association between all-cause mortality and extreme rainfall events with a 5-year return period. One day of extreme rainfall with a 5-year return period was associated with a cumulative relative risk (RRc) of 1.08 (95% CI, 1.05-1.11) for daily mortality from all causes. Rainfall events with a 2-year return period were associated with increased daily respiratory mortality (RRc, 1.14), while no significant effect was observed for cardiovascular mortality during the same period. Rainfall events with a 5-year return period were associated with an increased risk for both cardiovascular mortality (RRc, 1.05) and respiratory mortality (RRc, 1.29), with the respiratory mortality being significantly higher.
Points of Concern
According to the authors, moderate to high rainfall can exert protective effects through two main mechanisms: Improving air quality (rainfall can reduce the concentration of particulate matter 2.5 cm in diameter or less in the atmosphere) and behavioral changes in people (more time spent in enclosed environments, reducing direct exposure to outdoor air pollution and nonoptimal temperatures). As rainfall intensity increases, the initial protective effects may be overshadowed by a cascade of negative impacts including:
- Critical resource disruptions: Intense rainfall can cause severe disruptions to access to healthcare, infrastructure damage including power outages, and compromised water and food quality.
- Physiological effects: Increased humidity levels facilitate the growth of airborne pathogens, potentially triggering allergic reactions and respiratory issues, particularly in vulnerable individuals. Rapid shifts in atmospheric pressure and temperature fluctuations can lead to cardiovascular and respiratory complications.
- Indirect effects: Extreme rainfall can have profound effects on mental health, inducing stress and anxiety that may exacerbate pre-existing mental health conditions and indirectly contribute to increased overall mortality from nonexternal causes.
The intensity-response curves for the health effects of heavy rainfall showed a nonlinear trend, transitioning from a protective effect at moderate levels of rainfall to a risk for severe harm when rainfall intensity became extreme. Additionally, the significant effects of extreme events were modified by various types of climate and were more pronounced in areas characterized by low variability in precipitation or sparse vegetation cover.
The study demonstrated that various local factors, such as climatic conditions, climate type, and vegetation cover, can potentially influence cardiovascular and respiratory mortality and all-cause mortality related to precipitation. The findings may help physicians convey to their patients the impact of climate change on their health.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Climate change is intensifying the variability of precipitation caused by extreme daily and overall rainfall events. Awareness of the effects of these events is crucial for understanding the complex health consequences of climate change. Physicians have often advised their patients to move to a better climate, and when they did, the recommendation was rarely based on precise scientific knowledge. However, the benefits of changing environments were often so evident that they were indisputable.
Today, advanced models, satellite imagery, and biological approaches such as environmental epigenetics are enhancing our understanding of health risks related to climate change.
Extreme Rainfall and Health
The increase in precipitation variability is linked to climate warming, which leads to higher atmospheric humidity and extreme rainfall events. These manifestations can cause rapid weather changes, increasing interactions with harmful aerosols and raising the risk for various cardiovascular and respiratory conditions. However, a full understanding of the association between rain and health has been hindered by conflicting results and methodological issues (limited geographical locations and short observation durations) in studies.
The association between rainfall intensity and health effects is likely nonlinear. Moderate precipitation can mitigate summer heat and help reduce air pollution, an effect that may lower some environmental health risks. Conversely, intense, low-frequency, short-duration rainfall events can have particularly harmful effects on health, as such events can trigger rapid weather changes, increased proliferation of pathogens, and a rise in the risk of various pollutants, potentially exacerbating health conditions.
Rain and Mortality
Using an intensity-duration-frequency model of three rainfall indices (high intensity, low frequency, short duration), a study published in October 2024 combined these with mortality data from 34 countries or regions. Researchers estimated associations between mortality (all cause, cardiovascular, and respiratory) and rainfall events with different return periods (the average time expected before an extreme event of a certain magnitude occurs again) and crucial effect modifiers, including climatic, socioeconomic, and urban environmental conditions.
The analysis included 109,954,744 deaths from all causes; 31,164,161 cardiovascular deaths; and 11,817,278 respiratory deaths. During the study period, from 1980 to 2020, a total of 50,913 rainfall events with a 1-year return period, 8362 events with a 2-year return period, and 3301 events with a 5-year return period were identified.
The most significant finding was a global positive association between all-cause mortality and extreme rainfall events with a 5-year return period. One day of extreme rainfall with a 5-year return period was associated with a cumulative relative risk (RRc) of 1.08 (95% CI, 1.05-1.11) for daily mortality from all causes. Rainfall events with a 2-year return period were associated with increased daily respiratory mortality (RRc, 1.14), while no significant effect was observed for cardiovascular mortality during the same period. Rainfall events with a 5-year return period were associated with an increased risk for both cardiovascular mortality (RRc, 1.05) and respiratory mortality (RRc, 1.29), with the respiratory mortality being significantly higher.
Points of Concern
According to the authors, moderate to high rainfall can exert protective effects through two main mechanisms: Improving air quality (rainfall can reduce the concentration of particulate matter 2.5 cm in diameter or less in the atmosphere) and behavioral changes in people (more time spent in enclosed environments, reducing direct exposure to outdoor air pollution and nonoptimal temperatures). As rainfall intensity increases, the initial protective effects may be overshadowed by a cascade of negative impacts including:
- Critical resource disruptions: Intense rainfall can cause severe disruptions to access to healthcare, infrastructure damage including power outages, and compromised water and food quality.
- Physiological effects: Increased humidity levels facilitate the growth of airborne pathogens, potentially triggering allergic reactions and respiratory issues, particularly in vulnerable individuals. Rapid shifts in atmospheric pressure and temperature fluctuations can lead to cardiovascular and respiratory complications.
- Indirect effects: Extreme rainfall can have profound effects on mental health, inducing stress and anxiety that may exacerbate pre-existing mental health conditions and indirectly contribute to increased overall mortality from nonexternal causes.
The intensity-response curves for the health effects of heavy rainfall showed a nonlinear trend, transitioning from a protective effect at moderate levels of rainfall to a risk for severe harm when rainfall intensity became extreme. Additionally, the significant effects of extreme events were modified by various types of climate and were more pronounced in areas characterized by low variability in precipitation or sparse vegetation cover.
The study demonstrated that various local factors, such as climatic conditions, climate type, and vegetation cover, can potentially influence cardiovascular and respiratory mortality and all-cause mortality related to precipitation. The findings may help physicians convey to their patients the impact of climate change on their health.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Climate change is intensifying the variability of precipitation caused by extreme daily and overall rainfall events. Awareness of the effects of these events is crucial for understanding the complex health consequences of climate change. Physicians have often advised their patients to move to a better climate, and when they did, the recommendation was rarely based on precise scientific knowledge. However, the benefits of changing environments were often so evident that they were indisputable.
Today, advanced models, satellite imagery, and biological approaches such as environmental epigenetics are enhancing our understanding of health risks related to climate change.
Extreme Rainfall and Health
The increase in precipitation variability is linked to climate warming, which leads to higher atmospheric humidity and extreme rainfall events. These manifestations can cause rapid weather changes, increasing interactions with harmful aerosols and raising the risk for various cardiovascular and respiratory conditions. However, a full understanding of the association between rain and health has been hindered by conflicting results and methodological issues (limited geographical locations and short observation durations) in studies.
The association between rainfall intensity and health effects is likely nonlinear. Moderate precipitation can mitigate summer heat and help reduce air pollution, an effect that may lower some environmental health risks. Conversely, intense, low-frequency, short-duration rainfall events can have particularly harmful effects on health, as such events can trigger rapid weather changes, increased proliferation of pathogens, and a rise in the risk of various pollutants, potentially exacerbating health conditions.
Rain and Mortality
Using an intensity-duration-frequency model of three rainfall indices (high intensity, low frequency, short duration), a study published in October 2024 combined these with mortality data from 34 countries or regions. Researchers estimated associations between mortality (all cause, cardiovascular, and respiratory) and rainfall events with different return periods (the average time expected before an extreme event of a certain magnitude occurs again) and crucial effect modifiers, including climatic, socioeconomic, and urban environmental conditions.
The analysis included 109,954,744 deaths from all causes; 31,164,161 cardiovascular deaths; and 11,817,278 respiratory deaths. During the study period, from 1980 to 2020, a total of 50,913 rainfall events with a 1-year return period, 8362 events with a 2-year return period, and 3301 events with a 5-year return period were identified.
The most significant finding was a global positive association between all-cause mortality and extreme rainfall events with a 5-year return period. One day of extreme rainfall with a 5-year return period was associated with a cumulative relative risk (RRc) of 1.08 (95% CI, 1.05-1.11) for daily mortality from all causes. Rainfall events with a 2-year return period were associated with increased daily respiratory mortality (RRc, 1.14), while no significant effect was observed for cardiovascular mortality during the same period. Rainfall events with a 5-year return period were associated with an increased risk for both cardiovascular mortality (RRc, 1.05) and respiratory mortality (RRc, 1.29), with the respiratory mortality being significantly higher.
Points of Concern
According to the authors, moderate to high rainfall can exert protective effects through two main mechanisms: Improving air quality (rainfall can reduce the concentration of particulate matter 2.5 cm in diameter or less in the atmosphere) and behavioral changes in people (more time spent in enclosed environments, reducing direct exposure to outdoor air pollution and nonoptimal temperatures). As rainfall intensity increases, the initial protective effects may be overshadowed by a cascade of negative impacts including:
- Critical resource disruptions: Intense rainfall can cause severe disruptions to access to healthcare, infrastructure damage including power outages, and compromised water and food quality.
- Physiological effects: Increased humidity levels facilitate the growth of airborne pathogens, potentially triggering allergic reactions and respiratory issues, particularly in vulnerable individuals. Rapid shifts in atmospheric pressure and temperature fluctuations can lead to cardiovascular and respiratory complications.
- Indirect effects: Extreme rainfall can have profound effects on mental health, inducing stress and anxiety that may exacerbate pre-existing mental health conditions and indirectly contribute to increased overall mortality from nonexternal causes.
The intensity-response curves for the health effects of heavy rainfall showed a nonlinear trend, transitioning from a protective effect at moderate levels of rainfall to a risk for severe harm when rainfall intensity became extreme. Additionally, the significant effects of extreme events were modified by various types of climate and were more pronounced in areas characterized by low variability in precipitation or sparse vegetation cover.
The study demonstrated that various local factors, such as climatic conditions, climate type, and vegetation cover, can potentially influence cardiovascular and respiratory mortality and all-cause mortality related to precipitation. The findings may help physicians convey to their patients the impact of climate change on their health.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Men Wanted: New Efforts to Attract Male Nurses
Only 12% of the nurses providing patient care at hospitals and health clinics today are men. Although the percentage of nurses has increased — men made up just 2.7% of nurses in 1970 — nursing is still considered a “pink collar” profession, a female-dominated field.
“We’ve made strides over the last couple of decades, but [the number of men pursuing nursing careers] is leveling out,” said Jason Dunne, DNP, MSN, RN, chief academic officer at the Arizona College of Nursing, Phoenix. “There continues to be persistent gender stereotypes that [have] discouraged men from entering the profession.”
“The nursing shortage is very real,” Dunne said. “We need to be highly focused on the shortage and look at opportunities to bring diversity into the profession, and one big way to solve it is bringing more men into nursing.”
Representation Matters
Colleges recognize the need to diversify their nursing student population and have turned their attention to increasing the number of men attending informational sessions and career days. Dunne believes, “There is a general lack of awareness of nursing as a career choice [for men].”
The Nursing Consortium of Florida hosts a “Day in the Life of a Nurse” program to introduce high school students to nursing careers, and the University of Virginia School of Nursing invites male nursing students to speak at educational events to promote workforce diversity.
“When I was growing up, the males wouldn’t have been included in those sessions,” said Melissa Gilbert Gomes, PhD, APRN, PMHNP-BC, FNAP, FAAN, associate dean for diversity, equity, and inclusion at the University of Virginia School of Nursing, Charlottesville, Virginia. “It was nice to see their interest and to have a male student there for them to ask questions and to help them see that this could be a place for them.”
Nursing schools have also engaged in other efforts to encourage more men to consider nursing careers, from highlighting male nurses in marketing materials and engaging with men at career fairs to updating course curriculum to include content on men’s health and connecting male nursing students with men in nursing faculty or clinical settings.
Focusing on nursing as a lucrative career choice could also attract more men to the profession. On average, male registered nurses (RNs) make $7300 per year more than their female counterparts due to the gender pay gap. The median wage for male RNs in acute care, cardiology, and perioperative specialties is $90,000 annually.
At the University of Virginia School of Nursing, which the American Association for Men in Nursing (AAMN) named “Best School for Men in Nursing” in 2023, 20% of nursing students are men.
The school has a Men Advancing Nursing club and is in the process of chartering a new AAMN chapter. The goal, according to Gomes, is to create an environment where male nursing students feel represented and supported.
“Valuing the perspective that men bring [to nursing] is important,” she said. “Coming together [and] having that camaraderie and intrinsic motivation to specifically speak to areas that impact men ... is important.”
Promoting Patient Care
Highlighting the diversity of career options within the nursing profession is also essential. RNs can pursue careers in specialties ranging from pediatrics, orthopedics, and occupational health to anesthesia, cardiology, and nephrology. The specialty with the highest number of male RNs tends to be acute care, which encompasses emergency/trauma and medical-surgical.
John Schmidt, DNP, MSN, BSN, faculty member and program lead for the acute care nurse practitioner program at Purdue Global School of Nursing, refers to these specialties as having a high excitement factor.
“Men gravitate to nursing to help people,” he said. “In critical care, there is instant gratification. You see patients get better. It’s the same in the [intensive care unit] and the emergency department. We take care of them and can see how we made a difference.”
When hospitals and health systems create environments that support men in nursing, patients also benefit. Research shows that patients often prefer nurses of the same gender, and a more diverse healthcare workforce has been linked to improved patient outcomes. Reducing gender inequities among nursing staff could also improve job satisfaction and retention rates for men in nursing.
“When you’re in a vulnerable space as a patient ... it’s important to know that your care provider understands you [and] having men as nurses is a part of that,” said Gomes. “Even though patients might not be used to having a male nurse at the bedside, once they have the experience, it challenges preconceived notions [and] that connection is important.”
Hospitals must proactively support men in nursing to achieve the benefits of greater gender diversity in the nursing workforce. Male nurses have fewer role models and report higher levels of loneliness, isolation, and role strain.
Groups such as NYC Men in Nursing and mentorship programs such as Men in Nursing at RUSH University College of Nursing and RUSH University Medical Center, and the North Carolina Healthcare Association Diverse Healthcare Leaders Mentorship Program were designed to provide coaching, education, and networking opportunities and connect men in nursing.
Male nurses, Dunne added, must be role models and must take the lead in changing the conversations about gender roles in nursing. Establishing support systems and mentorship opportunities is instrumental in inspiring men to pursue nursing careers and creating visibility into the profession and “would create a level of parity for men in the profession and encourage them to want to stay in nursing as a long-term career.”
He told this news organization that creating scholarships for men enrolled in nursing school, increasing the involvement of male nurse leaders in recruitment efforts, and updating curriculum to ensure men are reflected in the materials is also essential.
“We’ve got to be willing and open to having the conversations to end the stereotypes that have plagued the profession,” said Dunne. “And we’ve got to push men in nursing to be front and center so folks see that there are opportunities for men in nursing.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Only 12% of the nurses providing patient care at hospitals and health clinics today are men. Although the percentage of nurses has increased — men made up just 2.7% of nurses in 1970 — nursing is still considered a “pink collar” profession, a female-dominated field.
“We’ve made strides over the last couple of decades, but [the number of men pursuing nursing careers] is leveling out,” said Jason Dunne, DNP, MSN, RN, chief academic officer at the Arizona College of Nursing, Phoenix. “There continues to be persistent gender stereotypes that [have] discouraged men from entering the profession.”
“The nursing shortage is very real,” Dunne said. “We need to be highly focused on the shortage and look at opportunities to bring diversity into the profession, and one big way to solve it is bringing more men into nursing.”
Representation Matters
Colleges recognize the need to diversify their nursing student population and have turned their attention to increasing the number of men attending informational sessions and career days. Dunne believes, “There is a general lack of awareness of nursing as a career choice [for men].”
The Nursing Consortium of Florida hosts a “Day in the Life of a Nurse” program to introduce high school students to nursing careers, and the University of Virginia School of Nursing invites male nursing students to speak at educational events to promote workforce diversity.
“When I was growing up, the males wouldn’t have been included in those sessions,” said Melissa Gilbert Gomes, PhD, APRN, PMHNP-BC, FNAP, FAAN, associate dean for diversity, equity, and inclusion at the University of Virginia School of Nursing, Charlottesville, Virginia. “It was nice to see their interest and to have a male student there for them to ask questions and to help them see that this could be a place for them.”
Nursing schools have also engaged in other efforts to encourage more men to consider nursing careers, from highlighting male nurses in marketing materials and engaging with men at career fairs to updating course curriculum to include content on men’s health and connecting male nursing students with men in nursing faculty or clinical settings.
Focusing on nursing as a lucrative career choice could also attract more men to the profession. On average, male registered nurses (RNs) make $7300 per year more than their female counterparts due to the gender pay gap. The median wage for male RNs in acute care, cardiology, and perioperative specialties is $90,000 annually.
At the University of Virginia School of Nursing, which the American Association for Men in Nursing (AAMN) named “Best School for Men in Nursing” in 2023, 20% of nursing students are men.
The school has a Men Advancing Nursing club and is in the process of chartering a new AAMN chapter. The goal, according to Gomes, is to create an environment where male nursing students feel represented and supported.
“Valuing the perspective that men bring [to nursing] is important,” she said. “Coming together [and] having that camaraderie and intrinsic motivation to specifically speak to areas that impact men ... is important.”
Promoting Patient Care
Highlighting the diversity of career options within the nursing profession is also essential. RNs can pursue careers in specialties ranging from pediatrics, orthopedics, and occupational health to anesthesia, cardiology, and nephrology. The specialty with the highest number of male RNs tends to be acute care, which encompasses emergency/trauma and medical-surgical.
John Schmidt, DNP, MSN, BSN, faculty member and program lead for the acute care nurse practitioner program at Purdue Global School of Nursing, refers to these specialties as having a high excitement factor.
“Men gravitate to nursing to help people,” he said. “In critical care, there is instant gratification. You see patients get better. It’s the same in the [intensive care unit] and the emergency department. We take care of them and can see how we made a difference.”
When hospitals and health systems create environments that support men in nursing, patients also benefit. Research shows that patients often prefer nurses of the same gender, and a more diverse healthcare workforce has been linked to improved patient outcomes. Reducing gender inequities among nursing staff could also improve job satisfaction and retention rates for men in nursing.
“When you’re in a vulnerable space as a patient ... it’s important to know that your care provider understands you [and] having men as nurses is a part of that,” said Gomes. “Even though patients might not be used to having a male nurse at the bedside, once they have the experience, it challenges preconceived notions [and] that connection is important.”
Hospitals must proactively support men in nursing to achieve the benefits of greater gender diversity in the nursing workforce. Male nurses have fewer role models and report higher levels of loneliness, isolation, and role strain.
Groups such as NYC Men in Nursing and mentorship programs such as Men in Nursing at RUSH University College of Nursing and RUSH University Medical Center, and the North Carolina Healthcare Association Diverse Healthcare Leaders Mentorship Program were designed to provide coaching, education, and networking opportunities and connect men in nursing.
Male nurses, Dunne added, must be role models and must take the lead in changing the conversations about gender roles in nursing. Establishing support systems and mentorship opportunities is instrumental in inspiring men to pursue nursing careers and creating visibility into the profession and “would create a level of parity for men in the profession and encourage them to want to stay in nursing as a long-term career.”
He told this news organization that creating scholarships for men enrolled in nursing school, increasing the involvement of male nurse leaders in recruitment efforts, and updating curriculum to ensure men are reflected in the materials is also essential.
“We’ve got to be willing and open to having the conversations to end the stereotypes that have plagued the profession,” said Dunne. “And we’ve got to push men in nursing to be front and center so folks see that there are opportunities for men in nursing.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Only 12% of the nurses providing patient care at hospitals and health clinics today are men. Although the percentage of nurses has increased — men made up just 2.7% of nurses in 1970 — nursing is still considered a “pink collar” profession, a female-dominated field.
“We’ve made strides over the last couple of decades, but [the number of men pursuing nursing careers] is leveling out,” said Jason Dunne, DNP, MSN, RN, chief academic officer at the Arizona College of Nursing, Phoenix. “There continues to be persistent gender stereotypes that [have] discouraged men from entering the profession.”
“The nursing shortage is very real,” Dunne said. “We need to be highly focused on the shortage and look at opportunities to bring diversity into the profession, and one big way to solve it is bringing more men into nursing.”
Representation Matters
Colleges recognize the need to diversify their nursing student population and have turned their attention to increasing the number of men attending informational sessions and career days. Dunne believes, “There is a general lack of awareness of nursing as a career choice [for men].”
The Nursing Consortium of Florida hosts a “Day in the Life of a Nurse” program to introduce high school students to nursing careers, and the University of Virginia School of Nursing invites male nursing students to speak at educational events to promote workforce diversity.
“When I was growing up, the males wouldn’t have been included in those sessions,” said Melissa Gilbert Gomes, PhD, APRN, PMHNP-BC, FNAP, FAAN, associate dean for diversity, equity, and inclusion at the University of Virginia School of Nursing, Charlottesville, Virginia. “It was nice to see their interest and to have a male student there for them to ask questions and to help them see that this could be a place for them.”
Nursing schools have also engaged in other efforts to encourage more men to consider nursing careers, from highlighting male nurses in marketing materials and engaging with men at career fairs to updating course curriculum to include content on men’s health and connecting male nursing students with men in nursing faculty or clinical settings.
Focusing on nursing as a lucrative career choice could also attract more men to the profession. On average, male registered nurses (RNs) make $7300 per year more than their female counterparts due to the gender pay gap. The median wage for male RNs in acute care, cardiology, and perioperative specialties is $90,000 annually.
At the University of Virginia School of Nursing, which the American Association for Men in Nursing (AAMN) named “Best School for Men in Nursing” in 2023, 20% of nursing students are men.
The school has a Men Advancing Nursing club and is in the process of chartering a new AAMN chapter. The goal, according to Gomes, is to create an environment where male nursing students feel represented and supported.
“Valuing the perspective that men bring [to nursing] is important,” she said. “Coming together [and] having that camaraderie and intrinsic motivation to specifically speak to areas that impact men ... is important.”
Promoting Patient Care
Highlighting the diversity of career options within the nursing profession is also essential. RNs can pursue careers in specialties ranging from pediatrics, orthopedics, and occupational health to anesthesia, cardiology, and nephrology. The specialty with the highest number of male RNs tends to be acute care, which encompasses emergency/trauma and medical-surgical.
John Schmidt, DNP, MSN, BSN, faculty member and program lead for the acute care nurse practitioner program at Purdue Global School of Nursing, refers to these specialties as having a high excitement factor.
“Men gravitate to nursing to help people,” he said. “In critical care, there is instant gratification. You see patients get better. It’s the same in the [intensive care unit] and the emergency department. We take care of them and can see how we made a difference.”
When hospitals and health systems create environments that support men in nursing, patients also benefit. Research shows that patients often prefer nurses of the same gender, and a more diverse healthcare workforce has been linked to improved patient outcomes. Reducing gender inequities among nursing staff could also improve job satisfaction and retention rates for men in nursing.
“When you’re in a vulnerable space as a patient ... it’s important to know that your care provider understands you [and] having men as nurses is a part of that,” said Gomes. “Even though patients might not be used to having a male nurse at the bedside, once they have the experience, it challenges preconceived notions [and] that connection is important.”
Hospitals must proactively support men in nursing to achieve the benefits of greater gender diversity in the nursing workforce. Male nurses have fewer role models and report higher levels of loneliness, isolation, and role strain.
Groups such as NYC Men in Nursing and mentorship programs such as Men in Nursing at RUSH University College of Nursing and RUSH University Medical Center, and the North Carolina Healthcare Association Diverse Healthcare Leaders Mentorship Program were designed to provide coaching, education, and networking opportunities and connect men in nursing.
Male nurses, Dunne added, must be role models and must take the lead in changing the conversations about gender roles in nursing. Establishing support systems and mentorship opportunities is instrumental in inspiring men to pursue nursing careers and creating visibility into the profession and “would create a level of parity for men in the profession and encourage them to want to stay in nursing as a long-term career.”
He told this news organization that creating scholarships for men enrolled in nursing school, increasing the involvement of male nurse leaders in recruitment efforts, and updating curriculum to ensure men are reflected in the materials is also essential.
“We’ve got to be willing and open to having the conversations to end the stereotypes that have plagued the profession,” said Dunne. “And we’ve got to push men in nursing to be front and center so folks see that there are opportunities for men in nursing.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lawmakers Rush to Stave Off Doctor Pay Cuts as Medicare Finalizes 2025 Rates
Federal lawmakers are rushing to soften the blow of Medicare’s 2025 effective pay cut for doctors in 2025, introducing a bill that could limit the cut. But they have little time to act.
In 2025, the conversion factor used to calculate payment to doctors and hospitals caring for Medicare patients will drop to $32.35, a nearly 3% decrease from the current level.
Congress likely will act before the cuts take effect, said Rep. Larry Bucshon, MD (R-IN), who specialized in cardiothoracic surgery before joining Congress. Lawmakers in past years have typically tinkered with the Medicare physician fee schedule at the last minute, tucking in fixes to December legislative packages and spending bills.
“I’m pretty optimistic that a good portion of the fee cuts will be mitigated and they won’t go through,” Bucshon told this news organization in an interview.
Bruce A. Scott, MD, president of the American Medical Association (AMA) said in a statement that CMS’ release of the final fee schedule on November 1 should trigger serious work on a change to the 2025 Medicare physician fee schedule.
“The fee schedule rule released [on November 1] starts the clock — with January 1 looming,” Scott said. “A legislative remedy will require hard work and compromise. The 66 million patients who rely on Medicare are counting on that.”
Both Bucshon and Scott also joined many lawmakers and medical associations in calling on Congress for a larger overhaul of the Medicare physician fee schedule, well beyond whatever temporary adjustment may be made in the months ahead to avoid or soften the 2025 cuts.
The physician fee schedule sets formulas and rules regarding how the largest US buyer of health services pays the almost 1.3 million clinicians who bill Medicare. Of these, 51% are physicians. The physician fee schedule also covers payments for nurse practitioners, physician assistants, physical therapists, and other health professionals.
Last Major Overhaul Unpopular
There’s broad dissatisfaction with Congress’ last major overhaul of the Medicare physician fee schedule. The 2015 Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) aimed to shift clinicians toward programs tying pay increases to quality measures. But the implementation of that aim through the Merit-based Incentive Payment System is widely considered a disappointment.
MACRA was intended to end the need for annual “doc fixes,” as Congress’ last-minute Medicare adjustments are known. Seventeen such tweaks passed before MACRA took effect.
But MACRA did not include a broad-based inflation adjuster, and some clinicians’ incomes are lagging as inflation rates — and practice costs — have risen. Scott said the Medicare Economic Index, which is a measure used to gauge increases in practice costs for clinicians, is expected to rise by 3.5%.
“To put it bluntly, Medicare plans to pay us less while costs go up. You don’t have to be an economist to know that is an unsustainable trend, though one that has been going on for decades,” Scott said. “For physician practices operating on small margins already, this means it is harder to acquire new equipment, harder to retain staff, harder to take on new Medicare patients, and harder to keep the doors open, particularly in rural and underserved areas.”
In a statement, Jen Brull, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, noted that this likely will be the fifth year in a row that Congress will need to do a patch to prevent cuts in pay to clinicians.
Bucshon, who will retire from the House in January, said he expects Congress to pass legislation tying Medicare payment rates to inflation — eventually.
“People want to find a way to fix this problem, but also do it in a way that does not cut benefits to anyone, and that’s the key,” Bucshon said. “We’re going to have to find a way to make sure that providers are properly reimbursed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal lawmakers are rushing to soften the blow of Medicare’s 2025 effective pay cut for doctors in 2025, introducing a bill that could limit the cut. But they have little time to act.
In 2025, the conversion factor used to calculate payment to doctors and hospitals caring for Medicare patients will drop to $32.35, a nearly 3% decrease from the current level.
Congress likely will act before the cuts take effect, said Rep. Larry Bucshon, MD (R-IN), who specialized in cardiothoracic surgery before joining Congress. Lawmakers in past years have typically tinkered with the Medicare physician fee schedule at the last minute, tucking in fixes to December legislative packages and spending bills.
“I’m pretty optimistic that a good portion of the fee cuts will be mitigated and they won’t go through,” Bucshon told this news organization in an interview.
Bruce A. Scott, MD, president of the American Medical Association (AMA) said in a statement that CMS’ release of the final fee schedule on November 1 should trigger serious work on a change to the 2025 Medicare physician fee schedule.
“The fee schedule rule released [on November 1] starts the clock — with January 1 looming,” Scott said. “A legislative remedy will require hard work and compromise. The 66 million patients who rely on Medicare are counting on that.”
Both Bucshon and Scott also joined many lawmakers and medical associations in calling on Congress for a larger overhaul of the Medicare physician fee schedule, well beyond whatever temporary adjustment may be made in the months ahead to avoid or soften the 2025 cuts.
The physician fee schedule sets formulas and rules regarding how the largest US buyer of health services pays the almost 1.3 million clinicians who bill Medicare. Of these, 51% are physicians. The physician fee schedule also covers payments for nurse practitioners, physician assistants, physical therapists, and other health professionals.
Last Major Overhaul Unpopular
There’s broad dissatisfaction with Congress’ last major overhaul of the Medicare physician fee schedule. The 2015 Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) aimed to shift clinicians toward programs tying pay increases to quality measures. But the implementation of that aim through the Merit-based Incentive Payment System is widely considered a disappointment.
MACRA was intended to end the need for annual “doc fixes,” as Congress’ last-minute Medicare adjustments are known. Seventeen such tweaks passed before MACRA took effect.
But MACRA did not include a broad-based inflation adjuster, and some clinicians’ incomes are lagging as inflation rates — and practice costs — have risen. Scott said the Medicare Economic Index, which is a measure used to gauge increases in practice costs for clinicians, is expected to rise by 3.5%.
“To put it bluntly, Medicare plans to pay us less while costs go up. You don’t have to be an economist to know that is an unsustainable trend, though one that has been going on for decades,” Scott said. “For physician practices operating on small margins already, this means it is harder to acquire new equipment, harder to retain staff, harder to take on new Medicare patients, and harder to keep the doors open, particularly in rural and underserved areas.”
In a statement, Jen Brull, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, noted that this likely will be the fifth year in a row that Congress will need to do a patch to prevent cuts in pay to clinicians.
Bucshon, who will retire from the House in January, said he expects Congress to pass legislation tying Medicare payment rates to inflation — eventually.
“People want to find a way to fix this problem, but also do it in a way that does not cut benefits to anyone, and that’s the key,” Bucshon said. “We’re going to have to find a way to make sure that providers are properly reimbursed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal lawmakers are rushing to soften the blow of Medicare’s 2025 effective pay cut for doctors in 2025, introducing a bill that could limit the cut. But they have little time to act.
In 2025, the conversion factor used to calculate payment to doctors and hospitals caring for Medicare patients will drop to $32.35, a nearly 3% decrease from the current level.
Congress likely will act before the cuts take effect, said Rep. Larry Bucshon, MD (R-IN), who specialized in cardiothoracic surgery before joining Congress. Lawmakers in past years have typically tinkered with the Medicare physician fee schedule at the last minute, tucking in fixes to December legislative packages and spending bills.
“I’m pretty optimistic that a good portion of the fee cuts will be mitigated and they won’t go through,” Bucshon told this news organization in an interview.
Bruce A. Scott, MD, president of the American Medical Association (AMA) said in a statement that CMS’ release of the final fee schedule on November 1 should trigger serious work on a change to the 2025 Medicare physician fee schedule.
“The fee schedule rule released [on November 1] starts the clock — with January 1 looming,” Scott said. “A legislative remedy will require hard work and compromise. The 66 million patients who rely on Medicare are counting on that.”
Both Bucshon and Scott also joined many lawmakers and medical associations in calling on Congress for a larger overhaul of the Medicare physician fee schedule, well beyond whatever temporary adjustment may be made in the months ahead to avoid or soften the 2025 cuts.
The physician fee schedule sets formulas and rules regarding how the largest US buyer of health services pays the almost 1.3 million clinicians who bill Medicare. Of these, 51% are physicians. The physician fee schedule also covers payments for nurse practitioners, physician assistants, physical therapists, and other health professionals.
Last Major Overhaul Unpopular
There’s broad dissatisfaction with Congress’ last major overhaul of the Medicare physician fee schedule. The 2015 Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) aimed to shift clinicians toward programs tying pay increases to quality measures. But the implementation of that aim through the Merit-based Incentive Payment System is widely considered a disappointment.
MACRA was intended to end the need for annual “doc fixes,” as Congress’ last-minute Medicare adjustments are known. Seventeen such tweaks passed before MACRA took effect.
But MACRA did not include a broad-based inflation adjuster, and some clinicians’ incomes are lagging as inflation rates — and practice costs — have risen. Scott said the Medicare Economic Index, which is a measure used to gauge increases in practice costs for clinicians, is expected to rise by 3.5%.
“To put it bluntly, Medicare plans to pay us less while costs go up. You don’t have to be an economist to know that is an unsustainable trend, though one that has been going on for decades,” Scott said. “For physician practices operating on small margins already, this means it is harder to acquire new equipment, harder to retain staff, harder to take on new Medicare patients, and harder to keep the doors open, particularly in rural and underserved areas.”
In a statement, Jen Brull, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, noted that this likely will be the fifth year in a row that Congress will need to do a patch to prevent cuts in pay to clinicians.
Bucshon, who will retire from the House in January, said he expects Congress to pass legislation tying Medicare payment rates to inflation — eventually.
“People want to find a way to fix this problem, but also do it in a way that does not cut benefits to anyone, and that’s the key,” Bucshon said. “We’re going to have to find a way to make sure that providers are properly reimbursed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Social Adversity Increases Mortality Risk in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension
BOSTON — Social adversity is associated with worse survival among patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH), according to a new retrospective study of a New York City population.
A sub-analysis of both HIV+ and HIV– patients showed worse mortality outcomes with social adversity in both groups.
“Almost the majority of patients that we treat have either some social adversity or no insurance or are undocumented, so as a group of residents, we decided to study the impact of these factors on their health and the care that can be provided. We started using the two cohorts and now we keep it going with every new resident,” said Luca Biavati, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
“The presence of any form of socioeconomic disadvantage is negatively impacting care and for a large part of the population, there are some factors that could probably be addressed by either an institutional or hospital policy,” said Dr. Biavati, who is an internal medicine resident at Jacobi Medical Center, New York.
Other factors are more difficult to address, such as lack of education. “[Some patients] don’t understand the gravity of their issue and medical condition until it’s too late, and then they’re not fit enough for the treatment, or just because of the social situation, they cannot qualify for advanced therapies,” said Dr. Biavati.
The researchers established two cohorts: One consisting of patients with HIV and heart failure who may or may not have had PH and one comprising patients with PH with or without HIV and heart failure. In the HIV/heart failure group, PH without social adversity was associated with a nearly threefold increase in all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 2.83; P = .004), whereas PH with social adversity was linked to a more than sevenfold increase in all-cause mortality (HR, 7.14; P < .001). Social adversity without PA was associated with a more than fourfold increase (HR, 4.47; P < .001).
Within the PH cohort, social adversity was associated with lower survival (P < .001). When the researchers broke down the results by types of social adversity, they found statistically significant relationships between greater mortality risk and economic instability within the HIV+ population (HR, 2.59; P = .040), transportation issues within the HIV– population (HR, 12.8; P < .001), and lack of social or family support within both the HIV– (HR, 5.49; P < .001) and the HIV+ population (HR, 2.03; P = .028).
The research has prompted interventions, which are now being studied at the institution, according to Dr. Biavati. “We have a policy of giving medications in bags when we discharge a patient with a social adversity. We literally go to the pharmacy, bring up the bag of medication, and we [put it] in their hands before they leave the hospital. They get a 1- or 3-month supply, depending on the medication, and then we usually discharge them with a clinical appointment already scheduled with either a pulmonary or primary care provider, and we usually call them before every appointment to confirm that they’re coming. That increases the chances of some success, but there’s still a very long way to go,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati was blinded to the results of the intervention, so he could not report on whether it was working. “But I can tell you that I’ve had busier clinics, so hopefully that means that they’re showing up more,” he said.
The problem is complex, according to Sandeep Jain, MD, who moderated the session. “Social adversity means lack of education. Lack of education means lack of compliance. Lack of compliance means what can you do if people are not taking medications? So it’s all matched together. It’s all lack of education and lack of money, lack of family support. And these drugs they have to take every single day. It’s not that easy. It’s very easy for us to say I had antiretroviral treatment for 6 months. It is almost impossible to continue regular treatment for that long [for a patient with social adversity]. You can’t blame them if they aren’t taking treatments. It’s very difficult for them,” said Dr. Jain.
That underscores the need for interventions that can address the needs of patients with social adversity. “We have to [practice] medicine considering the social situation of the patient and not just the medicine that we study in books. That’s kind of what we are faced with every day. We have therapies, and then life happens. It’s much harder to care for those patients,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati and Dr. Jain reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Social adversity is associated with worse survival among patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH), according to a new retrospective study of a New York City population.
A sub-analysis of both HIV+ and HIV– patients showed worse mortality outcomes with social adversity in both groups.
“Almost the majority of patients that we treat have either some social adversity or no insurance or are undocumented, so as a group of residents, we decided to study the impact of these factors on their health and the care that can be provided. We started using the two cohorts and now we keep it going with every new resident,” said Luca Biavati, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
“The presence of any form of socioeconomic disadvantage is negatively impacting care and for a large part of the population, there are some factors that could probably be addressed by either an institutional or hospital policy,” said Dr. Biavati, who is an internal medicine resident at Jacobi Medical Center, New York.
Other factors are more difficult to address, such as lack of education. “[Some patients] don’t understand the gravity of their issue and medical condition until it’s too late, and then they’re not fit enough for the treatment, or just because of the social situation, they cannot qualify for advanced therapies,” said Dr. Biavati.
The researchers established two cohorts: One consisting of patients with HIV and heart failure who may or may not have had PH and one comprising patients with PH with or without HIV and heart failure. In the HIV/heart failure group, PH without social adversity was associated with a nearly threefold increase in all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 2.83; P = .004), whereas PH with social adversity was linked to a more than sevenfold increase in all-cause mortality (HR, 7.14; P < .001). Social adversity without PA was associated with a more than fourfold increase (HR, 4.47; P < .001).
Within the PH cohort, social adversity was associated with lower survival (P < .001). When the researchers broke down the results by types of social adversity, they found statistically significant relationships between greater mortality risk and economic instability within the HIV+ population (HR, 2.59; P = .040), transportation issues within the HIV– population (HR, 12.8; P < .001), and lack of social or family support within both the HIV– (HR, 5.49; P < .001) and the HIV+ population (HR, 2.03; P = .028).
The research has prompted interventions, which are now being studied at the institution, according to Dr. Biavati. “We have a policy of giving medications in bags when we discharge a patient with a social adversity. We literally go to the pharmacy, bring up the bag of medication, and we [put it] in their hands before they leave the hospital. They get a 1- or 3-month supply, depending on the medication, and then we usually discharge them with a clinical appointment already scheduled with either a pulmonary or primary care provider, and we usually call them before every appointment to confirm that they’re coming. That increases the chances of some success, but there’s still a very long way to go,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati was blinded to the results of the intervention, so he could not report on whether it was working. “But I can tell you that I’ve had busier clinics, so hopefully that means that they’re showing up more,” he said.
The problem is complex, according to Sandeep Jain, MD, who moderated the session. “Social adversity means lack of education. Lack of education means lack of compliance. Lack of compliance means what can you do if people are not taking medications? So it’s all matched together. It’s all lack of education and lack of money, lack of family support. And these drugs they have to take every single day. It’s not that easy. It’s very easy for us to say I had antiretroviral treatment for 6 months. It is almost impossible to continue regular treatment for that long [for a patient with social adversity]. You can’t blame them if they aren’t taking treatments. It’s very difficult for them,” said Dr. Jain.
That underscores the need for interventions that can address the needs of patients with social adversity. “We have to [practice] medicine considering the social situation of the patient and not just the medicine that we study in books. That’s kind of what we are faced with every day. We have therapies, and then life happens. It’s much harder to care for those patients,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati and Dr. Jain reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Social adversity is associated with worse survival among patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH), according to a new retrospective study of a New York City population.
A sub-analysis of both HIV+ and HIV– patients showed worse mortality outcomes with social adversity in both groups.
“Almost the majority of patients that we treat have either some social adversity or no insurance or are undocumented, so as a group of residents, we decided to study the impact of these factors on their health and the care that can be provided. We started using the two cohorts and now we keep it going with every new resident,” said Luca Biavati, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
“The presence of any form of socioeconomic disadvantage is negatively impacting care and for a large part of the population, there are some factors that could probably be addressed by either an institutional or hospital policy,” said Dr. Biavati, who is an internal medicine resident at Jacobi Medical Center, New York.
Other factors are more difficult to address, such as lack of education. “[Some patients] don’t understand the gravity of their issue and medical condition until it’s too late, and then they’re not fit enough for the treatment, or just because of the social situation, they cannot qualify for advanced therapies,” said Dr. Biavati.
The researchers established two cohorts: One consisting of patients with HIV and heart failure who may or may not have had PH and one comprising patients with PH with or without HIV and heart failure. In the HIV/heart failure group, PH without social adversity was associated with a nearly threefold increase in all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 2.83; P = .004), whereas PH with social adversity was linked to a more than sevenfold increase in all-cause mortality (HR, 7.14; P < .001). Social adversity without PA was associated with a more than fourfold increase (HR, 4.47; P < .001).
Within the PH cohort, social adversity was associated with lower survival (P < .001). When the researchers broke down the results by types of social adversity, they found statistically significant relationships between greater mortality risk and economic instability within the HIV+ population (HR, 2.59; P = .040), transportation issues within the HIV– population (HR, 12.8; P < .001), and lack of social or family support within both the HIV– (HR, 5.49; P < .001) and the HIV+ population (HR, 2.03; P = .028).
The research has prompted interventions, which are now being studied at the institution, according to Dr. Biavati. “We have a policy of giving medications in bags when we discharge a patient with a social adversity. We literally go to the pharmacy, bring up the bag of medication, and we [put it] in their hands before they leave the hospital. They get a 1- or 3-month supply, depending on the medication, and then we usually discharge them with a clinical appointment already scheduled with either a pulmonary or primary care provider, and we usually call them before every appointment to confirm that they’re coming. That increases the chances of some success, but there’s still a very long way to go,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati was blinded to the results of the intervention, so he could not report on whether it was working. “But I can tell you that I’ve had busier clinics, so hopefully that means that they’re showing up more,” he said.
The problem is complex, according to Sandeep Jain, MD, who moderated the session. “Social adversity means lack of education. Lack of education means lack of compliance. Lack of compliance means what can you do if people are not taking medications? So it’s all matched together. It’s all lack of education and lack of money, lack of family support. And these drugs they have to take every single day. It’s not that easy. It’s very easy for us to say I had antiretroviral treatment for 6 months. It is almost impossible to continue regular treatment for that long [for a patient with social adversity]. You can’t blame them if they aren’t taking treatments. It’s very difficult for them,” said Dr. Jain.
That underscores the need for interventions that can address the needs of patients with social adversity. “We have to [practice] medicine considering the social situation of the patient and not just the medicine that we study in books. That’s kind of what we are faced with every day. We have therapies, and then life happens. It’s much harder to care for those patients,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati and Dr. Jain reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
Metformin May Reduce Long COVID in Non-Diabetic Population
LOS ANGELES — , according to data presented at the Infectious Disease Week (IDWeek) 2024 Annual Meeting.
Long COVID was determined by using the diagnostic code U09.9 or a computable phenotype based on symptoms and conditions. Most participants in this study were infected with the Omicron variant.
Researchers, led by Carolyn Bramante, MD, MPH, an internist, pediatrician, and obesity medicine specialist at the University of Minnesota Medical School in Minneapolis, simulated a randomized controlled trial of metformin vs control using the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) Electronic Health Record Database.
The intervention was a prescription for metformin within 6 days of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Those in the control group, which was designed to mimic placebo, had a prescription for fluvoxamine, fluticasone, ivermectin, or montelukast (all drugs that have been used off-label for COVID but have shown no effect on acute COVID outcomes in clinical trials). Exclusions included anyone with a previous metformin prescription or a comparator prescription; any indication for chronic metformin use; or a contraindication for metformin.
Why Study Metformin for Long COVID?
Dr. Bramante led a previous randomized controlled trial, COVID-OUT, with 1323 people that indicated metformin showed possible benefit for preventing the more severe components of COVID-19. She also led a 2020 review, in which she examined electronic health records from adults with type 2 diabetes or obesity. The researchers found that women taking metformin before they developed COVID-19 were significantly less likely to die after being hospitalized — although men didn’t see the same protective effect. Another randomized trial of 20 people found that 60% of those taking metformin vs 100% of those given a placebo had detectable SARS-CoV-2 viral load by day 4.
Other trials have highlighted the anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties of metformin. The existing evidence coupled with metformin’s well-established safety profile, led Dr. Bramante’s team to conduct the current simulated trial in people without diabetes or prediabetes. Dr. Bramante noted that metformin’s only US Food and Drug Administration–approved indication is for diabetes.
The current study featured a similar racial/ethnic makeup in the metformin and control groups: 16% and 17% were Black and 16% and 13% were Hispanic, respectively. Within 6 months, 4.0% in the metformin group developed long COVID or died compared with 8.5% in the control group (Relative Risk [RR], 0.47; 95% CI, 0.25-0.89). For prescriptions made on days 0-1 relative to infection, the RR was 0.39 (95% CI, 0.12-1.24). When metformin was prescribed on days 0-14, the RR was 0.75 (95% CI, 0.52-1.08).
The reason it’s important to have an active comparator is to control for things that can’t be measured, such as engagement in healthcare and the placebo effect, Dr. Bramante said.
Emily Erbelding, MD, MPH, director of the Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, who was not part of the study, noted the potential implications of the findings.
Proven Safety and Low Cost of Metformin
“We don’t have therapies for long COVID, and we don’t know how to prevent it in people who have SARS-CoV-2 infections,” Dr. Erbelding noted. “This analysis points to metformin, a drug that millions of people have taken safely for their diabetes or their borderline diabetes. It’s licensed, it’s out there, and it’s inexpensive. The fact that we have data that point to this potentially being a therapy is important. I think that’s the power of this.”
Dr. Erbelding said a strength of the study is the size of the N3C Electronic Health Record Database (with data on nearly 9 million COVID cases) the researchers used to simulate the randomized controlled trial.
“(These results) gives us a reason to think about doing a large randomized controlled study with metformin,” she said. However, there are some limitations, she noted.
“The definition of long COVID may not have been applied exactly the same way across all the patients and you don’t know what led the prescribers to prescribe metformin. There might have been confounders that couldn’t be controlled for or weren’t evident in the way they approached the data.”
This study has “relatively rigorous methodology for an observational study,” Dr. Erbelding said. “It’s novel to try to simulate a randomized controlled trial through a large, observational, electronic record–based cohort. Maybe we should be doing more of this because these bioinformatic systems exist now. And we need to get all the public health use out of them that we can.”
“The fact that they may be unlocking something new here that needs follow-up in a truly randomized controlled trial is important as well because there are a lot of people out there suffering from long COVID.”
Bramante and Erbelding disclosed no relevant financial relationships. This research was supported in part by the intramural/extramural research program of the National Center for Advancing Translational Science, National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — , according to data presented at the Infectious Disease Week (IDWeek) 2024 Annual Meeting.
Long COVID was determined by using the diagnostic code U09.9 or a computable phenotype based on symptoms and conditions. Most participants in this study were infected with the Omicron variant.
Researchers, led by Carolyn Bramante, MD, MPH, an internist, pediatrician, and obesity medicine specialist at the University of Minnesota Medical School in Minneapolis, simulated a randomized controlled trial of metformin vs control using the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) Electronic Health Record Database.
The intervention was a prescription for metformin within 6 days of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Those in the control group, which was designed to mimic placebo, had a prescription for fluvoxamine, fluticasone, ivermectin, or montelukast (all drugs that have been used off-label for COVID but have shown no effect on acute COVID outcomes in clinical trials). Exclusions included anyone with a previous metformin prescription or a comparator prescription; any indication for chronic metformin use; or a contraindication for metformin.
Why Study Metformin for Long COVID?
Dr. Bramante led a previous randomized controlled trial, COVID-OUT, with 1323 people that indicated metformin showed possible benefit for preventing the more severe components of COVID-19. She also led a 2020 review, in which she examined electronic health records from adults with type 2 diabetes or obesity. The researchers found that women taking metformin before they developed COVID-19 were significantly less likely to die after being hospitalized — although men didn’t see the same protective effect. Another randomized trial of 20 people found that 60% of those taking metformin vs 100% of those given a placebo had detectable SARS-CoV-2 viral load by day 4.
Other trials have highlighted the anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties of metformin. The existing evidence coupled with metformin’s well-established safety profile, led Dr. Bramante’s team to conduct the current simulated trial in people without diabetes or prediabetes. Dr. Bramante noted that metformin’s only US Food and Drug Administration–approved indication is for diabetes.
The current study featured a similar racial/ethnic makeup in the metformin and control groups: 16% and 17% were Black and 16% and 13% were Hispanic, respectively. Within 6 months, 4.0% in the metformin group developed long COVID or died compared with 8.5% in the control group (Relative Risk [RR], 0.47; 95% CI, 0.25-0.89). For prescriptions made on days 0-1 relative to infection, the RR was 0.39 (95% CI, 0.12-1.24). When metformin was prescribed on days 0-14, the RR was 0.75 (95% CI, 0.52-1.08).
The reason it’s important to have an active comparator is to control for things that can’t be measured, such as engagement in healthcare and the placebo effect, Dr. Bramante said.
Emily Erbelding, MD, MPH, director of the Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, who was not part of the study, noted the potential implications of the findings.
Proven Safety and Low Cost of Metformin
“We don’t have therapies for long COVID, and we don’t know how to prevent it in people who have SARS-CoV-2 infections,” Dr. Erbelding noted. “This analysis points to metformin, a drug that millions of people have taken safely for their diabetes or their borderline diabetes. It’s licensed, it’s out there, and it’s inexpensive. The fact that we have data that point to this potentially being a therapy is important. I think that’s the power of this.”
Dr. Erbelding said a strength of the study is the size of the N3C Electronic Health Record Database (with data on nearly 9 million COVID cases) the researchers used to simulate the randomized controlled trial.
“(These results) gives us a reason to think about doing a large randomized controlled study with metformin,” she said. However, there are some limitations, she noted.
“The definition of long COVID may not have been applied exactly the same way across all the patients and you don’t know what led the prescribers to prescribe metformin. There might have been confounders that couldn’t be controlled for or weren’t evident in the way they approached the data.”
This study has “relatively rigorous methodology for an observational study,” Dr. Erbelding said. “It’s novel to try to simulate a randomized controlled trial through a large, observational, electronic record–based cohort. Maybe we should be doing more of this because these bioinformatic systems exist now. And we need to get all the public health use out of them that we can.”
“The fact that they may be unlocking something new here that needs follow-up in a truly randomized controlled trial is important as well because there are a lot of people out there suffering from long COVID.”
Bramante and Erbelding disclosed no relevant financial relationships. This research was supported in part by the intramural/extramural research program of the National Center for Advancing Translational Science, National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — , according to data presented at the Infectious Disease Week (IDWeek) 2024 Annual Meeting.
Long COVID was determined by using the diagnostic code U09.9 or a computable phenotype based on symptoms and conditions. Most participants in this study were infected with the Omicron variant.
Researchers, led by Carolyn Bramante, MD, MPH, an internist, pediatrician, and obesity medicine specialist at the University of Minnesota Medical School in Minneapolis, simulated a randomized controlled trial of metformin vs control using the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) Electronic Health Record Database.
The intervention was a prescription for metformin within 6 days of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Those in the control group, which was designed to mimic placebo, had a prescription for fluvoxamine, fluticasone, ivermectin, or montelukast (all drugs that have been used off-label for COVID but have shown no effect on acute COVID outcomes in clinical trials). Exclusions included anyone with a previous metformin prescription or a comparator prescription; any indication for chronic metformin use; or a contraindication for metformin.
Why Study Metformin for Long COVID?
Dr. Bramante led a previous randomized controlled trial, COVID-OUT, with 1323 people that indicated metformin showed possible benefit for preventing the more severe components of COVID-19. She also led a 2020 review, in which she examined electronic health records from adults with type 2 diabetes or obesity. The researchers found that women taking metformin before they developed COVID-19 were significantly less likely to die after being hospitalized — although men didn’t see the same protective effect. Another randomized trial of 20 people found that 60% of those taking metformin vs 100% of those given a placebo had detectable SARS-CoV-2 viral load by day 4.
Other trials have highlighted the anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties of metformin. The existing evidence coupled with metformin’s well-established safety profile, led Dr. Bramante’s team to conduct the current simulated trial in people without diabetes or prediabetes. Dr. Bramante noted that metformin’s only US Food and Drug Administration–approved indication is for diabetes.
The current study featured a similar racial/ethnic makeup in the metformin and control groups: 16% and 17% were Black and 16% and 13% were Hispanic, respectively. Within 6 months, 4.0% in the metformin group developed long COVID or died compared with 8.5% in the control group (Relative Risk [RR], 0.47; 95% CI, 0.25-0.89). For prescriptions made on days 0-1 relative to infection, the RR was 0.39 (95% CI, 0.12-1.24). When metformin was prescribed on days 0-14, the RR was 0.75 (95% CI, 0.52-1.08).
The reason it’s important to have an active comparator is to control for things that can’t be measured, such as engagement in healthcare and the placebo effect, Dr. Bramante said.
Emily Erbelding, MD, MPH, director of the Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, who was not part of the study, noted the potential implications of the findings.
Proven Safety and Low Cost of Metformin
“We don’t have therapies for long COVID, and we don’t know how to prevent it in people who have SARS-CoV-2 infections,” Dr. Erbelding noted. “This analysis points to metformin, a drug that millions of people have taken safely for their diabetes or their borderline diabetes. It’s licensed, it’s out there, and it’s inexpensive. The fact that we have data that point to this potentially being a therapy is important. I think that’s the power of this.”
Dr. Erbelding said a strength of the study is the size of the N3C Electronic Health Record Database (with data on nearly 9 million COVID cases) the researchers used to simulate the randomized controlled trial.
“(These results) gives us a reason to think about doing a large randomized controlled study with metformin,” she said. However, there are some limitations, she noted.
“The definition of long COVID may not have been applied exactly the same way across all the patients and you don’t know what led the prescribers to prescribe metformin. There might have been confounders that couldn’t be controlled for or weren’t evident in the way they approached the data.”
This study has “relatively rigorous methodology for an observational study,” Dr. Erbelding said. “It’s novel to try to simulate a randomized controlled trial through a large, observational, electronic record–based cohort. Maybe we should be doing more of this because these bioinformatic systems exist now. And we need to get all the public health use out of them that we can.”
“The fact that they may be unlocking something new here that needs follow-up in a truly randomized controlled trial is important as well because there are a lot of people out there suffering from long COVID.”
Bramante and Erbelding disclosed no relevant financial relationships. This research was supported in part by the intramural/extramural research program of the National Center for Advancing Translational Science, National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM IDWEEK 2024
Minor Progress in Gender Pay Equity, But a Big Gap Persists
Despite some recent progress in compensation equity, women in medicine continue to be paid significantly lower salaries than men.
According to the Female Compensation Report 2024 by Medscape, male doctors of any kind earned an average salary of about $400,000, whereas female doctors earned approximately $309,000 — a 29% gap.
The report analyzed survey data from 7000 practicing physicians who were recruited over a 4-month period starting in October 2023. The respondents comprised roughly 60% women representing over 29 specialties.
In the 2022 report, the pay gap between the genders was 32%. But some women in the field argued substantial headway is still needed.
“You can try and pick apart the data, but I’d say we’re not really making progress,” said Susan T. Hingle, MD, an internist in Illinois and president of the American Medical Women’s Association. “A decline by a couple of percentage points is not significantly addressing this pay gap that over a lifetime is huge, can be millions of dollars.”
The gender gap was narrower among female primary care physicians (PCPs) vs medical specialists. Female PCPs earned around $253,000 per year, whereas male PCPs earned about $295,000 per year. Hingle suggested that female PCPs may enjoy more pay equity because health systems have a harder time filling these positions.
On the other hand, the gap for specialists rose from 27% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. Differences in how aggressively women and men negotiate compensation packages may play a role, said Hingle.
“Taking negotiation out of the equation would be progress to me,” said Hingle.
Pay disparity did not appear to be the result of time spent on the job — female doctors reported an average of 49 work hours per week, whereas their male counterparts reported 50 work hours per week.
Meanwhile, the pay gap progressively worsened over time. Among doctors aged 28-34 years, men earned an average of $53,000 more than women. By ages 46-49, men earned an average of $157,000 more than women.
“I had to take my employer to court to get equal compensation, sad as it is to say,” said a hospitalist in North Carolina.
Nearly 60% of women surveyed felt they were not being paid fairly for their efforts, up from less than half reported in Medscape’s 2021 report. Hingle said that this figure may not only reflect sentiments about the compensation gap, but also less support on the job, including fewer physician assistants (PAs), nurses, and administrative staff.
“At my job, I do the work of multiple people,” said a survey respondent. “Junior resident, senior resident, social worker, nurse practitioner, PA — as well as try to be a teacher, researcher, [and] an excellent doctor and have the time to make patients feel as if they are not in a rush.”
Roughly 30% of women physicians said they would not choose to go into medicine again if given the chance compared with 26% of male physicians.
“Gender inequities in our profession have a direct impact,” said Shikha Jain, MD, an oncologist in Chicago and founder of the Women in Medicine nonprofit. “I think women in general don’t feel valued in the care they’re providing.”
Jain cited bullying, harassment, and fewer opportunities for leadership and recognition as factors beyond pay that affect female physicians’ feelings of being valued.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite some recent progress in compensation equity, women in medicine continue to be paid significantly lower salaries than men.
According to the Female Compensation Report 2024 by Medscape, male doctors of any kind earned an average salary of about $400,000, whereas female doctors earned approximately $309,000 — a 29% gap.
The report analyzed survey data from 7000 practicing physicians who were recruited over a 4-month period starting in October 2023. The respondents comprised roughly 60% women representing over 29 specialties.
In the 2022 report, the pay gap between the genders was 32%. But some women in the field argued substantial headway is still needed.
“You can try and pick apart the data, but I’d say we’re not really making progress,” said Susan T. Hingle, MD, an internist in Illinois and president of the American Medical Women’s Association. “A decline by a couple of percentage points is not significantly addressing this pay gap that over a lifetime is huge, can be millions of dollars.”
The gender gap was narrower among female primary care physicians (PCPs) vs medical specialists. Female PCPs earned around $253,000 per year, whereas male PCPs earned about $295,000 per year. Hingle suggested that female PCPs may enjoy more pay equity because health systems have a harder time filling these positions.
On the other hand, the gap for specialists rose from 27% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. Differences in how aggressively women and men negotiate compensation packages may play a role, said Hingle.
“Taking negotiation out of the equation would be progress to me,” said Hingle.
Pay disparity did not appear to be the result of time spent on the job — female doctors reported an average of 49 work hours per week, whereas their male counterparts reported 50 work hours per week.
Meanwhile, the pay gap progressively worsened over time. Among doctors aged 28-34 years, men earned an average of $53,000 more than women. By ages 46-49, men earned an average of $157,000 more than women.
“I had to take my employer to court to get equal compensation, sad as it is to say,” said a hospitalist in North Carolina.
Nearly 60% of women surveyed felt they were not being paid fairly for their efforts, up from less than half reported in Medscape’s 2021 report. Hingle said that this figure may not only reflect sentiments about the compensation gap, but also less support on the job, including fewer physician assistants (PAs), nurses, and administrative staff.
“At my job, I do the work of multiple people,” said a survey respondent. “Junior resident, senior resident, social worker, nurse practitioner, PA — as well as try to be a teacher, researcher, [and] an excellent doctor and have the time to make patients feel as if they are not in a rush.”
Roughly 30% of women physicians said they would not choose to go into medicine again if given the chance compared with 26% of male physicians.
“Gender inequities in our profession have a direct impact,” said Shikha Jain, MD, an oncologist in Chicago and founder of the Women in Medicine nonprofit. “I think women in general don’t feel valued in the care they’re providing.”
Jain cited bullying, harassment, and fewer opportunities for leadership and recognition as factors beyond pay that affect female physicians’ feelings of being valued.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite some recent progress in compensation equity, women in medicine continue to be paid significantly lower salaries than men.
According to the Female Compensation Report 2024 by Medscape, male doctors of any kind earned an average salary of about $400,000, whereas female doctors earned approximately $309,000 — a 29% gap.
The report analyzed survey data from 7000 practicing physicians who were recruited over a 4-month period starting in October 2023. The respondents comprised roughly 60% women representing over 29 specialties.
In the 2022 report, the pay gap between the genders was 32%. But some women in the field argued substantial headway is still needed.
“You can try and pick apart the data, but I’d say we’re not really making progress,” said Susan T. Hingle, MD, an internist in Illinois and president of the American Medical Women’s Association. “A decline by a couple of percentage points is not significantly addressing this pay gap that over a lifetime is huge, can be millions of dollars.”
The gender gap was narrower among female primary care physicians (PCPs) vs medical specialists. Female PCPs earned around $253,000 per year, whereas male PCPs earned about $295,000 per year. Hingle suggested that female PCPs may enjoy more pay equity because health systems have a harder time filling these positions.
On the other hand, the gap for specialists rose from 27% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. Differences in how aggressively women and men negotiate compensation packages may play a role, said Hingle.
“Taking negotiation out of the equation would be progress to me,” said Hingle.
Pay disparity did not appear to be the result of time spent on the job — female doctors reported an average of 49 work hours per week, whereas their male counterparts reported 50 work hours per week.
Meanwhile, the pay gap progressively worsened over time. Among doctors aged 28-34 years, men earned an average of $53,000 more than women. By ages 46-49, men earned an average of $157,000 more than women.
“I had to take my employer to court to get equal compensation, sad as it is to say,” said a hospitalist in North Carolina.
Nearly 60% of women surveyed felt they were not being paid fairly for their efforts, up from less than half reported in Medscape’s 2021 report. Hingle said that this figure may not only reflect sentiments about the compensation gap, but also less support on the job, including fewer physician assistants (PAs), nurses, and administrative staff.
“At my job, I do the work of multiple people,” said a survey respondent. “Junior resident, senior resident, social worker, nurse practitioner, PA — as well as try to be a teacher, researcher, [and] an excellent doctor and have the time to make patients feel as if they are not in a rush.”
Roughly 30% of women physicians said they would not choose to go into medicine again if given the chance compared with 26% of male physicians.
“Gender inequities in our profession have a direct impact,” said Shikha Jain, MD, an oncologist in Chicago and founder of the Women in Medicine nonprofit. “I think women in general don’t feel valued in the care they’re providing.”
Jain cited bullying, harassment, and fewer opportunities for leadership and recognition as factors beyond pay that affect female physicians’ feelings of being valued.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID on the Floor Linked to Outbreaks on Two Hospital Wards
The viral burden of SARS-CoV-2 on floors, even in healthcare worker–only areas, was strongly associated with COVID-19 outbreaks in two acute-care hospitals, according to a new study from Ontario, Canada.
With every 10-fold increase in viral copies, the chance of an impending outbreak of COVID-19 rose 22-fold.
“These data add to the mounting evidence that built environment detection for SARS-CoV-2 may provide an additional layer of monitoring and could help inform local infection prevention and control measures,” they wrote.
The study was published online in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Preventing Future Suffering
The current study builds on the researchers’ previous work, which found the same correlation between viral load on floors and COVID outbreaks in long-term care homes.
Currently, the best-known method of environmental surveillance for COVID is wastewater detection. “Swabbing the floors would be another approach to surveillance,” senior author Caroline Nott, MD, infectious disease physician at the Ottawa Hospital, said in an interview.
“We do have environmental surveillance with wastewater, but while this may tell you what’s going on in the city, it doesn’t tell you what is going on in a particular ward of a hospital, for instance,” she added.
Nott and her colleagues believe that swabbing, which is easy and relatively inexpensive, will become another tool to examine the built environment. “Instead of having to close a whole hospital, for example, we could just close one room instead of an entire ward if swabbing showed a high concentration of COVID,” Nott said.
The current study was conducted at two hospitals in Ontario between July 2022 and March 2023. The floors of healthcare worker–only areas on four inpatient adult wards were swabbed. These areas included changing rooms, meeting rooms, staff washrooms, nursing stations, and interdisciplinary team rooms.
SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected on 537 of 760 floor swabs (71%). The overall positivity rate in the first hospital was 90% (n = 280). In the second hospital, the rate was 60% (n = 480).
Four COVID-19 outbreaks occurred in the first acute care hospital, and seven outbreaks occurred at the second hospital. Outbreaks occurred mostly among hospitalized patients (140 cases), but also in four hospital workers.
COVID-19 still requires vigilance, said Nott. “We weren’t prepared for COVID, and so as a result, many people died or have suffered long-term effects, especially vulnerable people like those being treated in hospital or in long-term care facilities. We want to develop methods to prevent similar suffering in the future, whether it’s a new COVID variant or a different pathogen altogether.”
Changing Surveillance Practice?
“This is a good study,” Steven Rogak, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering at the University of British Columbia (UBC) in Vancouver, Canada, said in an interivew. “The fundamental idea is that respiratory droplets and aerosols will deposit on the floor, and polymerase chain reaction [PCR] tests of swabs will provide a surrogate measurement of what might have been inhaled. There are solid statistics that it worked for the hospitals studied,” said Rogak, who studies aerosols at UBC’s Energy and Aerosols Laboratory. Rogak did not participate in the study.
“The authors note several limitations, including that increased healthcare worker testing may have been triggered by the higher values of PCR counts from the floor swabs. But this doesn’t seem to be a problem to me, because if the floor swabs motivate the hospital to test workers more, and that results in identifying outbreaks sooner, then great,” he said.
“Another limitation is that if the hospital has better HVAC or uses air purifiers, it could remove the most infectious aerosols, but the large droplets that fall quickly to the ground would remain, and this would still result in high PCR counts from floor swabs. In this case, perhaps the floor swabs would be a poorer indication of impending outbreaks,” said Rogak.
Determining the best timing and location for floor swabbing might be challenging and specific to the particular hospital, he added. ”For example, you would not want to take swabs from floors right after they are cleaned. Overall, I think this method deserves further development, and it could become a standard technique, but the details might require refinement for widespread application.”
Adrian Popp, MD, chair of the Infectious Disease Service at Huntington Hospital–Northwell Health in New York, said that, although interesting, the study would not change his current practice.
“I’m going to start testing the environment in different rooms in the hospital, and yes, I might find different amounts of COVID, but what does that mean? If pieces of RNA from COVID are on the floor, the likelihood is that they’re not infectious,” Popp said in an interview.
“Hospital workers do get sick with COVID, and sometimes they are asymptomatic and come to work. Patients may come into the hospital for another reason and be sick with COVID. There are many ways people who work in the hospital, as well as the patients, can get COVID. To me, it means that in that hospital and community there is a lot of COVID, but I can’t tell if there is causation here. Who is giving COVID to whom? What am I supposed to do with the information?”
The study was supported by the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association Clinical Innovation Opportunities Fund, the Ottawa Hospital Academic Medical Organization Innovation Fund, and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant. One author was a consultant for ProofDx, a startup company creating a point-of-care diagnostic test for COVID-19, and is an advisor for SIGNAL1, a startup company deploying machine-learning models to improve inpatient care. Nott, Rogak, and Popp reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The viral burden of SARS-CoV-2 on floors, even in healthcare worker–only areas, was strongly associated with COVID-19 outbreaks in two acute-care hospitals, according to a new study from Ontario, Canada.
With every 10-fold increase in viral copies, the chance of an impending outbreak of COVID-19 rose 22-fold.
“These data add to the mounting evidence that built environment detection for SARS-CoV-2 may provide an additional layer of monitoring and could help inform local infection prevention and control measures,” they wrote.
The study was published online in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Preventing Future Suffering
The current study builds on the researchers’ previous work, which found the same correlation between viral load on floors and COVID outbreaks in long-term care homes.
Currently, the best-known method of environmental surveillance for COVID is wastewater detection. “Swabbing the floors would be another approach to surveillance,” senior author Caroline Nott, MD, infectious disease physician at the Ottawa Hospital, said in an interview.
“We do have environmental surveillance with wastewater, but while this may tell you what’s going on in the city, it doesn’t tell you what is going on in a particular ward of a hospital, for instance,” she added.
Nott and her colleagues believe that swabbing, which is easy and relatively inexpensive, will become another tool to examine the built environment. “Instead of having to close a whole hospital, for example, we could just close one room instead of an entire ward if swabbing showed a high concentration of COVID,” Nott said.
The current study was conducted at two hospitals in Ontario between July 2022 and March 2023. The floors of healthcare worker–only areas on four inpatient adult wards were swabbed. These areas included changing rooms, meeting rooms, staff washrooms, nursing stations, and interdisciplinary team rooms.
SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected on 537 of 760 floor swabs (71%). The overall positivity rate in the first hospital was 90% (n = 280). In the second hospital, the rate was 60% (n = 480).
Four COVID-19 outbreaks occurred in the first acute care hospital, and seven outbreaks occurred at the second hospital. Outbreaks occurred mostly among hospitalized patients (140 cases), but also in four hospital workers.
COVID-19 still requires vigilance, said Nott. “We weren’t prepared for COVID, and so as a result, many people died or have suffered long-term effects, especially vulnerable people like those being treated in hospital or in long-term care facilities. We want to develop methods to prevent similar suffering in the future, whether it’s a new COVID variant or a different pathogen altogether.”
Changing Surveillance Practice?
“This is a good study,” Steven Rogak, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering at the University of British Columbia (UBC) in Vancouver, Canada, said in an interivew. “The fundamental idea is that respiratory droplets and aerosols will deposit on the floor, and polymerase chain reaction [PCR] tests of swabs will provide a surrogate measurement of what might have been inhaled. There are solid statistics that it worked for the hospitals studied,” said Rogak, who studies aerosols at UBC’s Energy and Aerosols Laboratory. Rogak did not participate in the study.
“The authors note several limitations, including that increased healthcare worker testing may have been triggered by the higher values of PCR counts from the floor swabs. But this doesn’t seem to be a problem to me, because if the floor swabs motivate the hospital to test workers more, and that results in identifying outbreaks sooner, then great,” he said.
“Another limitation is that if the hospital has better HVAC or uses air purifiers, it could remove the most infectious aerosols, but the large droplets that fall quickly to the ground would remain, and this would still result in high PCR counts from floor swabs. In this case, perhaps the floor swabs would be a poorer indication of impending outbreaks,” said Rogak.
Determining the best timing and location for floor swabbing might be challenging and specific to the particular hospital, he added. ”For example, you would not want to take swabs from floors right after they are cleaned. Overall, I think this method deserves further development, and it could become a standard technique, but the details might require refinement for widespread application.”
Adrian Popp, MD, chair of the Infectious Disease Service at Huntington Hospital–Northwell Health in New York, said that, although interesting, the study would not change his current practice.
“I’m going to start testing the environment in different rooms in the hospital, and yes, I might find different amounts of COVID, but what does that mean? If pieces of RNA from COVID are on the floor, the likelihood is that they’re not infectious,” Popp said in an interview.
“Hospital workers do get sick with COVID, and sometimes they are asymptomatic and come to work. Patients may come into the hospital for another reason and be sick with COVID. There are many ways people who work in the hospital, as well as the patients, can get COVID. To me, it means that in that hospital and community there is a lot of COVID, but I can’t tell if there is causation here. Who is giving COVID to whom? What am I supposed to do with the information?”
The study was supported by the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association Clinical Innovation Opportunities Fund, the Ottawa Hospital Academic Medical Organization Innovation Fund, and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant. One author was a consultant for ProofDx, a startup company creating a point-of-care diagnostic test for COVID-19, and is an advisor for SIGNAL1, a startup company deploying machine-learning models to improve inpatient care. Nott, Rogak, and Popp reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The viral burden of SARS-CoV-2 on floors, even in healthcare worker–only areas, was strongly associated with COVID-19 outbreaks in two acute-care hospitals, according to a new study from Ontario, Canada.
With every 10-fold increase in viral copies, the chance of an impending outbreak of COVID-19 rose 22-fold.
“These data add to the mounting evidence that built environment detection for SARS-CoV-2 may provide an additional layer of monitoring and could help inform local infection prevention and control measures,” they wrote.
The study was published online in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Preventing Future Suffering
The current study builds on the researchers’ previous work, which found the same correlation between viral load on floors and COVID outbreaks in long-term care homes.
Currently, the best-known method of environmental surveillance for COVID is wastewater detection. “Swabbing the floors would be another approach to surveillance,” senior author Caroline Nott, MD, infectious disease physician at the Ottawa Hospital, said in an interview.
“We do have environmental surveillance with wastewater, but while this may tell you what’s going on in the city, it doesn’t tell you what is going on in a particular ward of a hospital, for instance,” she added.
Nott and her colleagues believe that swabbing, which is easy and relatively inexpensive, will become another tool to examine the built environment. “Instead of having to close a whole hospital, for example, we could just close one room instead of an entire ward if swabbing showed a high concentration of COVID,” Nott said.
The current study was conducted at two hospitals in Ontario between July 2022 and March 2023. The floors of healthcare worker–only areas on four inpatient adult wards were swabbed. These areas included changing rooms, meeting rooms, staff washrooms, nursing stations, and interdisciplinary team rooms.
SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected on 537 of 760 floor swabs (71%). The overall positivity rate in the first hospital was 90% (n = 280). In the second hospital, the rate was 60% (n = 480).
Four COVID-19 outbreaks occurred in the first acute care hospital, and seven outbreaks occurred at the second hospital. Outbreaks occurred mostly among hospitalized patients (140 cases), but also in four hospital workers.
COVID-19 still requires vigilance, said Nott. “We weren’t prepared for COVID, and so as a result, many people died or have suffered long-term effects, especially vulnerable people like those being treated in hospital or in long-term care facilities. We want to develop methods to prevent similar suffering in the future, whether it’s a new COVID variant or a different pathogen altogether.”
Changing Surveillance Practice?
“This is a good study,” Steven Rogak, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering at the University of British Columbia (UBC) in Vancouver, Canada, said in an interivew. “The fundamental idea is that respiratory droplets and aerosols will deposit on the floor, and polymerase chain reaction [PCR] tests of swabs will provide a surrogate measurement of what might have been inhaled. There are solid statistics that it worked for the hospitals studied,” said Rogak, who studies aerosols at UBC’s Energy and Aerosols Laboratory. Rogak did not participate in the study.
“The authors note several limitations, including that increased healthcare worker testing may have been triggered by the higher values of PCR counts from the floor swabs. But this doesn’t seem to be a problem to me, because if the floor swabs motivate the hospital to test workers more, and that results in identifying outbreaks sooner, then great,” he said.
“Another limitation is that if the hospital has better HVAC or uses air purifiers, it could remove the most infectious aerosols, but the large droplets that fall quickly to the ground would remain, and this would still result in high PCR counts from floor swabs. In this case, perhaps the floor swabs would be a poorer indication of impending outbreaks,” said Rogak.
Determining the best timing and location for floor swabbing might be challenging and specific to the particular hospital, he added. ”For example, you would not want to take swabs from floors right after they are cleaned. Overall, I think this method deserves further development, and it could become a standard technique, but the details might require refinement for widespread application.”
Adrian Popp, MD, chair of the Infectious Disease Service at Huntington Hospital–Northwell Health in New York, said that, although interesting, the study would not change his current practice.
“I’m going to start testing the environment in different rooms in the hospital, and yes, I might find different amounts of COVID, but what does that mean? If pieces of RNA from COVID are on the floor, the likelihood is that they’re not infectious,” Popp said in an interview.
“Hospital workers do get sick with COVID, and sometimes they are asymptomatic and come to work. Patients may come into the hospital for another reason and be sick with COVID. There are many ways people who work in the hospital, as well as the patients, can get COVID. To me, it means that in that hospital and community there is a lot of COVID, but I can’t tell if there is causation here. Who is giving COVID to whom? What am I supposed to do with the information?”
The study was supported by the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association Clinical Innovation Opportunities Fund, the Ottawa Hospital Academic Medical Organization Innovation Fund, and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant. One author was a consultant for ProofDx, a startup company creating a point-of-care diagnostic test for COVID-19, and is an advisor for SIGNAL1, a startup company deploying machine-learning models to improve inpatient care. Nott, Rogak, and Popp reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM INFECTION CONTROL & HOSPITAL EPIDEMIOLOGY
Is Being ‘Manly’ a Threat to a Man’s Health?
When my normally adorable cat Biscuit bit my ankle in a playful stalking exercise gone wrong, I washed it with soap and some rubbing alcohol, slapped on a Band-Aid, and went about my day.
The next morning, when it was swollen, I told myself it was probably just a hematoma and went about my day.
The next day, when the swelling had increased and red lines started creeping up my leg, I called my doctor. Long story short, I ended up hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
This is all to say that, yes, I’m sort of an idiot, but also to introduce the idea that maybe I minimized my very obvious lymphangitis because I am a man.
This week, we have empirical evidence that men downplay their medical symptoms — and that manlier men downplay them even more.
I’m going to talk about a study that links manliness (or, scientifically speaking, “male gender expressivity”) to medical diagnoses that are based on hard evidence and medical diagnoses that are based on self-report. You see where this is going but I want to walk you through the methods here because they are fairly interesting.
This study used data from the US National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. This study enrolled 20,000 adolescents who were in grades 7-12 in the 1994-1995 school year and has been following them ever since — about 30 years so far.
The authors wanted to link early gender roles to long-term outcomes, so they cut that 20,000 number down to the 4230 males in the group who had complete follow-up.
Now comes the first interesting question. How do you quantify the “male gender expressivity” of boys in 7th-12th grade? There was no survey item that asked them how masculine or manly they felt. What the authors did was look at the surveys that were administered and identify the questions on those surveys where boys and girls gave the most disparate answers. I have some examples here. 
Some of these questions make sense when it comes to gender expressivity: “How often do you cry?” for example, has a lot of validity for the social construct that is gender. But some questions where boys and girls gave very different answers — like “How often do you exercise?” — don’t quite fit that mold. Regardless, this structure allowed the researchers to take individual kids’ responses to these questions and combine them into what amounts to a manliness score — how much their answers aligned with the typical male answer.
The score was established in adolescence — which is interesting because I’m sure some of this stuff may change over time — but notable because adolescence is where many gender roles develop.
Now we can fast-forward 30 years and see how these manliness scores link to various outcomes. The authors were interested in fairly common diseases: diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Let’s start simply. Are males with higher gender expressivity in adolescence more or less likely to have these diseases in the future?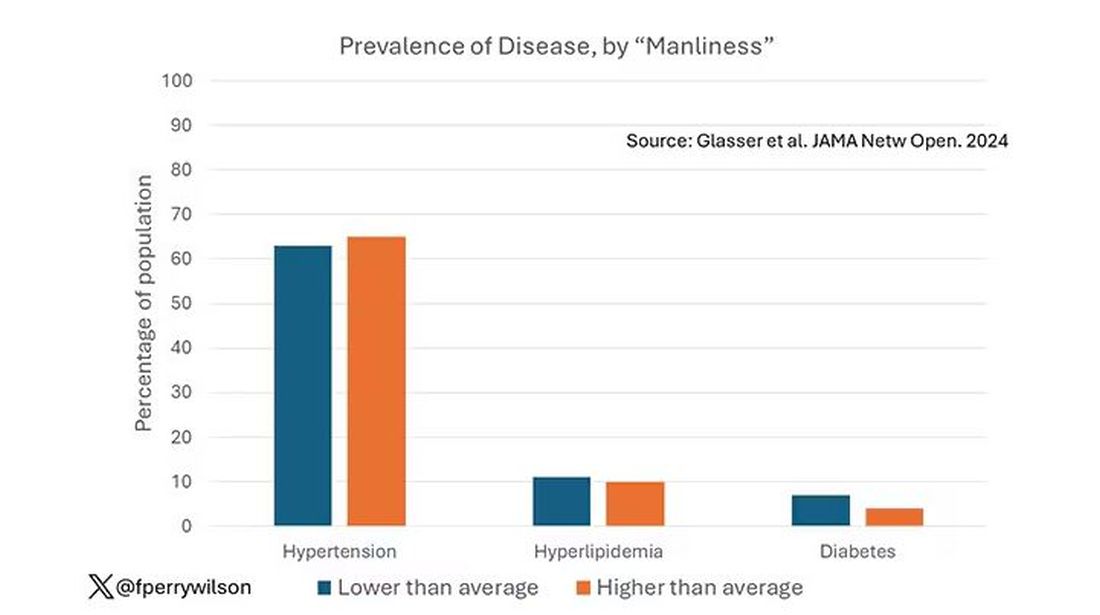
Not really. Those above the average in male gender expressivity had similar rates of hypertension and hyperlipidemia as those below the median. They were actually a bit less likely to have diabetes.
But that’s not what’s really interesting here.
I told you that there was no difference in the rate of hypertension among those with high vs low male gender expressivity. But there was a significant difference in their answer to the question “Do you have hypertension?” The same was seen for hyperlipidemia. In other words, those with higher manliness scores are less likely to admit (or perhaps know) that they have a particular disease.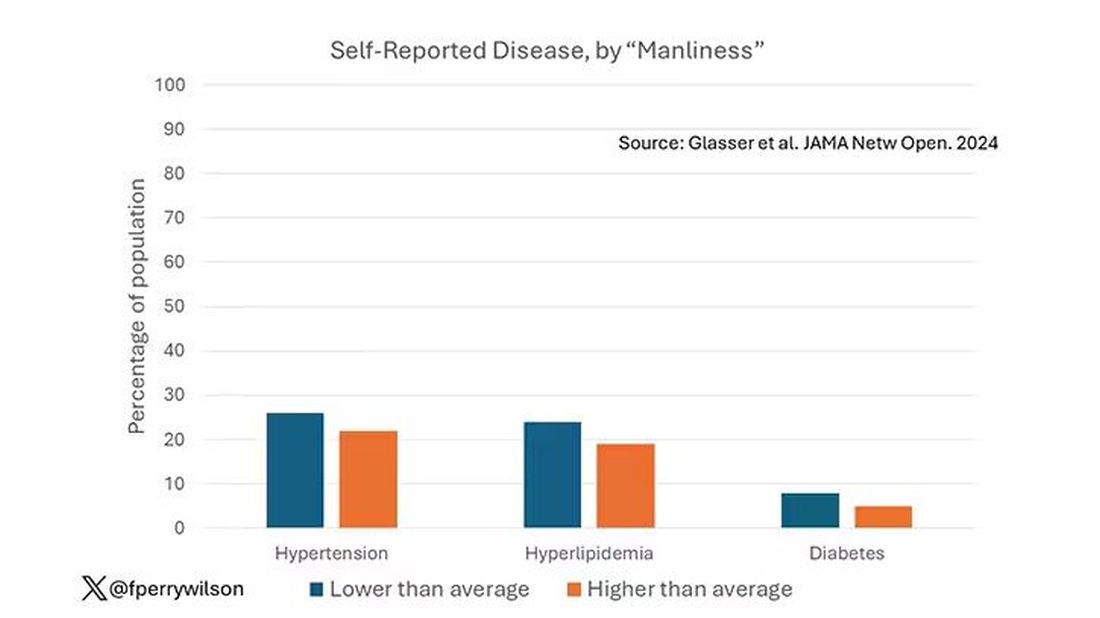
You can see the relationship across the manliness spectrum here in a series of adjusted models. The x-axis is the male gender expressivity score, and the y-axis is the percentage of people who report having the disease that we know they have based on the actual laboratory tests or vital sign measurements. As manliness increases, the self-report of a given disease decreases.
There are some important consequences of this systematic denial. Specifically, men with the diseases of interest who have higher male gender expressivity are less likely to get treatment. And, as we all know, the lack of treatment of something like hypertension puts people at risk for bad downstream outcomes.
Putting this all together, I’m not that surprised. Society trains boys from a young age to behave in certain ways: to hide emotions, to eschew vulnerability, to not complain when we are hurt. And those lessons can persist into later life. Whether the disease that strikes is hypertension or Pasteurella multocida from a slightly psychotic house cat, men are more likely to ignore it, to their detriment.
So, gents, be brave. Get your blood tests and check your blood pressure. If there’s something wrong, admit it, and fix it. After all, fixing problems — that’s a manly thing, right?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When my normally adorable cat Biscuit bit my ankle in a playful stalking exercise gone wrong, I washed it with soap and some rubbing alcohol, slapped on a Band-Aid, and went about my day.
The next morning, when it was swollen, I told myself it was probably just a hematoma and went about my day.
The next day, when the swelling had increased and red lines started creeping up my leg, I called my doctor. Long story short, I ended up hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
This is all to say that, yes, I’m sort of an idiot, but also to introduce the idea that maybe I minimized my very obvious lymphangitis because I am a man.
This week, we have empirical evidence that men downplay their medical symptoms — and that manlier men downplay them even more.
I’m going to talk about a study that links manliness (or, scientifically speaking, “male gender expressivity”) to medical diagnoses that are based on hard evidence and medical diagnoses that are based on self-report. You see where this is going but I want to walk you through the methods here because they are fairly interesting.
This study used data from the US National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. This study enrolled 20,000 adolescents who were in grades 7-12 in the 1994-1995 school year and has been following them ever since — about 30 years so far.
The authors wanted to link early gender roles to long-term outcomes, so they cut that 20,000 number down to the 4230 males in the group who had complete follow-up.
Now comes the first interesting question. How do you quantify the “male gender expressivity” of boys in 7th-12th grade? There was no survey item that asked them how masculine or manly they felt. What the authors did was look at the surveys that were administered and identify the questions on those surveys where boys and girls gave the most disparate answers. I have some examples here. 
Some of these questions make sense when it comes to gender expressivity: “How often do you cry?” for example, has a lot of validity for the social construct that is gender. But some questions where boys and girls gave very different answers — like “How often do you exercise?” — don’t quite fit that mold. Regardless, this structure allowed the researchers to take individual kids’ responses to these questions and combine them into what amounts to a manliness score — how much their answers aligned with the typical male answer.
The score was established in adolescence — which is interesting because I’m sure some of this stuff may change over time — but notable because adolescence is where many gender roles develop.
Now we can fast-forward 30 years and see how these manliness scores link to various outcomes. The authors were interested in fairly common diseases: diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Let’s start simply. Are males with higher gender expressivity in adolescence more or less likely to have these diseases in the future?
Not really. Those above the average in male gender expressivity had similar rates of hypertension and hyperlipidemia as those below the median. They were actually a bit less likely to have diabetes.
But that’s not what’s really interesting here.
I told you that there was no difference in the rate of hypertension among those with high vs low male gender expressivity. But there was a significant difference in their answer to the question “Do you have hypertension?” The same was seen for hyperlipidemia. In other words, those with higher manliness scores are less likely to admit (or perhaps know) that they have a particular disease.
You can see the relationship across the manliness spectrum here in a series of adjusted models. The x-axis is the male gender expressivity score, and the y-axis is the percentage of people who report having the disease that we know they have based on the actual laboratory tests or vital sign measurements. As manliness increases, the self-report of a given disease decreases.
There are some important consequences of this systematic denial. Specifically, men with the diseases of interest who have higher male gender expressivity are less likely to get treatment. And, as we all know, the lack of treatment of something like hypertension puts people at risk for bad downstream outcomes.
Putting this all together, I’m not that surprised. Society trains boys from a young age to behave in certain ways: to hide emotions, to eschew vulnerability, to not complain when we are hurt. And those lessons can persist into later life. Whether the disease that strikes is hypertension or Pasteurella multocida from a slightly psychotic house cat, men are more likely to ignore it, to their detriment.
So, gents, be brave. Get your blood tests and check your blood pressure. If there’s something wrong, admit it, and fix it. After all, fixing problems — that’s a manly thing, right?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When my normally adorable cat Biscuit bit my ankle in a playful stalking exercise gone wrong, I washed it with soap and some rubbing alcohol, slapped on a Band-Aid, and went about my day.
The next morning, when it was swollen, I told myself it was probably just a hematoma and went about my day.
The next day, when the swelling had increased and red lines started creeping up my leg, I called my doctor. Long story short, I ended up hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
This is all to say that, yes, I’m sort of an idiot, but also to introduce the idea that maybe I minimized my very obvious lymphangitis because I am a man.
This week, we have empirical evidence that men downplay their medical symptoms — and that manlier men downplay them even more.
I’m going to talk about a study that links manliness (or, scientifically speaking, “male gender expressivity”) to medical diagnoses that are based on hard evidence and medical diagnoses that are based on self-report. You see where this is going but I want to walk you through the methods here because they are fairly interesting.
This study used data from the US National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. This study enrolled 20,000 adolescents who were in grades 7-12 in the 1994-1995 school year and has been following them ever since — about 30 years so far.
The authors wanted to link early gender roles to long-term outcomes, so they cut that 20,000 number down to the 4230 males in the group who had complete follow-up.
Now comes the first interesting question. How do you quantify the “male gender expressivity” of boys in 7th-12th grade? There was no survey item that asked them how masculine or manly they felt. What the authors did was look at the surveys that were administered and identify the questions on those surveys where boys and girls gave the most disparate answers. I have some examples here. 
Some of these questions make sense when it comes to gender expressivity: “How often do you cry?” for example, has a lot of validity for the social construct that is gender. But some questions where boys and girls gave very different answers — like “How often do you exercise?” — don’t quite fit that mold. Regardless, this structure allowed the researchers to take individual kids’ responses to these questions and combine them into what amounts to a manliness score — how much their answers aligned with the typical male answer.
The score was established in adolescence — which is interesting because I’m sure some of this stuff may change over time — but notable because adolescence is where many gender roles develop.
Now we can fast-forward 30 years and see how these manliness scores link to various outcomes. The authors were interested in fairly common diseases: diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Let’s start simply. Are males with higher gender expressivity in adolescence more or less likely to have these diseases in the future?
Not really. Those above the average in male gender expressivity had similar rates of hypertension and hyperlipidemia as those below the median. They were actually a bit less likely to have diabetes.
But that’s not what’s really interesting here.
I told you that there was no difference in the rate of hypertension among those with high vs low male gender expressivity. But there was a significant difference in their answer to the question “Do you have hypertension?” The same was seen for hyperlipidemia. In other words, those with higher manliness scores are less likely to admit (or perhaps know) that they have a particular disease.
You can see the relationship across the manliness spectrum here in a series of adjusted models. The x-axis is the male gender expressivity score, and the y-axis is the percentage of people who report having the disease that we know they have based on the actual laboratory tests or vital sign measurements. As manliness increases, the self-report of a given disease decreases.
There are some important consequences of this systematic denial. Specifically, men with the diseases of interest who have higher male gender expressivity are less likely to get treatment. And, as we all know, the lack of treatment of something like hypertension puts people at risk for bad downstream outcomes.
Putting this all together, I’m not that surprised. Society trains boys from a young age to behave in certain ways: to hide emotions, to eschew vulnerability, to not complain when we are hurt. And those lessons can persist into later life. Whether the disease that strikes is hypertension or Pasteurella multocida from a slightly psychotic house cat, men are more likely to ignore it, to their detriment.
So, gents, be brave. Get your blood tests and check your blood pressure. If there’s something wrong, admit it, and fix it. After all, fixing problems — that’s a manly thing, right?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New mRNA Vaccine May Shield Against C difficile Infections
A group of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, has developed a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine, delivered via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the same type as the COVID-19 vaccine produced by Moderna and Pfizer — targeting Clostridioides difficile (formerly Clostridium difficile). According to the authors, the results of their preclinical study, published in Science, demonstrated this technology as a promising platform for C difficile vaccine development and could be the starting point for curbing intestinal infections that, in their most severe forms (pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon), can be fatal.
An Increasingly Pressing Issue
C difficile is the leading cause of infectious diarrhea acquired in healthcare settings.
A 2019 study reported a global incidence of C difficile infections at 2.2 per 1000 hospital admissions per year and 3.5 per 10,000 patient-days per year.
The Vaccine Candidate
Vaccine candidates tested so far have used toxoids or recombinant proteins targeting the combined repetitive oligopeptide (CROP) or receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the two primary C difficile toxins, TcdA and TcdB. The US researchers are now exploring the mRNA-LNP vaccine approach to target multiple antigens simultaneously. They developed a bivalent vaccine (including the CROP and RBD domains of both toxins) and a trivalent vaccine (with an additional virulence factor, the metalloprotease Pro-Pro endopeptidase-1).
Mice vaccinated with the bivalent and trivalent vaccines produced immunoglobulin G antibody titers two to four times higher than those elicited by recombinant protein with an adjuvant. The vaccination stimulated the proliferation of follicular T helper cells and the antigen-specific response of B lymphocytes, laying the foundation for a strong and long-lasting humoral response. The vaccines were also immunogenic in hamsters.
Vaccinated mice not only survived a toxin dose five times higher than the 100% lethal dose but also demonstrated the vaccine’s protective effect through serum transfer; unvaccinated mice given serum from vaccinated mice survived the lethal challenge. More importantly, when exposed to a lethal dose of the bacterium itself, all vaccinated mice survived.
To demonstrate the vaccine’s efficacy in patients with a history of C difficile infection and high recurrence risk — ideal candidates for vaccination — the researchers vaccinated mice that had previously survived a sublethal infection. Six months after the initial infection and vaccination, these mice remained protected against mortality when reexposed to the bacterium.
Additionally, a quadrivalent vaccine that included an immunogen targeting C difficile spores — key agents in transmission — also proved effective. Low levels of bacteria and toxins in the feces of mice vaccinated in this way suggested that spore vaccination could limit initial colonization.
In tests with nonhuman primates, two doses of the vaccines targeting either the vegetative form or the spores elicited strong immune responses against bacterial toxins and virulence factors. Human trials may indeed be on the horizon.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A group of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, has developed a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine, delivered via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the same type as the COVID-19 vaccine produced by Moderna and Pfizer — targeting Clostridioides difficile (formerly Clostridium difficile). According to the authors, the results of their preclinical study, published in Science, demonstrated this technology as a promising platform for C difficile vaccine development and could be the starting point for curbing intestinal infections that, in their most severe forms (pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon), can be fatal.
An Increasingly Pressing Issue
C difficile is the leading cause of infectious diarrhea acquired in healthcare settings.
A 2019 study reported a global incidence of C difficile infections at 2.2 per 1000 hospital admissions per year and 3.5 per 10,000 patient-days per year.
The Vaccine Candidate
Vaccine candidates tested so far have used toxoids or recombinant proteins targeting the combined repetitive oligopeptide (CROP) or receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the two primary C difficile toxins, TcdA and TcdB. The US researchers are now exploring the mRNA-LNP vaccine approach to target multiple antigens simultaneously. They developed a bivalent vaccine (including the CROP and RBD domains of both toxins) and a trivalent vaccine (with an additional virulence factor, the metalloprotease Pro-Pro endopeptidase-1).
Mice vaccinated with the bivalent and trivalent vaccines produced immunoglobulin G antibody titers two to four times higher than those elicited by recombinant protein with an adjuvant. The vaccination stimulated the proliferation of follicular T helper cells and the antigen-specific response of B lymphocytes, laying the foundation for a strong and long-lasting humoral response. The vaccines were also immunogenic in hamsters.
Vaccinated mice not only survived a toxin dose five times higher than the 100% lethal dose but also demonstrated the vaccine’s protective effect through serum transfer; unvaccinated mice given serum from vaccinated mice survived the lethal challenge. More importantly, when exposed to a lethal dose of the bacterium itself, all vaccinated mice survived.
To demonstrate the vaccine’s efficacy in patients with a history of C difficile infection and high recurrence risk — ideal candidates for vaccination — the researchers vaccinated mice that had previously survived a sublethal infection. Six months after the initial infection and vaccination, these mice remained protected against mortality when reexposed to the bacterium.
Additionally, a quadrivalent vaccine that included an immunogen targeting C difficile spores — key agents in transmission — also proved effective. Low levels of bacteria and toxins in the feces of mice vaccinated in this way suggested that spore vaccination could limit initial colonization.
In tests with nonhuman primates, two doses of the vaccines targeting either the vegetative form or the spores elicited strong immune responses against bacterial toxins and virulence factors. Human trials may indeed be on the horizon.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A group of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, has developed a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine, delivered via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the same type as the COVID-19 vaccine produced by Moderna and Pfizer — targeting Clostridioides difficile (formerly Clostridium difficile). According to the authors, the results of their preclinical study, published in Science, demonstrated this technology as a promising platform for C difficile vaccine development and could be the starting point for curbing intestinal infections that, in their most severe forms (pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon), can be fatal.
An Increasingly Pressing Issue
C difficile is the leading cause of infectious diarrhea acquired in healthcare settings.
A 2019 study reported a global incidence of C difficile infections at 2.2 per 1000 hospital admissions per year and 3.5 per 10,000 patient-days per year.
The Vaccine Candidate
Vaccine candidates tested so far have used toxoids or recombinant proteins targeting the combined repetitive oligopeptide (CROP) or receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the two primary C difficile toxins, TcdA and TcdB. The US researchers are now exploring the mRNA-LNP vaccine approach to target multiple antigens simultaneously. They developed a bivalent vaccine (including the CROP and RBD domains of both toxins) and a trivalent vaccine (with an additional virulence factor, the metalloprotease Pro-Pro endopeptidase-1).
Mice vaccinated with the bivalent and trivalent vaccines produced immunoglobulin G antibody titers two to four times higher than those elicited by recombinant protein with an adjuvant. The vaccination stimulated the proliferation of follicular T helper cells and the antigen-specific response of B lymphocytes, laying the foundation for a strong and long-lasting humoral response. The vaccines were also immunogenic in hamsters.
Vaccinated mice not only survived a toxin dose five times higher than the 100% lethal dose but also demonstrated the vaccine’s protective effect through serum transfer; unvaccinated mice given serum from vaccinated mice survived the lethal challenge. More importantly, when exposed to a lethal dose of the bacterium itself, all vaccinated mice survived.
To demonstrate the vaccine’s efficacy in patients with a history of C difficile infection and high recurrence risk — ideal candidates for vaccination — the researchers vaccinated mice that had previously survived a sublethal infection. Six months after the initial infection and vaccination, these mice remained protected against mortality when reexposed to the bacterium.
Additionally, a quadrivalent vaccine that included an immunogen targeting C difficile spores — key agents in transmission — also proved effective. Low levels of bacteria and toxins in the feces of mice vaccinated in this way suggested that spore vaccination could limit initial colonization.
In tests with nonhuman primates, two doses of the vaccines targeting either the vegetative form or the spores elicited strong immune responses against bacterial toxins and virulence factors. Human trials may indeed be on the horizon.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.